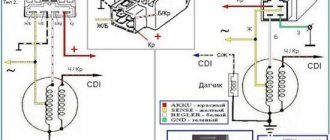
Diagram of a single-phase regulator relay for Viper Activ
I bought myself a Chinese Viper Activ moped practically for nothing.
We immediately replaced the battery in it, since the original one was dead, I drove it for only 2 days. After which the battery was simply discharged to the limit. Battery charging tests have begun. Everything was normal, the relay regulator was at idle. the engine produced a normal voltage of 14.4V, and it was not clear what was wrong. But as soon as the battery was removed, the generator produced virtually no light, even at full engine speed. So, the headlights barely shone, and soon the light disappeared altogether. As it turned out, the regulator relay died. Having found a diagram of the original relay, I was a little shocked by the savings of the Chinese and started digging on the Internet. After looking at a bunch of diagrams and stocking up on knowledge about shunt relay regulators, I got to work
The circuit practically repeats the original Viper circuit, only slightly improved in reliability and capable of outperforming the standard one several times
Diagram of a single-phase regulator relay
List of components used: C1 = 33nF 250V C2 = 2200mF 35V C3 = 0.22 50V C4 = 4.7mF FU1 = 10A K1 = 12V 10A R1-3= 1k R4 = 5.1k R5 = 2.4k R6 = 22 VD1 = 10A 50V VD2 = 3A 50V VD3 = 1N4007 VD4 = 1N4148 VS1-2= BT151 VT1 = 2N5401
This circuit is a single-phase shunt relay regulator, the shunt is two thyristors. Cutting off both half-waves and passing excess current through the freewheeling diodes of the diode bridge, I decided to do this for several reasons:
Firstly, diodes do not allow breakdown of thyristors in the reverse direction. Secondly, excess current is also dissipated on the diode bridge, which slightly relieves the load on the thyristors
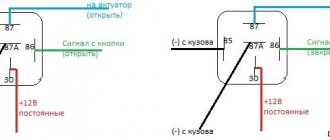
We also made a small circuit on the relay to disconnect the battery from the power supply when the engine is running, which prevents it from being discharged at low engine speeds
To connect this relay, you need to slightly upgrade the viper generator. The end of the lighting winding connected to the frame must be disconnected from the body and sent to the green wire. I ran the second wire going to the relay input along the white cable, disconnecting it from the onboard network. And then the output connected the network on board. To power the battery, I ran a separate wire
Be careful when connecting
The circuit was mounted mounted and inserted into the radiator from an old regulator relay from a Minsk motorcycle. Everything was insulated, varnished and dried. The top of the case is covered with a piece of PCB
The photo of the device was not preserved; the Viper went to a new owner along with the relay.
That's all for now, good luck with the repetition. With uv. Admin check
Sale on AliExpress. Hurry up to buy cheaper!
How to check PP with a multimeter on a moped?
The relay regulator on a Chinese scooter is checked using a multimeter with a voltmeter function. For this purpose, a simple DT-830 (or equivalent) is usually used. It is better to carry out diagnostics and measurement of output voltage with the device removed.
Verification algorithm:
- You need to unscrew the fairing with the central phase and find on the frame a device with 4 wires: red, green, yellow and white.
- Then start the scooter and check the voltage at idle: measure it between the green and red wires, setting the multimeter to the maximum value of 20 V.
- If the multimeter display shows a figure of 14.6-14.8 V, this is normal. For stabilizers on Chinese mopeds, this is the operating standard voltage. If at idle the multimeter shows a value of 15-16 V, this is a high voltage indicator. This indicates a malfunction of the relay regulator.
- Then you need to check the voltage supplied to the lighting lamps. An alternating voltage is supplied to the central low beam (high beam) lamp, so the multimeter should be switched to the alternating current measurement mode with a parameter of 20 V.
- Next, we measure the voltage between the green and yellow wires (green is the general electrical network of the moped). If the multimeter shows a network voltage of up to 12 V, then the electrical appliances are operating without additional load.
- If at idle this value is 16 V or higher, and with a sharp increase in engine speed it jumps to 25 V, the device does not stabilize the voltage and, therefore, does not work. With such readings, the device must be replaced with a new one.
Using a multimeter, they check the relay regulator on a Chinese scooter
On 4T scooters, the relay regulator is checked using a tester. Typically a mechanical tester is used for these purposes, although there are also electronic models.
