About lean mixture and two-stroke engine
If your carburetor is not set up quite correctly, a situation may occur that the engine will run on a lean mixture.
A lean mixture is when there is less gasoline in it and more air. It would seem - well, what’s wrong, well, it will burn more quietly, but it won’t overheat. But in fact, the opposite is true! A two-stroke engine does not have a separate lubrication system. Oil gets into moving parts (piston and cylinder walls, as well as crankshaft main bearings, connecting rod needle bearing) from the fuel mixture. A lean mixture is not only a lack of gasoline, but also a lack of oil. The crankshaft rotates at enormous speeds - thousands of revolutions per minute, so the bearings must always be well lubricated. Ultimately, an insufficient amount of lubricant will lead to severe heating of engine parts. The bearings will burn out and may fall apart. The piston head will burn out. Broken pieces of parts will damage the inside of the engine.
Of course, it’s not necessary that everything will fall apart at once, but thermal seizure of the piston, one might say, is guaranteed.
Therefore, it is extremely important to control the quality of the mixture. This can be done visually by turning out the candle (I have already written about this more than once). Signs of a lean mixture are a white insulator.
What can cause a lean mixture? First of all, an unadjusted carburetor. You can read how to adjust the carburetor in a separate article.
Another reason is air leaks in the fuel lines. This is usually a bad or missing gasket.
And the third reason is the zero-resistance filters installed instead of the standard foam filter. If you have installed FTS on your scooter, it is necessary to adjust the carburetor, because such a filter, by its design, leans the mixture.
In general, on a two-stroke engine it is better to overdo the mixture than to run it too lean. Although a rich mixture leads to the formation of soot, this soot is not as bad as overheating.
Please note: This article and the images in it are subject to copyright. Partial or complete reproduction on other resources without permission is prohibited.
Lubrication system and fuel preparation
The operation of a two-stroke engine requires effective lubrication of moving parts. There is no centralized separate lubrication system with an oil pump, like in four-stroke engines, so oil is added to gasoline in a ratio of 1:25 - 1:50. The resulting composition, being in the piston and crank chambers, lubricates the connecting rod bearings, cylinder walls and piston rings. When the air mixture ignites, the oil burns and is removed along with the exhaust gases.
The motor oil must be special - for a two-stroke engine, usually it is marked 2T on the canister. The use of conventional automobile oil is unacceptable for a number of reasons:
Lubricant can be supplied to a two-stroke engine in two ways. The first and simplest is to mix it with fuel in the required proportion. The second is a separate lubrication system of a two-stroke engine, when a composition of fuel and oil is prepared immediately before entering the engine in a special pipe. In this case, a separate oil tank is installed, and its supply is carried out using a special plunger pump.
This system is widely used on modern motorcycles and scooters. In addition to ease of use (now you no longer need to add oil to the tank by eye every fill-up), serious oil savings occur because its injection depends on engine speed. At idle speed the oil proportion can be as low as 1:200.
Two-stroke engine design
The design of such a motor is simpler than that of a four-stroke. A two-stroke internal combustion engine does not have a gas distribution mechanism. The engine consists of a cylinder block in which the crankshaft is located on bearings.
The connecting rod head fits into a special place for it - the shaft journal. Between the connecting rod head and the shaft journal there are liners that are secured with castle nuts.
The upper part of the connecting rod is attached to the piston via a pin. A pin is a hollow cylinder that serves as a connecting element in the connecting rod-piston structure.
Compression rings are installed on the piston in special grooves around the perimeter in the upper part, on which engine compression depends.
The driving element in an internal combustion engine is the fuel-air mixture, which, when burned, creates energy that pushes the piston down. The up and down movement of the piston causes the crankshaft to rotate. A flywheel is attached to the crankshaft, which transmits rotation further, that is, to the gearbox shaft and so on.
The two-stroke engine is cooled through the fins of the outdoor unit. In addition to external cooling, some of the cooling comes from the oil contained in gasoline.
Two-stroke engines are filled with gasoline to which special motor oil has been added. For example, for a Shtil lawn mower, for 5 liters of gasoline, you need to add 100 grams, that is, the ratio of gasoline to oil is 50:1. This is exactly the amount of oil that perfectly lubricates the rubbing surfaces of the cylinder with the piston rings.
