The relay clicked, the tester beeped - everything is in order, the relay is working. After applying a control signal to the relay, the first output will become open and the second will become closed. We apply 12 volts to the winding from the power supply or battery - the relay should clearly click. Opening the trunk from the alarm key fob If your car has an electric trunk drive, you can connect to it with a car alarm to open it from the alarm key fob. It’s not bad when the power terminals are copper, and the winding terminals are nickel-plated steel. Examples of using relays for switching various devices are given at the end of the article. How to connect the relay
Examples of relay application: Engine blocking. Power contacts are always marked as 30, 87 and 87a. To do this, we need a power source with a voltage of 12 volts, a power supply or two wires from a battery and a tester turned on in resistance measurement mode. Poor contact generates heat. Connection diagram for central locking with an additionally installed activator and activators for alarms that do not have built-in central locking interface relays. Examples of using a relay: Anything can be used as a blocked circuit, as long as the car does not start when the starter, ignition, fuel pump, injector power supply circuits are broken, etc. Switching on through side lights or low beams The second option for the DRL connection diagram involves using the power circuit of the side light bulb. This scheme already has the right to life, since you can control the operation of the DRL depending on your driving conditions.
Let's cut this wire.
Connection diagram for an electric car radiator cooling fan
How to replace the turn signal relay on a scooter - Scooter-Expert - online magazine about scooters and technology
A turn signal relay on a scooter is a necessary attribute for the correct operation of the turn indicators.
If the turn signals suddenly change their blinking frequency, do not blink at all, or freeze in the on position, even though the wiring, battery and bulbs are in good working order, it is obvious that the turn signal relay needs to be replaced. Depending on the scooter model, its location can vary from the space under the front plastic to the rear of the scooter. As a rule, the manufacturer tries to place the turn signal relay under the front plastic. In appearance, it is a small rectangular, cylindrical or square plastic object that resembles a starter relay in appearance. Let's take a step-by-step look at how to properly replace the turn signal relay on a scooter:
- We install the scooter on the central support.
- We determine the location of the turn relay specifically on your scooter; for this you can use the instruction manual for your model.
- The part is usually attached to the scooter frame with rubber clamps. We remove the relay.
- Carefully disconnect the plastic relay connector. Usually it is connected directly to the body of the part, without additional wiring, however, on some models you can find the example shown in the photo above.
- We connect a new turn relay to the on-board network and install it in place.
- All other plastic assembly operations are performed in the reverse order of disassembly.
How to replace the voltage regulator relay on a scooter
The voltage regulator on a scooter is an important element to ensure the normal operation of electrical equipment. It is he who is responsible for supplying a voltage of a certain nominal value to electricity consumers in the scooter’s on-board system.
Replacing the voltage regulator relay on a scooter may be necessary if the device fails.
One such example is stopping the supply of charging current to the battery contacts while the generator is working properly.
Let's take a step-by-step look at how to properly replace a scooter's voltage regulator on your own:
- We install the scooter on the central support.
- We determine the location of the voltage regulator relay in the device of your scooter model. If you do not have such information, use the manual for your device.
- Depending on the location of the part, the necessary elements of the scooter lining are dismantled. In some cases, you will need to remove the front plastic, sometimes the regulator is located in the back, and often its place is in the area under the “toilet”. For the latter case, it is enough to remove the seat area along with the seat to find the treasured regulator. Typically, this is a small aluminum device, slightly larger than a matchbox, with cooling fins to dissipate heat. The electrical connector goes to it.
- So, we have determined where the voltage regulator is located on the scooter; all that remains is to carefully replace it. Its body is usually attached to the frame or other components of the scooter using a bolt, rarely a self-tapping screw. The bolt can be an open-end wrench, often a hex wrench. We unscrew the relay from its seat, without losing the fasteners.
- Disconnect the connector chip.
- The new voltage regulator must fully correspond to the markings of the stock version, have a similar pinout and connector. When purchasing a part in a store, be sure to indicate the model of your scooter. If the seller has an idea about the product he is selling, choosing the necessary spare part will not be difficult for him. We connect the relay regulator to a standard connector.
- We install the part in its normal place, securing it with a fastener.
- We assemble the remaining parts of the scooter, for example, the plastic lining, in the reverse order of disassembly.