In order to take a measurement, you need:
- switch the device to the “KiloOhm” mode and remove the regulator;
- then place the probes on the first pair of terminals (AB). The tester should show a value of no more than 18 kOhm;
- after that, we change the position of the probes on the terminals in the opposite direction (VA) and measure the voltage again - the arrow on the device should show 0;
- then we install the probes on the next pair of terminals (SD) and measure the readings on this pair;
- swap the probes (DS) and measure the indicator again;
- the remaining measurements have no contact and are not checked. The indicator when checking them should be zero.
In this way, regulators are tested on popular Japanese models with small engine volumes from brands such as Honda (Leard, Dio, Tact), Suzuki, Yamaha.
Replacing a faulty relay regulator on a scooter is not difficult.
What is a voltage regulator relay for Viper, Delta, Alfa mopeds
Since I created a comprehensive site, I want to devote a little time to Chinese mopeds, or rather, today we will touch on the voltage relay regulator of Viper, Delta, Alfa mopeds. I found the relevant information and want to share it with you.
The wiring of the Chinese mopeds Viper, Delta, Alfa is very interesting. The ignition is separate, the lighting is separate, which is similar in many other scooters and motorcycles. But the lighting itself is very confusing. We have two lighting branches, one is the electricity from the generator, the other is from the battery. At the same time, the generator itself also powers the battery. And to connect these two wires, a voltage regulator relay is used.
It is designed to rectify the voltage and stabilize it so that the battery and lighting do not receive more current than usual (remember how the light bulbs burned in old motorcycles, all because there was no stabilizer). This is the main task of this voltage regulator relay. And if you look at the number of wires of such a relay-regulator, we see four of them. One, green, is the ground (in scooters the ground is often green), the other is red, it goes to the battery. The third and fourth come from the generator. And here you can get confused. Each wire comes with a voltage of 12 V, but if you look closely at the structure of the generator, it is clear that one has a slightly lower voltage, this is done for the sake of relativity, so that the relay can compare two voltages. It is important here not to confuse the wires, since in some scooters they are marked with white and yellow colors, while in others there are two white ones. But they are not the same, they cannot be confused.
How to replace a faulty relay regulator on a scooter?
If the charging current is not supplied to the battery contacts when the generator is working properly, the stabilizer needs to be changed. Replacing it yourself is not difficult.
To do this you need to do the following:
- Place the scooter on the central support.
- Find the location of the device in a specific moped model. If you can’t find it right away, you can use the instruction manual.
- Dismantle the cladding. Depending on the moped model, the stabilizer may be located on the front (under the front plastic), in the rear, or under the seat. In this case, the underseat space is removed along with the seat.
- Unscrew the device from its seat while maintaining the fasteners. As a rule, the relay is attached to the scooter frame with a bolt, or less often with a self-tapping screw.
- Disconnect the connector and secure the new regulator with the fastener. The installed device must have a pinout and connector similar to the one replaced, and be suitable in terms of parameters for this particular scooter model.
- Connect the relay-regulator on the scooter to a standard connector and assemble the remaining spare parts in the reverse order of disassembly.
What is a voltage regulator relay for Viper, Delta, Alfa mopeds:
It should be noted that depending on the generator that is installed on the moped, different relay regulators are installed. A relay shown in the photo is installed on a single-phase generator (5-6 coils), while a SH6108-12 relay is installed on a two-phase generator (2 coils) (installed on Japanese scooters)
I bought another viper asset. Once again I was convinced that the native regulators are complete g.... (I apologize for the expression) Dead Akuma again! It's a shame! It is necessary to solder a new regulator circuit and slightly rewind the generator winding. then it will make sense)) With uv. Eduard Orlov
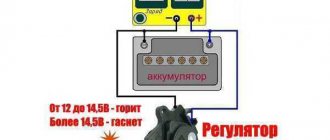
The battery must be protected from overcharging. A network voltage higher than 14.5 V is unacceptable. The battery will boil. It’s also bad if the voltage is below 13.8V and there is no additional charge. But this does not threaten Chinese mopeds. A common problem with a two-coil, or rather single-coil, generator is overcharging and a non-durable regulator. Therefore, I advise you to attach additional. device, voltmeter. In case of overcharging, you can extinguish lamps of at least 21 candles by connecting to the battery. It's as hot as a brake light.
What is a voltage regulator used for?
The relay regulator stabilizes the voltage of the scooter generator at the required level, not allowing it to increase or decrease the value above or below the norm. This prevents on-board voltage surges from going beyond the established limits (depending on the boards this is 12-14 V) and ruining the work of consumers whose service life is designed to be no more than 13 V.
That is, this part takes on the impulses that arise during the operation of the scooter (turning on the headlights, the starter button) and transfers the resulting thermal shock to itself. In this case, all the heat that could settle on the contacts is generated in it and removed through the device.
