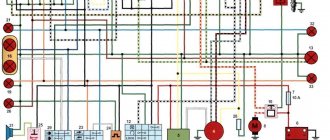
The Czechoslovak motorcycle has a number of advantages compared to other Soviet units, but is almost the same in terms of electrical equipment. The JAVA 638 wiring diagram is quite simple. Even an inexperienced motorist can handle repairs and maintenance.
Adjusting the ignition of the JAVA 638 is very important for the correct operation of the engine. You can do it yourself at home. To do this you need:
- Remove the spark plugs from both cylinders and remove the sump cover.
- After removing the spark plugs, install the indicator in the hole of the right cylinder.
- Now you need to fix the piston at top dead center. To do this, turn the crankshaft using a key.
- Then the cylinder contact spacing is adjusted. They should only touch slightly (distance approximately 0.35 millimeters ).
- A light bulb is connected to the contact on which the advance is set. This is done before setting up the ignition on the JAVE 638, to accurately measure the distances between the contacts.
- Zero is measured on the indicator, after which the position is fixed.
- The advance is different for each gasoline. So, when using the 92nd and 95th, the adjustment is 2.7-3.1 millimeters, for the 80th – 2.9-3.3 millimeters.
- If the installation is correct, the light goes out. Otherwise, adjustment will be carried out by a movable disk.
- An identical procedure is carried out on the other cylinder.
- When the adjustment is completed, crank the crankshaft several times using the kickstarter. Then the control ignition advance is performed. This completes the YAVA 638 ignition installation.
It is important to understand that if the ignition is incorrectly measured, the engine's operating life will be reduced.
Lock connection
- 30 - “+” from the battery (when turned on in the ignition switch mode, “+” supplies the following terminals:
- 58 - one turn of the switch - dimensions;
- 56 — two turns of the switch — headlight (low/high);
- 15 - turn the key to the right - ignition (on high coils) and other consumers.
If you want the sound signal and brake light to sound when the ignition is turned off, you need to connect these consumers to terminal 51. For example, on all my motorcycles, when the ignition is turned off, everything turns off. So that no one “beeps” a motorcycle without a key.
Source
Features of operation
It should be taken into account that the motorcycle managed to change several owners over a couple of years, so the original instructions rarely ended up in the hands of the last owner.
Original photo of JAWA motorcycle model 634
But in fact, it was not difficult for an experienced user to understand the electrical wiring diagram (see also about the features of the IZ Jupiter 5 wiring diagram). Moreover, we had to service the equipment ourselves due to the lack of service stations.
Old lady java ignition switch wiring diagram
The electrical equipment of Java motorcycles includes current sources, an ignition system and a lighting and alarm system.
Motorcycles are usually equipped with a dynamo-battery electrical system. Their current sources are a battery and a generator. The rated voltage in the electrical system is 6 V or 12 V.
Ignition
Position I (Fig. 89) corresponds to parking the motorcycle. The key is inserted or not inserted. The current from the battery through fuse 21 (see Fig. 85), terminal 30/51 of the ignition switch and switch 23 flows to brake light lamp 2, and through the second terminal 30/51 to sound signal 13. When the rear wheel is braked, the switch is activated 23 and brake light lamp 2 lights up, and when you press button 12, the circuit connecting the sound signal to ground is closed and it turns on. The contacts of the reverse current relay (regulator relay) are open, and no current flows to the generator.
Position II (Fig. 89) is used when driving during the day. The key is inserted and turned to the right. Terminals 30/51 and 15 are connected, and the current from the battery goes to the ignition coil 14 (see Fig. 85) and to the neutral indicator lamp 6 and the generator control lamp 7. This lamp is connected in parallel with the reverse current relay contacts and illuminates when they are open, indicating that power is being supplied from the battery.
With the ignition key in this position, the engine can be started. At a crankshaft speed of approximately 1500 per minute, the generator voltage reaches 6 V, and at the moment when it becomes greater than that of the battery, the contacts of the reverse current relay will close, as a result of which the current from the generator will flow to the electrical system (suitable for the battery the current will charge it).
The control lamp will go out because the resistance of its filament is greater than the resistance of the relay contacts.
Position III (Fig. 89) is activated to start the engine without a battery.
The key is turned to the left. Terminals 61 and 15 are connected. Current from the generator goes directly to the ignition coil. This position is used when the battery is faulty or missing. To start the engine, engage second gear, disengage the clutch and accelerate the motorcycle. When it gains sufficient speed, engage the clutch and, if the engine does not immediately start working, continue to increase the speed of the motorcycle. As a rule, the engine of a properly tuned motorcycle starts very quickly.
Position IV corresponds to driving at night on an illuminated road.
The key is inserted, the light switch is turned to the first position. In this case, terminals 30/51 and 58 of the ignition switch are connected. Power from the battery or generator is supplied to the taillight lamp and to lamps 18 (see Fig. 85) for the speedometer lighting and lamp 11. Such lighting is used at night when parking or driving on well-lit roads.
Position V (Fig. 89) is used when driving at night on an unlit road. The key is inserted and the light switch is turned to position II. Terminals 30/51, 58 and 56 are closed. In addition to the consumers turned on when the key is set to position IV, current from terminal 56 flows through switch 8 (see Fig. 85) to lamp 10 of headlight 9.