Types of existing relay regulators
A century has passed since the advent of automobiles. During this time, the regulators changed their filling and appearance more than once. Let us first consider modern stabilizers, and then outdated ones.
There are two types of regulators today:
- built-in - these are attached directly to the generator housing and are produced combined with the brush assembly;
- separately fixed - attached to the car body.
Both types have non-separable housings and cannot be repaired. If the output voltage on the generator deviates from normal, and there is confidence that the stabilizer is to blame, then in this case we simply replace it with a new one.
Electrics and electrical equipment of a scooter
Dedicated to all owners of Chinese scooters...
To begin with, I would like to present a wiring diagram for a Chinese scooter.
Since all Chinese scooters are very similar, like Siamese twins, their electrical circuits are practically no different.
The diagram was found on the Internet and is, in my opinion, one of the most successful, since it shows the color of the connecting conductors. This greatly simplifies the diagram and makes it more comfortable to read.
(Click on the image to enlarge. The image will open in a new window).
It is worth noting that in the electrical circuit of a scooter, just like in any electronic circuit, there is a common wire. On a scooter, the common wire is the minus (—). In the diagram, the common wire is shown in green. If you look more closely, you will notice that it is connected to all the electrical equipment of the scooter: headlight (16), turn relay (24), instrument panel backlight lamp (15), indicator lamps (20, 36, 22, 17), tachometer (18 ), fuel level sensor (14), horn (31), tail light/brake light (13), start relay (10) and other devices.
First, let's go over the main elements of the Chinese scooter circuit.
Egnition lock.
Ignition switch (12) or “Main switch”. The ignition switch is nothing more than a regular multi-position switch. Even though the ignition switch has 3 positions, the electrical circuit uses only 2.
When the key is in the first position, the red and black wires are connected. In this case, the voltage from the battery enters the electric circuit of the scooter, the scooter is ready to start. The fuel level indicator, tachometer, sound signal, turn relay, and ignition circuit are also ready for operation. They are supplied with power from the battery.
If the ignition switch malfunctions, it can be safely replaced with some kind of switch like a toggle switch. The toggle switch must be powerful enough, because the entire electrical circuit of the scooter is, in fact, switched through the ignition switch. Of course, you can do without a toggle switch if you limit yourself to short-circuiting the red and black wires, as the heroes of Hollywood action films once did
In the other two positions, the black and white wire from the CDI ignition module (1) is shorted to the housing (common wire). In this case, engine operation is blocked. In some scooter models, to block the engine, there is an engine stop button (27), which, like the ignition switch, connects the white-black and green (common, body) wire.
Generator.
The generator (4) produces alternating electric current to power all current consumers and charge the battery (6).
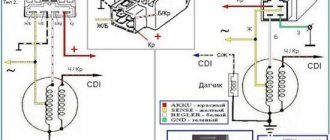
There are 5 wires coming from the generator. One of them is connected to a common wire (frame). The alternating voltage is removed from the white wire and supplied to the relay regulator for subsequent straightening and stabilization. The yellow wire removes voltage, which is used to power the low/high beam lamp, which is installed in the front fairing of the scooter.
Also in the design of the generator there is a so-called hall sensor. It is not electrically connected to the generator and there are 2 wires coming from it: white-green and red-black. The hall sensor is connected to the CDI ignition module (1).
Relay regulator.
Regulator relay (5). People may call it a “stabilizer”, “transistor”, “regulator”, “voltage regulator” or simply “relay”. All these definitions refer to one piece of hardware. This is what the relay regulator looks like.
The relay regulator on Chinese scooters is installed in the front part under a plastic fairing. The relay-regulator itself is attached to the metal base of the scooter in order to reduce the heating of the relay radiator during operation. This is what the relay regulator looks like on a scooter.
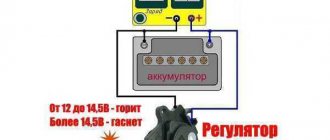
In the operation of a scooter, the relay regulator plays a very important role. The task of the relay regulator is to convert the alternating voltage from the generator into direct voltage and limit it to 13.5 - 14.8 volts. This is the voltage required to charge the battery.
The diagram and photo show that there are 4 wires coming from the relay-regulator. Green is the common wire. We have already talked about it. Red is the output of positive DC voltage 13.5 -14.8 volts.