In addition to stabilizing the voltage, the relay also converts alternating current into direct current, which is necessary for charging the battery.
Moped manufacturers install charging relays with different parameters on scooters and select them individually for each. Depending on the regulator circuit, the connectors also differ. Chinese models usually have 5 terminals (male), while Japanese models have 4.
Method for checking the voltage regulator of a scooter
Chinese scooters are designed in such a way that their relay-regulator, which is also called a voltage regulator, often burns out. The voltage regulator is an electronic circuit with 4 terminals for connecting to the scooter's electrical network.
A malfunction of the voltage regulator leads to very disastrous consequences:
First, backlight lamps and the central low/high beam lamp burn out. This happens due to the fact that the voltage from the generator is not limited to 12 volts, which leads to the lamps receiving an increased voltage of 16 to 27 volts and higher. The voltage supplied to the lamps fluctuates and depends on engine speed. Even at idle, the lamps shine so much that they blind, although they should shine at half their maximum brightness.
If you do not fix the malfunction of the voltage regulator and leave everything as is (many do this - they just drive without lights), then over time the battery will fail because its charging voltage exceeds the permissible limit. If the voltage regulator is faulty, the battery receives a voltage of more than 15 volts, while the standard charging voltage should be in the range of 13.5 - 14.8 volts. All this leads to the fact that the battery begins to leak - acid begins to seep through the valves. This is noticeable to the naked eye. And although when the normal charging mode is restored, the battery restores its operation, its service life is sharply reduced.
Signs that a check is needed
If the battery on your scooter often runs out, and it is still quite new, this means that there is a problem with the operation of the relay regulator. As practice shows, it burns out quite often. If the device is faulty, the battery stops charging completely and loses its capacity. This means you won’t be able to start the scooter with a button; you’ll have to start it with a kickstarter.
Another characteristic sign of incorrect operation of the device may be the frequent burnout of incandescent light bulbs. They themselves are durable and have a good durability, but are quite sensitive to voltage changes. This happens because the optimal voltage in the scooter network is considered to be 12-13 V. Increasing this value even by 2 V reduces the service life of electronics and components by 2 times.
The greater the deviation from the norm, the greater the likelihood that something will burn out in the scooter. Therefore, when starting the scooter from the starter due to a power surge and a faulty relay, the bulbs usually burn out.
Signs of a malfunctioning regulator are identical for all models of Chinese scooters. They are especially typical for charging relays for scooters of Chinese models with an engine capacity of 50 cc. Therefore, before making a decision to replace something in electronics, testing systems and devices should begin with the relay regulator.
For all models of Chinese scooters, the symptoms of a malfunction of the regulator are identical.
Viper Active - electrical repair manual
The most popular scooter in Russia and Ukraine is Viper Active .
And here everything is simple, decent appearance, an established network of product suppliers, an attractive price and a truly bassy and beautiful exhaust sound, which is sometimes misleading, and it seems that the Viper Active is not equipped with a 49.9 cubic centimeter engine, as indicated manufacturer. In most cases, this is exactly the case. As statistics show, almost 80 percent of equipment from China, which is allegedly equipped with a 49.9 cc engine, when opened and measured, is equipped with 62cc, 65cc and 82cc engines. It’s the same story with Vipers, namely the Viper Active often suffers from a 110 cubic centimeter engine, which is naturally disguised as fifty dollars. There's a good chance you'll miss the mark when registering, so you should consider these factors when purchasing.
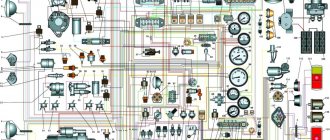
Repairing the Viper Active is not difficult and you can easily do it yourself, even if you do not have enough experience for this and have not interacted with equipment. For repairs, you will also need the Viper Active electrical repair instructions , which you will find below.
In fact, this circuit is probably better equipped than all the others. There is Russian language, detailed color details and a high-quality description of each element. Each part is numbered and indicated at the bottom in a footnote.
Another scheme for Viper Active:
You can also read other articles on the topic:
Source
Viper asset generator circuit
Gray wolf ! Manufacturers are struggling, they cannot get rid of this diode in the feta structure, because it is parasitic, and then bam - it turns out that it is intended for something! Some low-voltage fetas even have a Schottky diode built in to eliminate the internal parasitic one, because the latter has extremely poor speed characteristics.[/quote]
Well, I don’t know the intricacies of production. Maybe so. But you confirmed that its characteristics are an order of magnitude worse than those of the transistor itself. I just advised you to do what, as you said, the manufacturers themselves do - connect Schottky diodes in parallel. Thanks for the useful information!