The electrical systems of other motorcycles operate similarly to the circuit discussed above.
Knowing the electrical circuit diagram of a motorcycle makes it easier to find a fault.
Rice. 85. Motorcycle electrical circuit diagrams: a - “Java-250” model 354/04; b — “Java-350” model 354/04; c - “Java-250” models 559/02, 559/04, 559/07; d — “Java-350” models 354/06, 360/00 1 — rear light; 2 — brake light lamp (6 V, 15 W); 3 — license plate lamp (6 V, 5 W); 4 - couplings; 5 - central switch with ignition switch; 6 — neutral gear indicator lamp (6 V, 1.5 W); 7 — generator warning lamp; 8 — low and high beam switch; 9 - headlight; 10 — low and high beam lamp (6 V; 25 + 25 W); 11 — parking (city) light lamp (6 V; 1.5 W); 12 — button to turn on the sound signal; 13 — sound signal; 14 — ignition coil; 15 - high voltage wire; 16 — spark plug; 17 — contact for switching on the neutral indicator lamp; 18 — speedometer lighting lamps; 19 - generator; 20 — relay-regulator; 21 - fuse (15 a); 22 - battery; 23 - brake light switch. Wire color symbols: B - white; F - yellow; 3 - green; K - red; C - blue; H - black
Electrical diagram
The electrical circuit of the YAVA 638 has been modernized based on the wiring of the previous model. The experimental 12-volt equipment was completely replaced and required the installation of a larger battery. Features of this innovation:
- the appearance of a 210-watt generator;
- possibility of installing an additional fog lamp;
- The stroller consumers were provided with current from a standard generator.
Thanks to the new system, the level of luminous flux was increased, which ensured driving safety at night. Spark formation has also improved, which contributes to more uniform and dynamic engine operation.
The new generator contains such basic elements as a rotor, stator and a metal casing. Its efficiency significantly exceeds the previously used 6-volt generator. This system allows charging even when the engine is running at low speeds.
However, the created system generated direct current, which needed to be converted into alternating current. For this purpose, a rectifier was built into the system. Its convenient location under the saddle makes it easy to carry out maintenance yourself.
However, when installing such equipment, the problem of overheating of the generator walls arose. It became impossible to use the rectifier inside a metal casing, so it was located under the driver's seat, providing air flow to cool the system.
The permissible power to a temperature of 150 degrees Celsius was 15 amperes. With the stroller and the use of all devices, it became possible to connect one additional consumer that does not require more than 40 watts of power.
Unfortunately, using a motorcycle in high temperature conditions of more than 30 degrees can lead to electrical equipment failure. For example, if the YAVA 638 does not start, there is a high probability that the stator winding has overheated or even the insulation has been damaged.
In general, we can say that innovations in the motorcycle have had a good effect not only on electricity consumers. Thanks to the new spark supply system, the engine began to work more evenly, as a result of which the bike became more dynamic. We can say that this unit was one of the best on the Soviet market.
Current sources
On a motorcycle, current sources are two devices:
- Battery;
- Generator.
Original power supply circuit for a Java 350 634 motorcycle
In the above figure, the generator is designated by the letter – G, and the battery – GB.
Also marked:
- Letter L – generator stator excitation winding;
- Letters EL2 – ignition system;
- Letter S – ignition switch;
- The battery charge or discharge level lamp is designated EL1.
JAWA Motorcycle Generator
The “634” model was equipped with a six-pole generator with a power of 75 watts and a voltage of 6 volts:
- Equipped with two breakers (one for each cylinder);
- Six pole coils with iron shoes;
- And a self-excitation system (works without a battery).
Illustration from JAWA service book
JAWA motorcycle battery
A 6 Volt 14 Ah battery was installed on the motorcycle (as in the IZh Planet 3 wiring diagram).
Features of the battery include:
- Location under the seat;
- The negative terminal was connected to the frame;
- Directly next to the battery there was a 15 A fuse on the bracket;
- The battery had a vent tube leading to the bottom of the motorcycle.
The battery was located under the motorcycle seat near the rear brake light.
For reference: the lack of spare parts led to the fact that owners were forced to operate the motorcycle without a battery. This was possible thanks to the design of the generator, as well as minor alterations to the electrical circuit.
Fantastic popularity
In the 70s, the domestic industry also did not stand still and offered consumers a number of motorcycle models (see also the article on the Ural motorcycle wiring diagram).
However:
- in terms of the ratio of speed qualities and comfort;
- and also combined with reliability and ease of DIY maintenance;
motorcycles from Czechoslovakia had no equal. Statistics eloquently testify to this: in 1976, more than 1,000,000 owners of a JAWA family motorcycle were recorded in the country.
Corporate photo of the Sporting Goods chain, which sold JAWA motorcycles in the USSR
Such enormous popularity was explained quite simply - the lack of technical ability for citizens to travel:
- Even with the funds to purchase, a passenger car had to wait in line for the suffering for several years;
- Domestic motorcycles were characterized by low reliability and were not suitable for comfortable trips of many kilometers (see also the details of the IZH Planet 5 wiring diagram).
For reference: the Czech-made motorcycle received its index “350” from an engine whose volume was 350 cubic meters. cm. The two-cylinder power unit had a power of 12 to 18 hp. depending on the year of manufacture.