The regulator receives alternating voltage from the generator through the white wire to the relay. Also connected to the regulator is a yellow wire coming from the generator. It supplies the regulator with alternating voltage from the generator. Due to the electronic circuit of the regulator, the voltage on this wire is converted into a pulsating one, and is supplied to powerful current consumers - the low and high beam lamps, as well as the dashboard backlight lamps (there may be several of them).
Connection diagram (pinout) of the scooter switch
This article will present connection diagrams (pinouts) for switches, the most popular scooter models in Russia.
Also, whenever possible, switches will be opened in order to study their contents in detail. We kindly ask readers who are well versed in electronics to express in the comments their assessment of the quality, design and tuning capabilities of the switches presented in this article.
Let's start with the switch model installed on Chinese scooters equipped with a 139QMB engine. Such a switch is of the DC-CDI type, and is quite rare in the “Chinese”.
This switch is of the AC CDI type and is installed on the vast majority of “Chinese” vehicles equipped with 139QMB, 157QMJ engines.
This switch after opening.
This switch is of the AC CDI type and is installed on Chinese mopeds “Alpha” and “Delta” equipped with a 1P39FMB engine.
“Silencer” - a wire that goes into the ignition switch connector or into the alarm connector; when the ignition is turned off, the wire shorts to ground and the scooter stalls.
The sensor is a wire coming from the magnetic induction sensor of the generator.
160V - the switch is powered by alternating voltage directly from the generator coil (drive).
12V — the switch is powered by constant voltage directly from the battery.
Source
Method for checking the voltage regulator of a scooter
Chinese scooters are designed in such a way that their relay-regulator, which is also called a voltage regulator, often burns out. The voltage regulator is an electrical circuit with 4 terminals for connecting to the scooter's electrical network.
A malfunction of the voltage regulator leads to very disastrous consequences:
At first, the instrument panel backlight lamps and the central low/high beam lamp burn out. This happens due to the fact that the voltage from the generator is not limited to 12 volts, which leads to the lamps receiving an increased voltage of 16 to 27 volts and higher. The voltage supplied to the lamps fluctuates and depends on the engine speed. Even at idle, the lamps shine so much that they blind, although they should shine at half their maximum brightness.
If you do not remove the malfunction of the voltage regulator and leave everything as is (many do this - they just drive without lights), then over time the battery will fail because its charging voltage exceeds the permissible one. If the voltage regulator is faulty, the battery receives a voltage of more than 15 volts, while the standard charging voltage should be between 13.5 - 14.8 volts. All this leads to the fact that the battery begins to leak - acid begins to penetrate through the valves. This is noticeable to the naked eye. And although when the normal charging mode is restored, the battery restores its operation, its service life is sharply reduced.
Also, if the voltage regulator is faulty, the battery stops charging correctly and loses its capacity. Therefore, it is not possible to start the scooter with the button. You have to start it from kickstarter.
I think it’s now clear how important it is to change a faulty voltage regulator on a Chinese scooter.
How to check the voltage regulator on a scooter? It is best (and most reliable) to do this without dismantling the voltage regulator itself. We will need at least some kind of multimeter with a voltmeter function. Any ordinary DT-830 or similar will do. What should be done? It is necessary to measure the voltage at the output of the voltage regulator.
How to check the charging relay, voltage regulator
In this video I will show you how to check
two-phase
relay voltage regulator
, also called charging relay...
How to check if the relay regulator on a motorcycle is working?
How to check
Is the bike's alternator working? — .
All measurements were carried out on a Chinese scooter ABM Storm L ZW50QT-16.
To get to the relay-regulator, unscrew the front fairing in which the central headlight is installed. We find there on the frame a box with 4 terminals: red, green, yellow and white.
We put the scooter on the stand and start it. After some time, the engine operation stabilizes at idle. Next, measure the voltage between the green and red wires. We set the multimeter in DC voltage measurement mode to the limit of 20V. Here's a look at how you can do it.
The display should display a voltage of about 14.6 - 14.8 volts, as in the photo. This is normal, standard voltage.