The principle of operation of the internal combustion engine
The working cycle of a two-stroke engine consists of intake and exhaust occurring per revolution of the crankshaft, while a 4-stroke engine has the following cycles - intake, compression, power stroke, exhaust. And they leak within two revolutions of the flywheel. In a 4-stroke engine, intake and exhaust are carried out in the form of different processes; in a two-stroke engine they are combined with compression of the fuel mixture and expansion of the working gases. Operating principle of a two-stroke engine:
A two-stroke diesel engine works on the same principle, only it does not have a spark plug, and the fuel is ignited by compression. Therefore, the compression ratio in diesel engines is much higher than gasoline engines.
Adjusting the carburetor on a 2t scooter: setting it up together
We continue to discuss DIY motorcycle repairs.
The carburetor has been cleaned, the next step is to adjust the carburetor of the 2t scooter. Over the summer, you have to adjust and adjust the operation of the engine several times.
Anyone who is at least a little familiar with the structure of the carburetor will be able to set it up on their equipment themselves. On 2-stroke engines, carburetors are adjusted according to the same principle. Therefore, the topic will be of interest to owners of any brand of 2t 50cc scooters. Whether you have a Honda Dio 27, 34, 35, stroke, Yamaha Jog, BVS or other 2-stroke mopeds.
A few words about the required frequency of adjustments
Of course, it is better to perform such maintenance more often, without waiting until the engine begins to stall or simply does not start. It is recommended, as a preventative measure, to perform this procedure approximately once every six months.
adjusting the carburetor 2T scooter
Having bought a motorcycle, scooter or other motorized equipment, owners have to become familiar with the operation and adjustment of their main components. One of the important elements of a two-stroke or four-stroke power unit is the carburetor, which is responsible for supplying fuel to the combustion chamber and mixing gasoline with air in the required ratio. Many people do not know how to adjust the carburetor on a scooter using the adjusting screw. This need arises if the device does not start well, shows increased appetite, or the tachometer needle indicates unstable speed.
Diagnostics
Before installing the air filter, turn on the ignition and jerk the kickstarter foot several times until the engine starts.
If it does not start, then the most common reason is that the cold start system is malfunctioning.
We check this way: cover the carburetor hole with your fingers to maximally enrich the mixture with gasoline, and continue to push the kickstarter.
If the engine starts and the speed does not drop during operation, then look for the reason in the cold start system.
If the cold start system is working properly, then after starting the engine the speed will rise and gradually, within 10 minutes, begin to fall. On a warm engine, gradually unscrew the large screw (amount of mixture) until the speed drops to medium, confident idle.
At the same time, drops of gasoline should not splash or pour out of the carburetor.
Purge problem
The higher the crankshaft speed, the more power. But the design of two-stroke engines has this peculiarity - the faster the piston begins to move, the worse the combustion chamber of the cylinder is purged, since the exhaust gas supply and exhaust windows remain open for a very short time.
Chamber purging is the removal of gases and injection of fuel into the cylinder from the crankcase. Fuel begins to be sucked in and remain in the crankcase as the piston moves upward. Then, when the piston goes down, the inlet port closes and the purge window opens, through which a new portion of fuel is supplied and the gases of the previous spent fuel mixture are expelled (see the figure above, in the middle).
This simple design of a two-stroke engine eliminates the need to install a gas distribution mechanism (GRM), a purge pump, valves and a lubrication unit.
Purging while a two-stroke engine is idling (idling) is carried out differently. During operation at XX, purging is carried out by opening the damper to a small angle. This kind of purging is not of high quality, so at idle speed, as many have probably noticed, the engine of a chainsaw or lawn mower does not work stably. As for a chainsaw, for example, Echo (Echo), then you need to pull the choke halfway.
A single-cylinder two-stroke engine has a contour blower, that is, a slot blower. At the bottom of the cylinder in the wall there is a special slot through which gas distribution occurs. During the compression and power strokes, that is, when the piston is up, the intake and purge ports must be closed.
Contour purge - this pre-piston volume (cylinder under the piston) is a purge pump. This design makes it possible to make engines of the smallest dimensions.
