"Ural"
- Soviet and Russian heavy motorcycle, produced at the Irbit motorcycle plant (Sverdlovsk region, Irbit). In the vast majority of cases it is used with a stroller. Motorcycle models are available both with and without sidecar wheel drive. The stroller wheel drive is switchable, non-differential. “Ural” is a further development of the M-72 motorcycle, a copy of the German BMW R71.
The following models were produced in 2013:
- with a stroller: “Ural-T”, “Tourist”, “Patrol 2WD”, “Gear-UP”, “Retro” [1] ;
- singles (without a stroller): “Retro Solo” and “Solo sT” [1].
These motorcycles are equipped with a four-stroke boxer two-cylinder engine with a volume of 750 cm³ and a power of 41 hp. With. (30 kW), 4-speed gearbox with reverse gear and cardan drive of the rear wheel [2].
List of models [edit | edit code]
Road motorcycles [ edit | edit code]
- IMZ M-72 (1940-1961) - the first motorcycle of the Irbit plant, a copy of the BMW R71, was modernized throughout its production, the latest model even received a short-lever fork and aluminum wheel hubs;
- IMZ M-52 (single) (1950-1957) - a model with the chassis of the M-72 and a 500 cm³ engine. Only a limited edition of 678 motorcycles was produced;
- IMZ M-61 (1957-1963) - a transitional model with the chassis from the M-72 and a new engine (650 cm³), the travel of the front fork and rear suspension has been increased. The front fork has been changed. The crew section has been lightened;
- “Ural” M-62 (1961-1965) - new gearbox, increased suspension travel, automatic ignition timing introduced, camshaft cam profile changed to reduce wear. The steering has been changed (chain throttle and duralumin clutch and brake levers);
- “Ural-2” M-63 (1963-1971) - a frame with a pendulum suspension of the rear wheel on spring-hydraulic shock absorbers (later a similar suspension was introduced on the sidecar wheel), ground clearance was significantly increased due to the introduction of a new exhaust system.
- “Ural-3” M-66 (1971-1975) - the engine was significantly modernized, the power increased to 32 hp. With. Engine durability has been increased due to full-flow oil purification and the use of a new crankshaft design. The motorcycle has direction indicators and new lights;
- "Ural" M-67 (1973-1976) - twelve-volt electrical equipment was used. The design of the motorcycle frame has been changed;
- “Ural” M-67-36 (1976-1984) - due to changes in the design of the cylinder heads, the use of K-301G carburetors with an increased diffuser diameter and an increase in the diameter of the exhaust system, the engine power was increased from 23.5 to 26.5 kW. (36 hp). The right turn signal on the motorcycle itself has been removed.
- “Ural” IMZ-8.103-30 (1985-1986 [ source not specified 2336 days
]) - the frame and rear suspension, optics, electrical equipment were modernized, a brake was installed on the sidecar wheel, instead of two mufflers, one was installed on the right side; - “Ural” IMZ-8.103-10 (1987-1994) - differed from the previous model by the presence of reverse gear, slightly lighter weight, noise and fuel consumption;
- “Ural” IMZ-8.103-40 Tourist - equipped with a lever front fork;
- “Ural” IMZ-8.123 Solo - a single unit based on the IMZ-8.103-10, engine power 40 hp. pp., 18-inch wheels;
- "Ural" IMZ-8.1037 GEAR-UP;
- "Ural" IMZ-8.1243 Voyage;
- "Ural" IMZ-8.1024 Cobra;
- “Ural” IMZ-8.1238 Wolf (1999-2011) - a motorcycle in the chopper style [3] [4] ;
- "Ural" IMZ-8.1036 Retro
Sports motorcycles [ edit | edit code]
- M-35;
- M-52S for road racing;
- M-52K for cross-country competitions;
- M-61K for cross-country competitions;
- M-62K for cross-country competitions;
- M-75M;
- M-76;
- M-77 for road racing.
- M-80;
- K-1000 for cross-country competitions;
- “Cross” IMZ-8-201 for cross-country competitions.
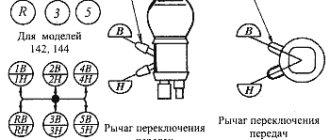
Motorcycle control mechanisms Ural M 62
The control mechanisms of the Ural M 62 motorcycles are divided into hand and foot.
The clutch and brake levers of the front wheel of the M-61 motorcycle are located on the handlebars with the ends outward.
The carburetor throttle control knob is a single cable coil type. The cable in the handle is wound onto the drum and, through a special adapter, transmits force to the throttle valve control cables of each carburetor.