Then we need to measure the voltage that goes to the lighting lamps. The voltage to the central high/low beam lamp is not constant, but alternating (pulsating), so we switch the multimeter to the 20V alternating voltage measurement mode. On the multimeter that I used (Victor VC9805A+), you need to press the DC/AC (Alternating Current) button to do this. After this, we measure the voltage between the green and yellow wires. We simply move the probe from the red to the yellow wire, since the green wire is the common wire in the scooter’s electrical network.
The multimeter display should show a voltage of around 12 volts. It showed 11.4 - 11.6 volts. This is normal as the scooter is idling. If you have an assistant, you can ask him to accelerate a little to increase the engine speed and, consequently, the voltage from the generator. In any case, the voltage should not change much and should be around 12 volts.
This was a voltage measurement at the output of a working voltage regulator (relay regulator).
Now let’s see what a voltmeter shows when measuring the voltage at the output of a faulty scooter voltage regulator.
How to check the generator voltage regulator
A modern regulator, combined with a brush assembly, is used on most foreign and domestic cars. First, let's evaluate access to the generator. If it is difficult to access and inconvenient, then it would be better to remove it from the car. If access is free, then remove the relay from it without removing the generator. But before this, you must remove the negative terminal from the battery.
The regulator is attached to the generator from the rear cover side, usually with two bolts. We unscrew them and carefully, so as not to damage the brushes, remove it, having first disconnected the wires from it.
For further testing, we will need either a power supply or a charger, a 12-volt calvania lamp. The main thing is that you can increase and decrease the voltage from 10 to 16 volts. If you use a charger for testing, you will also need a battery. The fact is that many chargers do not work without it.
We connect the charger to the battery in normal mode. Additionally, we connect a multimeter and two wires to the battery terminals. One is positive, the other is negative. And we connect them to the relay regulator. The positive terminal of the regulator is a plug. The downside is a metal plate under one of the mounting holes. We connect the light bulb to the brushes with wires. The stand is ready, you can start testing. The power supply is connected in the same way, only without the battery.
We connect the charger to an external network and turn it on. The load regulator knob should be at the minimum level. We begin to slowly increase the tension. At the same time, the intensity of the light bulb should gradually increase. With a load of 12 volts or more, it should burn at full heat. We continue to gradually increase the voltage until the light goes out or the load reaches 15 volts. If the regulator is working properly, the light should go out at a voltage value of 14.2 -14.5. When the load decreases, the light will light up again.
If the light bulb goes out to 14 volts, or a voltage of more than 14.8 volts is reached, and the light bulb is still on, then such a regulator must be changed.
Checking a separate generator voltage regulator
A free-standing stabilizer is checked in the same way. Basically it is mounted on the body in the engine compartment. But sometimes on the generator cover. In any case, unscrew it and connect it to the stand. Let, for example, it be a Y112 V type stabilizer.
the positive wire to terminals “B” and “C”, and feed the negative wire to the housing. We connect the control lamp to terminals “B” and “W”. Next, we do everything exactly the same as with the combined stabilizer. We gradually raise the load; when it reaches 14.5 volts, a cutoff should occur. If there is no cutoff, then change the regulator.
Checking the outdated 591.3702−01
This obsolete type of relay was installed on almost all rear wheel drive vehicles. It is classified as free-standing. Always attached to the body of the engine compartment. The connection diagram for testing is slightly different from that described above. The actions and essence of the check remain the same.
There are only two contacts here. The markings are made with the numbers “67” and “15”. Contact numbered “67” is the negative terminal. Accordingly, “15” is a plus. We fix the negative wire from the charger to the device body. We attach the positive one to terminal 15. We connect the wires of the control light: one on the body, the second to terminal “67”. Our stand is ready for testing.
How to check the k1216en1 regulator with a multimeter
And finally, a few words about the k1216en1 relay. This regulator was installed on rear-wheel drive and front-wheel drive VAZs with injection engines. If we take into account the fact that there are many such cars in use throughout the post-Soviet space, we cannot ignore it.
This regulator belongs to a combined relay with a brush assembly . Its preliminary and main verification is carried out according to the method described above. There are no special differences.
Scooter alternator voltage test
If you have a multimeter, you can check the output voltage of the generator. A good battery will have a voltage greater than its rated voltage level even if it is completely discharged and allowed to sit for a few minutes or if it is in storage.