Disadvantages of two-stroke engines:
1. Higher fuel consumption. Let us remind you that the approximate consumption can be calculated using the formula: for a two-stroke 300 grams per horsepower, for a four-stroke 200 grams. 2. Noisy. At maximum speed, two-stroke engines tend to be slightly louder than four-stroke engines. 3. Comfort. Four-stroke engines do not vibrate as much at low speeds (Applies only to two-cylinder engines. Single-cylinder and two-stroke and four-stroke engines vibrate approximately the same) and do not smoke as much as two-stroke ones. 4. Durability. Quite a controversial point. There is an opinion that two-stroke engines are less durable. On the one hand, this is understandable, because the oil for lubricating the rubbing elements of the engine is supplied along with gasoline, which means it does not work as efficiently as in four-stroke engines where the rubbing elements literally float in oil. But on the other hand, a four-stroke engine is much more complex in design than its competitor, consists of a much larger number of parts, and the golden principle of mechanics “The simpler the more reliable” has not yet been canceled.
How to increase power
Like 4-stroke engines, 2-stroke engines can be improved, so-called chip tuning.
To increase the power of the internal combustion engine, you can do the following:
- Bore the exhaust hole so that the exhaust gases escape completely.
- Improve the blowing effect. Purging is the removal of exhaust gases and filling the working volume of the cylinder with a new portion of the fuel mixture. It must be done so that fuel can be injected into the combustion chamber through the inlet window. If fuel does not enter the combustion chamber in the required volume, fuel will accumulate in the engine crankcase. Therefore, for high-quality filling of the working part of the cylinder with fuel, it is necessary to increase the diameter of the exhaust window opening (exhaust gas emission).
- You can use a swirl diffuser on a carburetor. A swirl diffuser is also called a zero diffuser. Due to this diffuser, more fuel will enter the cylinder in a shorter period of time.
- Mount a special resonator on the muffler, suitable for the speed of the specific engine. The resonator makes sure that the unburned fuel mixture returns back to the cylinders. This is effective when incomplete combustion of the mixture occurs in the cylinder.
In order for the part of the cylinder under the piston to be filled completely, it is necessary to inspect the inlet and outlet channels; perhaps there are scratches, burrs, or chips on the holes. Such small defects affect the speed of movement of fuel and gases.
For a better effect of increasing power, the cylinder head (cylinder head) can be milled and then ground.
It is not recommended to reduce the weight of engine parts, since due to an increase in the difference in the counterweight and a violation of the center of gravity, the end runout of the flywheel and crankshaft may increase.
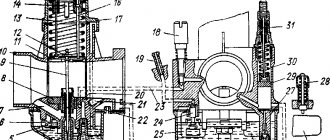
Tuning the carburetor of a two-stroke engine
One of the main components in the fuel mixture supply mechanism in a vehicle such as a scooter is the carburetor. Before moving directly to the description of the adjustment process, let's talk about why it is needed at all.
Carburetor - a device that ensures the formation and supply of a fuel mixture (consisting of air, gasoline and oil) directly to the engine
What exactly is the purpose of a carburetor? In a nutshell, this is a device that ensures the formation and supply of a fuel mixture (consisting of air, gasoline and oil) directly to the engine. That is, the quality of this mixture and, accordingly, the power that the power unit produces depends on it.
Scooters typically use carburetors of a type called “float” carburetors. The main element is a Venturi tube, which houses a damper that regulates the amount of air supplied to the mixture, as well as a needle that supplies gasoline. By unscrewing the throttle, we thereby open the throttle and raise the needle, increasing the amount of air-fuel mixture entering the engine.
Why do you need to regulate?
During the adjustment process, the scooter carburetor needle is adjusted, the position of which affects the proportions of the air-fuel mixture, as well as a number of other adjustments.
Adjusting the scooter carburetor needle is done during the adjustment process
Each tuning operation has a different effect on engine operation and fuel preparation:
- adjusting the idle speed ensures stable operation of a running engine when the transmission is turned off;
- changing the quality of the air-gasoline mixture using a special screw allows you to deplete or enrich it;
- adjusting the position of the carburetor needle affects the change in the quality of the fuel mixture;
- Ensuring a stable level of gasoline inside the float chamber avoids flooding of spark plugs.