The M62 motorcycle uses a two-cable throttle control. A chain is wound onto the drum, rigidly connected to a slider, to which the throttle valve control cables are attached.
There is no ignition timing lever on the M62 motorcycle, since it is equipped with an automatic ignition timing device.
The brake control mechanisms of the Ural M 61 and M 62 motorcycles are identical in design.
The brake pads of the hand and foot brakes are interchangeable.
Each pair of pads is tightened by two springs.
The expanding fists of the hand and foot brakes have small slots on their outer ends on which the levers are secured.
The hand brake lever is connected to a cable, and the foot brake lever is connected to a control rod.
The hand brake is adjusted using the adjusting screw on the brake drum cover.
The foot brake is adjusted using the adjusting wing nut at the front end of the brake rod.
Return to contents — ↑
Technical characteristics of modern models [edit | edit code]
Tourist, Tourist 2WD, Gear-UP, Troika Lux [edit | edit code]
| Tourist | Tourist-2WD | Gear-UP | Troika Lux | |
| Model: | IMZ-8.1037 Tourist | IMZ-8.1037 Tourist-2WD | IMZ-8.1037 Gear-UP | IMZ-8.1037 Troika Lux |
| Dimensions L×W×H, mm: | 2580×1700×1100 | 2580×1700×780 | 2580×1700×1100 | |
| Ground clearance, mm: | 125 | |||
| Dry weight, kg: | 350 | |||
| Total weight, kg: | up | |||
| Fuel tank, l: | 19 | |||
| Maximum speed, km/h: | 105 | |||
| Fuel consumption in the city, l/100 km: | 6-7 | |||
| Fuel consumption on the highway, l/100 km: | 4-5 | |||
| Engine: | 745 cm³, 42 l. p., 4-stroke, 2 cylinders, opposed OHV | |||
| Launch: | electric starter and kickstarter | |||
| Electrical system: | 12 V, generator 500 W | |||
| Ignition system: | contact | |||
| Checkpoint: | 4-speed, with reverse | |||
| Main gear: | gimbal | |||
| Gear ratios: [15] | I - 3.6; II - 2.62; III - 1.61; IV - 1.3; Rear: 4.2 | |||
| Main gear ratio: | 4,62 | |||
| Tires: | 4.00x - 19″ | |||
| Wheels: | knitted, painted, 19″ | spoked, chrome-plated, 19″ | knitted, painted, 19″ | spoked, chrome-plated, 19″ |
| Brakes: | front - hydraulic, disc; rear - drums | |||
| Suspension: | front - lever with spring-hydraulic shock absorbers; rear - pendulum with spring-hydraulic shock absorbers, adjustable for load | front - telescopic; rear - pendulum with spring-hydraulic shock absorbers, adjustable for load | ||
| Seat: | separate, double adjustable | solid | separate, double adjustable | solid |
| The package includes additional equipment: | Painted stroller wheel rack, driver's mudguards, passenger handles, parking brake | Chrome-plated rack for the stroller wheel, searchlight, driver's mudguards, stroller glass, shovel, canister, chrome-plated driver's protective bar, chrome-plated stroller protective bar | Stroller wheel rack, searchlight, shovel, canister, driver's mudguards, passenger handles, parking brake, driver's protective bar, stroller's protective bar | Chrome-plated luggage rack on the stroller wheel, chrome-plated passenger handles, velor upholstery of the stroller, leather passenger seat in the stroller, stroller glass, parking brake, driver's roll bar |
Retro, Retro-Solo, Wolf, Solo-sT [ edit | edit code]
| Retro | Retro Solo | Wolf | Solo-sT | |
| Model: | RETRO | RETRO SOLO | WOLF | Solo-sT |
| Dimensions L×W×H, mm: | 2224×1630×1020 | 2224×840×1060 | 2530×850×1300 | n/a |
| Ground clearance, mm: | 140 | 115 | 125 | |
| Dry weight, kg: | 343 | 220 | 260 | 198 |
| Total weight, kg: | 610 | 400 | 430 | n/a |
| Fuel tank, l: | 19 | |||
| Maximum speed, km/h: | 120 | 150 | ||
| Fuel consumption in the city, l/100 km: | 6-7 | 5-6 | ||
| Fuel consumption on the highway, l/100 km: | 4-5 | |||
| Engine: | 745 cm³, 42 l. p., 4-stroke, 2 cylinders, opposed OHV | |||
| Launch: | electric starter and kickstarter | |||
| Electrical system: | 12 V, generator 500 W | |||
| Ignition system: | microprocessor | |||
| Checkpoint: | 4-speed, with reverse | |||
| Main gear: | gimbal | |||
| Gear ratios: [15] | I - 3.6; II - 2.28; III - 1.56; IV - 1.19; Rear: 4.36 | |||
| Main gear ratio: | 4,62 | 3,89 | ||
| Tires: | 110/90-18″ | front 90/90-18″ rear 130/90-16″ | front 3.50-18″ rear 4.00-18″ | |