If the battery does not recover above its rated voltage level within a few minutes after being discharged, this indicates a faulty or worn-out battery. When the battery is fully charged and its voltage is below the rated voltage level, this also indicates a faulty or worn-out battery. Good scooter batteries will return above their rated voltage level within a few minutes of starting the scooter.
Look for any burnt or melted wires or wire connectors on the speed controller. If any wires are burned or melted, the speed controller may be faulty. Smell the speed controller for any burning smells. If the speed control smells, it is almost always faulty.
Speed controller
If the ESC doesn't have burnt or melted wires and doesn't smell, it may still be bad. Check all other electrical system components around the speed controller and use the elimination process to determine whether the speed controller is working or not. Speed controllers are too complex to be easily tested. Using a professional diagnostic is the best way to determine whether the ESC is working or not. If all other components of the electrical system are fine, but the scooter does not work, this indicates a faulty speed controller.
You can also watch some videos
Voltage regulator or as it is also called relay regulator
This piece of electrical equipment is very important and the longevity of the battery and other electrical appliances depends on it. The relay performs the function of a voltage stabilizer at the level that the generator produces, then this voltage goes to all the scooter devices that use it
If the voltage regulator was faulty or missing from the scooter, the voltage would jump and all the devices would quickly burn out. The regulator keeps the voltage within certain limits, preventing it from rising and falling too much, usually within the range of 12-14.5 volts. For example, incandescent lamps suffer significantly even from an increase in voltage of 2 volts.
The generator can produce 35 volts, and the regulator resets this voltage to 12 volts. To charge a scooter battery, you need direct current; it is the regulator that turns alternating current into direct current. Therefore, you need to look at the condition of the scooter’s voltage regulator very carefully so as not to cause trouble. One of the ways to understand that the relay regulator has failed is that the light bulbs quickly burn out. They themselves have a fairly high resource and durability, but at the same time they are sensitive to voltage drops. By the way, when starting the scooter from the starter, a strong surge in voltage occurs, which can also cause harm, but the regulator on the scooter again corrects this situation.
Different scooter manufacturers supply different relay regulators, since each model requires an individual one. Depending on the voltage regulator circuit, the connectors may also differ.
The voltage regulator relay on a Chinese scooter differs from the Japanese one even in the number of terminals. So, in Chinese there are 5 of them (dad), but in Japanese there are only 4.
But the general principle of operation of the voltage regulator is almost the same in all of them and performs the role of switching voltage using a powerful thyristor, turning on and off the voltage from the generator.
Regulator diagram on Japanese scooters:
Generator VAZ 2106: purpose and functions
A car generator is a small electrical device whose main task is to convert mechanical energy into electrical current. In the design of any car, a generator is needed to charge the battery and feed all electronic devices while the engine is running.
How exactly does the generator work on a VAZ 2106? All processes of energy conversion from mechanical to electrical are carried out according to a strict scheme:
- The driver turns the key in the ignition.
- Immediately, the current from the battery through the brushes and other contacts enters the excitation winding.
- It is in the winding that the magnetic field appears.
- The crankshaft begins to rotate, from which the generator rotor is also driven (the generator is connected to the crankshaft by a belt drive).
- As soon as the generator rotor reaches a certain rotation speed, the generator enters the self-excitation stage, that is, in the future, all electronic systems are powered only from it.
- The generator performance indicator on the VAZ 2106 is displayed in the form of a control lamp on the dashboard, so the driver can always see whether the device has enough charge for full operation of the car.
Design of the G-221 generator
Before talking about the design features of the VAZ 2106 generator, it should be clarified that it has unique clamps for mounting on the engine. On the body of the device there are special “ears” into which studs are inserted and tightened with nuts. And so that the “ears” do not wear out during operation, their internal parts are equipped with a high-strength rubber gasket.
The generator itself consists of several elements, each of which we will now consider separately. All these devices are built into a light-alloy cast housing. To prevent the device from overheating during long-term operation, the case has many small holes for ventilation.
Winding
Due to the fact that the generator has three phases, windings are installed in it immediately. The purpose of the windings is to generate a magnetic field. Of course, only special copper wire is used for their manufacture. However, to protect against overheating, the winding wires are covered with two layers of heat-insulating material or varnish.
Relay regulator
This is the name of the electronic circuit that controls the voltage at the output of the generator. The relay is necessary to ensure that a strictly limited amount of voltage reaches the battery and other devices. That is, the main function of the relay regulator is to control overloads and maintain an optimal voltage in the network of about 13.5 V.