A power unit with an adjusted carburetor operates stably in any conditions, is economical, throttle response, develops rated power and maintains speed, and does not cause problems for its owner.
Step-by-step instruction
And in conclusion: to some extent the answer to the question “how is the carburetor adjusted on a scooter” can be determined by the color of the spark plug insulator. If the color is black or dark gray, this means that the device is not configured. If the insulator is light brown, the quality of the fuel mixture is normal.
During the operation of motorcycle equipment, the carburetor periodically requires attention in the form of preventive maintenance so as not to lose its working properties.
Read also: How to make a sawmill from a chainsaw with your own hands
The first thing to do after removing the carburetor from the motorcycle is to wash it from the outside and only then begin to disassemble it; this will prevent further dirt from getting inside the carburetor and will protect you from blowing this dirt out of the narrow channels of the carburetor.
Read also: Range of equal flange steel
One of the main components in the fuel mixture supply mechanism in a vehicle such as a scooter is the carburetor. Before moving directly to the description of the adjustment process, let's talk about why it is needed at all.
Carburetor - a device that ensures the formation and supply of a fuel mixture (consisting of air, gasoline and oil) directly to the engine
What exactly is the purpose of a carburetor? In a nutshell, this is a device that ensures the formation and supply of a fuel mixture (consisting of air, gasoline and oil) directly to the engine. That is, the quality of this mixture and, accordingly, the power that the power unit produces depends on it.
Scooters typically use carburetors of a type called “float” carburetors. The main element is a Venturi tube, which houses a damper that regulates the amount of air supplied to the mixture, as well as a needle that supplies gasoline. By unscrewing the throttle, we thereby open the throttle and raise the needle, increasing the amount of air-fuel mixture entering the engine.
Naturally, the movements of the valve and the needle must be clearly synchronized to ensure its (mixture) homogeneity. The float chamber is designed to ensure the constant presence of gasoline in the tube. The principle of its operation is based on the fact that when the fuel level drops, the float lowers and opens a channel for supplying gasoline to the tube. When it is full, the float rises and closes the valve, thereby stopping the flow of fuel.
If the scooter's engine power drops, it is impossible to start the engine or the engine stalls - these are signs of a carburetor failure
Signs that the carburetor is faulty may include:
Another way to assess the quality of the carburetor (more precisely, the correctness of its operation) is as follows - unscrew the spark plug and look at its color. If it is white, it means the fuel mixture is lean, that is, there is too much air in it, and if the spark plugs have a black tint, it means the carburetor is “pouring” too much fuel. With any of these options, one thing is clear - it needs adjustment.
It should be noted that, globally, this process does not depend on the engine stroke, therefore the answer to the question of how to correctly adjust the carburetor on a Chinese 4t scooter and how to correctly adjust the carburetor on a 2t scooter will be the same. Let's now move on to describing the sequence of actions.
Read also: Connectors containing precious metals photo
Tips and tricks
Setting up the carburetor on a 4t 50cc scooter is an important and responsible procedure for servicing motorcycle equipment.
When performing adjustment operations, it is important to follow a number of rules:
- perform adjustments only after the engine reaches operating temperature;
- rotate the adjusting elements smoothly, observing the operation of the engine;
- Make sure there is no debris inside the fuel chamber and the jets are clean.
Before starting work on setting up the carburetor, you must study the operating instructions and clearly determine the location of the quality and idle screws. If you have a 150cc scooter, the carburetor adjustment is done in a similar way. After all, the process of regulating the fuel system is the same for engines of different powers.
How to adjust the carburetor on a scooter
This procedure can be conditionally divided into two parts - adjusting the idle speed and adjusting the quality of the carburetor mixture. However, first, the carburetor must be removed and cleaned.
Refer to your vehicle's manual to ensure proper disassembly. Thoroughly clean all its channels, as well as the jets. Unscrew the spark plug - even if it does not have the visual defects described above, it is better to replace it. Fortunately, their price is usually not high. On the fuel metering needle, find the locking ring and install it in the middle groove. After all these steps, install the carburetor back.
After checking and cleaning, which we have just completed, we proceed directly to the adjustment. You will need to find elements such as the screw that regulates the quality of the fuel mixture (hereinafter referred to as the KTS screw), as well as the idle screw. Screw the KTS screw all the way (this is done clockwise), and then unscrew it one and a half turns, and then start the engine.
Using your scooter's tachometer reading, adjust the idle speed screw so that the engine speed is at 1800 rpm. Go back to the KTS screw and, by rotating it, achieve maximum engine speed, then tighten the screw half a turn. Find the idle screw again and return the speed to 1800 rpm, while not forgetting to check the operation of the engine by ear - there should be no failures or extraneous sounds.
When the specified value is set, you need to check the operation of the power unit. Turn the lever that controls the throttle a couple of times, adding gas and releasing it.
If you don’t hear any extraneous noise in the sound of the engine and it doesn’t stall, the carburetor adjustment has been made correctly, that is, you can safely get on the scooter and go about your business.
If the problem is not resolved, then it is necessary to look for the cause in other components of the vehicle.
It is worth noting that sometimes adjustment is not enough - it is also necessary to check and, in some cases, adjust the fuel level in the float chamber.
Locate and unscrew the butter screw, which is located at the very bottom of the device. Next, you should lift the tube and check the fuel level. It is necessary to carry out these actions with the engine running, and keep the upper edge of the tube slightly above the carburetor itself. The fuel level should be slightly lower than the junction of the lower and upper parts of the carburetor.
Video tutorial on adjusting the carburetor on a scooter:
If the level is lower than required, you will need to remove the cover and adjust the timing of the valve by carefully bending its holder (this should be done in very small ranges). You can perform this entire procedure at the very beginning, so if you don’t want to remove the part once again, start the process of servicing the fuel system by adjusting the fuel level in the scooter’s carburetor.
How to adjust engine idle speed
Work on setting up the power system is carried out after the engine has warmed up to operating temperature. All types of carburetors installed on scooters are equipped with a screw designed to regulate idle speed. Changing the position of the adjusting element allows you to ensure that the engine operates at stable speeds during idling.
Depending on the vehicle model, the adjusting elements are located in different places, so you need to carefully study the instructions and determine where the idle speed adjustment screw is located on the scooter.
Rotating the screw in a clockwise direction allows you to increase the crankshaft speed. Turning in the opposite direction, accordingly, ensures a decrease in speed. To perform adjustment operations, it is necessary to warm up the power unit of the scooter for a quarter of an hour.
How to clean the carburetor of a two-stroke engine
Cleaning the carburetor of a 2-stroke engine
If you need advice on professional carburetor cleaning, check out this article. In it you will learn how to clean the carburetor of a two-stroke engine and under what circumstances you may need to clean it. Cleaning a small engine carburetor is usually done when rebuilding a carburetor, but there are a number of reasons why you may only need to clean it.
Proper cleaning of a two-stroke engine carburetor involves complete disassembly and reassembly of the device. Below are explained the steps on how to properly disassemble, clean and reassemble the carburetor of a two-stroke engine.
see also
Principle of operation. The entire working cycle in the engine is carried out in two strokes
1. Compression stroke. The piston moves from the bottom dead center of the piston (in this position the piston is at the bottom dead center, hereinafter we call this position for short BDC) to the top dead center of the piston (hereinafter TDC), blocking first the purge and then the exhaust window. After the piston closes the exhaust window in the cylinder, compression of the combustible mixture that previously entered it begins. At the same time, in the crank chamber, due to its tightness and after the piston closes the purge windows, a vacuum is created under the piston, under the influence of which a combustible mixture enters the crank chamber from the carburetor through the inlet window and the slightly open valve.
2. Power stroke. When the piston is positioned near TDC, the compressed working mixture is ignited by an electric spark from the spark plug, as a result of which the temperature and pressure of the gases increase sharply. Under the influence of thermal expansion of gases, the piston moves to BDC, while the expanding gases perform useful work. At the same time, going down, the piston creates high pressure in the crank chamber (compressing the air-fuel mixture in it). Under the influence of pressure, the valve closes, thus preventing the combustible mixture from entering the intake manifold again and then into the carburetor. When the piston reaches the exhaust window, it opens and exhaust gases begin to be released into the atmosphere, the pressure in the cylinder decreases. With further movement, the piston opens the purge window and the combustible mixture compressed in the crank chamber flows through the channel, filling the cylinder and purging it of exhaust gas residues.