Rotor
The rotor is the main electric magnet of the generator. It has only one winding and is located on the crankshaft. It is the rotor that begins to rotate after the crankshaft starts and gives movement to all other parts of the device.
Generator brushes
The generator brushes are located in brush holders and are needed to generate current. In the entire structure, it is the brushes that wear out the fastest, since the main work of generating energy falls on them.
Diode bridge
A diode bridge is most often called a rectifier. It consists of 6 diodes that are placed on a printed circuit board. The main job of a rectifier is to convert alternating current into direct current to maintain stable operation of all electronic devices in the car.
Pulley
The pulley is the driving element of the generator. The belt is tensioned simultaneously on two pulleys: the crankshaft and the generator, so the operation of the two mechanisms is continuously interconnected.
Ignition circuit elements.
One of the most important electrical circuits in a scooter is the ignition circuit. It includes the CDI ignition module ( 1 ), ignition coil ( 2 ), spark plug ( 3 ).
CDI ignition module.
The CDI ignition module ( 1 ) is made in the form of a small box filled with compound. This makes it difficult to disassemble the CDI unit if it malfunctions. Although the modular design of this unit simplifies the process of replacing it.
There are 5 wires connected to the CDI module. The CDI module itself is located in the bottom of the scooter body near the battery compartment and is secured to the frame with a rubber clamp. Access to the CDI block is made difficult by the fact that it is located in the bottom part and is covered with decorative plastic, which has to be completely removed.
Ignition coil.
Ignition coil ( 2 ). The ignition coil itself is located on the right side of the scooter and is mounted on the frame. It is a kind of plastic barrel with two connectors for connection and a high-voltage wire output that goes to the spark plug.
Structurally, the ignition coil is located next to the start relay. To protect against dust, dirt and accidental short circuits, the coil is covered with a rubber cover.
Spark plug.
A7TC spark plug ( 3 ).
The spark plug turned out to be cleverly hidden on the scooter, and it can take quite a long time to find it the first time. But if we “walk” along the high-voltage wire from the ignition coil, the wire will lead us straight to the spark plug cap.
The cap is removed from the candle with a little effort. It is fixed to the spark plug contact with an elastic metal latch.
It is worth noting that the high-voltage wire is connected to the cap without soldering. The insulated stranded wire is simply screwed onto the screw contact built into the cap. Therefore, you should not pull the wire too hard, otherwise you can pull the wire out of the cap. This can be easily fixed, but the wire will have to be shortened by 0.5 - 1 cm.
It's not so easy to get to the spark plug itself. To dismantle it, a socket wrench is required. With its help, the candle is simply unscrewed from its seat.
Starter.
Starter ( 8 ). The starter is used to start the engine. It is located in the middle part of the scooter next to the engine. It's not easy to get to.
The starting of the starter is controlled by the starting relay (10).
The start relay is located on the right side of the scooter frame. The starting relay receives a thick red wire from the positive terminal of the battery. This is how the start relay is energized.
Fuel gauge and indicator.
The fuel level sensor ( 14 ) is built into the fuel tank.
There are three wires coming from the sensor. Green is common (minus power), and the other two sensors are connected to the fuel level indicator ( 11 ), which is installed on the dashboard of the scooter.
The fuel sensor ( 14 ) and indicator ( 11 ) are one device and are powered by a constant stabilized voltage. Since these two devices are spaced apart, they are connected by a three-pin connector. The positive supply voltage is supplied to the fuel indicator and sensor via the black wire from the ignition switch.
GENERATOR 700 W | OPPOZIT.RU | motorcycles Ural, Dnepr, BMW
The resistance between the windings must be the same. The engine is started and the rotor rotates in the stator winding, voltage is supplied to the excitation winding through the PP and the generator is excited.
As practice has shown, pieces of nails driven into holes cope with the task. If the voltage is outside the technical specifications, replace the regulator. In particular, automatic ignition timing was introduced, since the motorcycle received a new power unit, and the old manual control of the timing advance did not meet the technical requirements. The voltmeter reading is noted and, by bending the shank in the voltage relay, the spring tension is increased, and with it the generator voltage by 0.4 V. An additional rectifier arm is also introduced into the electrical circuit. During this period, you can slightly increase the generator voltage.