Ignition principle. Since the fuel mixture takes time to ignite, the spark appears at the plug a little earlier than the piston reaches TDC. Ideally, the faster the piston moves, the earlier the ignition should be, because the piston reaches TDC faster from the moment of spark. There are mechanical and electronic devices that change the ignition angle depending on engine speed. Almost for scooters before 2000. There were no such systems and the ignition timing was set based on optimal speed.
COMBUSTIBLE MIXTURES
For the combustion of gasoline in the cylinders of a motorcycle, it is necessary that the fuel meets air, the meeting point of gasoline and air is the carburetor, and a mixture of these substances is formed here. For normal combustion of air, the mixture changes its composition depending on the time of year, engine load and other factors. Even small errors can lead to deviations in carburetor operation.
negatively affect engine performance.
Signs: motorcycle revs and speed decrease, spark plug is black or dark brown;
In addition to these types, there are 2 more intermediate ones, in which the manifestations of symptoms are weaker than in the extremes - these are “enriched” and “depleted” mixtures. In these options the excess is insignificant.
Medium and high speed tuning
Using the quality adjustment screw, the fuel proportions at idle speed are ensured. For medium and high rotation speeds, the engine operating mode is adjusted using a different method. After turning the gas handle, the fuel nozzle starts working, supplying gasoline to the diffuser. An incorrectly selected jet cross-section causes a deviation in the fuel composition, and the engine may stall when gaining power.
To ensure uninterrupted operation of the motor at a higher frequency, it is necessary to perform a number of operations:
- remove debris from internal cavities;
- set the gasoline level in the carburetor;
- adjust the operation of the fuel valve;
- check the cross-section of the jet.
The correct operation of the engine is indicated by its quick response when turning the throttle.
Adjusting the snowmobile carburetor
One of the conditions for improving output parameters is the use of a carburetor with a larger flow hole. However, simply enlarging the bore will not improve these parameters. At low speeds, these parameters can only worsen. The carburetor bore must match the engine design. Additionally, it can be said that not only maximum performance and maximum speed, but also the stability of the engine must be taken into account. It should be remembered that increasing the carburetor will only add little power. The engine and carburetor must be selected together.
The operation of a carburetor is based on the physical principle that when air passes through a Venturi, its speed increases sharply due to a decrease in pressure in a place located behind the Venturi. The fuel, located in the float chamber of the carburetor under the influence of atmospheric pressure, due to the pressure difference, tends to rise through the jets to the place of discharge, where it is picked up by the air flow, mixed with it and in this form is supplied to the engine. When the engine stops, the air pressure in front of the constriction, behind it and in the float chamber is equalized, and the fuel supply therefore stops.
A fuel level control system in the float chamber is necessary to maintain stable engine operating parameters. This purpose is served by two floats hingedly connected to a needle shut-off valve. When the fuel level in the float chamber rises, the floats, together with the shut-off needle, rise and the needle closes the passage hole located in the needle valve seat. Fuel flow stops. When the fuel level in the float chamber decreases, the floats with the shut-off needle are lowered, the passage hole opens, and fuel enters the carburetor float chamber. This maintains a constant fuel level in the carburetor float chamber.
Checking the fuel level in the float chamber involves measuring the distance between the float chamber needle valve flag and the base surface of the carburetor. Next, compare the measurement results with the specifications specified in the “SNOWMOBILE REPAIR AND SERVICE MANUAL” (SHOPMANUAL) for the desired snowmobile model. You can adjust the level by changing the position of the flag.
Idle speed is a mode of engine operation when the engine rotates at a very low angular speed, and the throttle valve is closed or open very little. The air flow is very small and its speed is not high enough to create sufficient vacuum to supply fuel. The idle system automatically comes into operation.
When the throttle valve is closed, fuel is metered through the pilot jet, mixing with a small amount of air, the amount of which is adjusted using the tuning screw. Then, the air-fuel mixture prepared in this way is supplied through the bypass hole into the engine, providing idle operating parameters.
If the throttle valve is opened slightly, the air flow speed increases, creating the vacuum necessary for fuel to flow through these channels.
In this system, there are two parameters that can be changed: the position of the air volume adjustment screw and the size of the pilot jet.
The throttle valve, located in the intake air duct, serves to control mixture formation in its low and middle position. The size of the cutoff on the throttle valve affects the acceleration dynamics. Throttle valves are numbered from 0.5 to 4.5 through 0.5, depending on the size of the cutoff on the throttle valve. Flaps with designations from 1.5 to 3.5 are common. The larger the designation, the larger the cut, the greater the air flow and the leaner the mixture. The throttle function can be considered as another air control system.
Signs that adjustment is needed
Based on certain signs that appear in abnormal engine operation, we can conclude that the carburetor needs adjustment.
The list of deviations is quite wide:
- the power plant does not develop the required power under load;
- when the scooter accelerates sharply, failures in engine operation are felt;
- a cold engine is difficult to start with the starter after a long period of parking;
- the scooter's power unit consumes fuel in increased quantities;
- there is no quick response of the engine to a sharp turn of the accelerator handle;
- The engine may suddenly stop due to insufficient fuel mixture.
The carburetor should be adjusted if there are signs that adjustment is necessary.
If one or more of these symptoms is present, you should adjust the carburetor, and then diagnose its condition and check the operation of the engine.
How does a two-stroke carburetor work?
Structure
The carburetor is essentially a pipe that controls the air and gasoline entering the engine. A two-stroke or two-barrel carburetor works the same as a regular carburetor, except that more air and gasoline can be supplied to the engine because there are more cylinders or pipes and therefore more air flow.
Throttle/valve
The throttle body, or throttle valve, controls the amount of air that is allowed through the carburetor (pipe). When this valve opens, air enters the carburetor and mixes with gasoline. A typical 4-stroke internal combustion engine requires only a small amount of gasoline to run, about 10 mg per combustion stroke.
Venturi
Venturi is a constriction in a pipe. Inside the Venturi there is a small hole called a "jet". The venturi creates a vacuum that sucks gasoline from a float chamber, which is supplied from the gas tank by a fuel pump that maintains the gasoline at near-atmospheric pressure. The process is actually quite simple. When the throttle valve opens, air enters the carburetor. The venturi creates the vacuum necessary to suck in air and a small amount of gasoline ("mist"), which then mixes with air, which is then drawn into the engine's combustion chamber.
Throttle
A choke is used to enhance control over the air and gasoline - the fuel. For example, if you are trying to start a cold engine, you may have difficulty mixing air and fuel properly due to certain variables inherent in the properties of gasoline and air. In particular, cold gasoline does not evaporate as easily and tends to condense on the carburetor walls. To overcome this, a device called a "choke" is used. The throttle restricts the air flow at the carburetor inlet. This creates a stronger vacuum, which uses less air but more gasoline to create a "rich" fuel that is easier to ignite when the engine is cold. As the engine warms up, less fuel is required.
Related articles:
Main problems and malfunctions of the carburetor.
Mesh filter. There are usually only two problems with this element:
- Blockage.
- Breaking.
In order to find out the cause of the breakdown, unscrew the fuel filter cap to remove the strainer. If dirt has simply accumulated on it, then washing it in gasoline or blowing it out will help.
If there is visible damage to the mesh filter, be sure to install a new one. There may also be damage to the fuel supply pipe (during repairs, it is practiced to check this element).
In most cases, the carburetor starter does not function due to blockages. Acetone or the same gasoline should be used for washing.
Blowing clogged carburetor parts with compressed air is an acceptable and convenient repair practice.
The throttle body, carburetor parts, intake or exhaust pipes - all of these parts are subject to depressurization. You can definitely check it in a primitive way - spread soap foam on the problem area.
How to change the quality of the fuel mixture
For all scooter engines, it is important to receive fuel with an adjusted ratio of gasoline to air. A lean mixture leads to improper operation of the engine, a drop in power and overheating of the engine, while a rich mixture leads to an increase in consumption and the formation of soot.
Adjustment operations are performed by changing the position of the quality screw and moving the throttle needle.
Turning the screw to the right causes the mixture to become richer, and unscrewing in the opposite direction causes it to become leaner. The same happens with the needle: when the needle is raised, the mixture becomes richer, and when lowered, it becomes poorer. The integrated use of both methods allows you to achieve optimal results during setup. However, not all carburetors have this feature, so, as a rule, one of two options is used.