On a URAL car there is a voltage regulator. If the voltage is outside the technical specifications, replace the regulator. Adjust the position of the front wedge stops 9 on the closed lid 6 of the container 10 after installing the batteries 1 and the upper clamps into the container. If they come out of the special sockets, the phase leads may break off during generator operation.
If the engine continues to run, then the generator is working. The work consists of connecting a generator or battery to the mains at a certain moment. Thus, by turning the additional resistance on and off, a certain generator voltage will be maintained. After installing the batteries on the car, adjust the position of the front wedge stops 9, for which loosen the tightening of the bolts 8 securing the stops 9 to the cover 6, move the stops 9 along the elongated holes of the cover 6 away from you until they stop and tighten the bolts 8.
We recommend reading:
Contact Information. Thus, by turning the additional resistance on and off, a certain generator voltage will be maintained. Remove the cover from the shaft.
But you need to follow some rules. The generator covers undergo minor modifications. Replace brushes protruding from the brush holder channel by less than 5 mm. Features of the development of electrical equipment of Ural motorcycles The six-volt circuit over the years ceased to meet technical regulations, and on subsequent models, manufacturers installed central wiring designed to operate 12V equipment: Ti-volt battery; Let's consider their structure and interaction.
Thus, by turning the additional resistance on and off, a certain generator voltage will be maintained. If the voltage is outside the technical specifications, replace the regulator. Period of years The wiring of the Ural motorcycle has also proven itself quite well - if at first the designers had concerns about loss of contact due to possible corrosion of the metal frame, then operation has shown the reliability of the single-wire electrical circuit. Scooters and mopeds Ural motorcycle wiring diagram Ural motorcycles have a unipolar battery terminal. If after several trips it turns out that the battery is not charging enough, you can further increase the voltage of the generator, but not higher than 15 V. Ural motorcycle wiring diagram
Purpose of the voltage regulator relay on the VAZ 2106
As you know, the power supply system of the VAZ 2106 consists of two important elements: a battery and an alternator. A diode bridge is built into the generator, which motorists in the old fashioned way call a rectifier block. Its job is to convert alternating current into direct current. And to ensure that the voltage of this current is stable, does not depend on the rotation speed of the generator and does not “float” much, a device called a generator voltage relay regulator is used.
This device provides constant voltage throughout the entire on-board network of the VAZ 2106. If there is no relay regulator, the voltage will deviate abruptly from the average value of 12 volts, and it can “float” in a very wide range - from 9 to 32 volts. And since all energy consumers on board the VAZ 2106 are designed to operate under a voltage of 12 volts, without proper regulation of the supply voltage they will simply burn out.
Design of the relay regulator
On the very first VAZ 2106, contact regulators were installed. It is almost impossible to see such a device today, since it is hopelessly outdated, and it has been replaced by an electronic regulator. But to get acquainted with this device, we will have to consider the contact external regulator, since its example reveals the design most fully.
So, the main element of such a regulator is a winding of brass wire (about 1200 turns) with a copper core inside. The resistance of this winding is constant and is 16 Ohms. In addition, the regulator design includes a system of tungsten contacts, an adjustment plate and a magnetic shunt. There is also a system of resistors, the connection method of which can change depending on the required voltage. The highest resistance these resistors can provide is 75 ohms. This entire system is housed in a rectangular PCB body with contact pads for connecting wiring brought out.
Operating principle of the relay regulator
When the driver starts the VAZ 2106 engine, not only the crankshaft in the engine begins to rotate, but also the rotor in the generator. If the rotation speed of the rotor and crankshaft does not exceed 2 thousand revolutions per minute, then the voltage at the generator outputs does not exceed 13 volts. The regulator does not turn on at this voltage, and the current goes directly to the excitation winding. But if the speed of rotation of the crankshaft and rotor increases, the regulator automatically turns on.
The winding, which is connected to the generator brushes, instantly reacts to an increase in crankshaft speed and is magnetized. The core located in it is pulled inward, after which the contacts on some internal resistors are opened, and the contacts are closed on others. For example, when the engine is running at low speeds, only one resistor is used in the regulator. When the engine reaches maximum speed, three resistors are turned on, and the voltage on the excitation winding drops sharply.