| Wheels: | spoked, chrome-plated, 18″ | spoked, chrome-plated, 18″ | spoked, chrome plated | spoked, chrome-plated, 18″ |
| Brakes: | front - hydraulic, disc; rear - drums | front - hydraulic, disc; rear - hydraulic, disc | front - hydraulic, disc; rear - hydraulic, disc | |
| Suspension: | front - telescopic; rear - pendulum with spring-hydraulic shock absorbers, adjustable for load | front - telescopic; rear - pendulum with spring-hydraulic shock absorbers, adjustable for load | ||
| Seat: | separate, double adjustable | separate, double adjustable | separate | separate |
| The package includes additional equipment: | Velor upholstery of the stroller, leather passenger seat in the stroller, stroller glass, parking brake, driver's roll bar | Driver safety bars | ||
differences in checkpoints
Good time. I'm interested in the question: what are the external differences between the Ural and Dnepr gearboxes?
It seems to me that there are tides under the filter and also the presence of reverse gear
Early boxes had the same filters. On the later ones on the Dnieper there is a dry element, on the Ural ones there is an oil element, the so-called pan. The bottom box is 2 cm longer and the shape is more angular.
Which boxes have a back and which don't?
[quote:c7de9bd4fe=”wodila-77"]it seems to me that there are tides under the filter and also the presence of reverse gear
I have an M66 1973 without a rear and an oblique air vent
some Ural vehicles do not have reverse gear
I don’t know before who the year was, but there were no ZHs in the Urals, that’s why they installed boxes from the Dnieper
to say that all Urals have reverse gear is incorrect because most Urals gearboxes that I have seen did not have it, but it seems like it is possible to install it
The photo shows an early box with a hatch and a bevel cut for an M-72 air vent. They were installed on the Urals and K-750 of early releases. I honestly don’t remember what markings it seems 6204 was on all M-72 (IMZ and KMZ) in the Urals it was before M-66 on K-750, MV-750, K-650. An oblique cut for the air filter and the presence of a hatch are its main differences from the KMZ MT-804 boxes, two modifications for a dry air filter and an oil air filter (plate) straight cut and the Ural box 6604 oil air filter (plate) a straight cut.
Yes 6604 without reverse gear, MT-804 with reverse gear.
Jay buddy, I don’t want to argue and try to prove something, just a friend asked about the differences at the Ural and Dnieper checkpoints and the first of these differences is that at all checkpoints the Dnieper is s.h. present, and on MOST of the Ural gearboxes that you can find, it is not there, but it seems like there is a possibility of installing it. And also, as far as I know, at the Dnepr gearbox there is a semi-automatic that allows you to change gears without a clutch; at the Ural gearbox, it seems to be missing (I won’t confirm)
on m-67 75 year. I couldn't find the back pederaci. Am I a durag?
The Dnerovskaya box has a number of advantages over the Uralovskaya one, because it was designed for warriors.
MOST Ural gearboxes that can be found do not have it, but it seems like it is possible to install it
Why did they still have gearbox adjustment screws and a manual gear shift lever until M-67-36?
I didn’t even think that such topics existed. Guys, don’t you know how the Dnieper engine differs from the Ural one?
Well, you damn it, it’s not clear. You're just polluting the airwaves.
Source
Total information
Motorcycle type: with sidecar. Wheelbase, mm – 1430. Ground clearance, mm – 130. Track, mm – 1100
Dimensions, mm: – length – 2420; – width – 1650.
Height (by ignition key) – 1000
Motorcycle weight, kg: – dry – 335; – worker – 380.
Fuel consumption on the highway, l/100 km – 7. Fuel reserve on the highway, km – 310. Highest speed, km/h – 85.
Capacity (oil), l: – engine crankcase – 2.0; – gearbox housing – 0.8; – reverse gear housing – 0.150; – air purifier – 0.2.
Fuel tank capacity, l – 22.
Transmission
On the M 61 and M 62 a clutch is installed, similar in design to the K 750 clutch, but the K 750 clutch is adjusted by one adjusting screw screwed into the clutch release lever, and the M 61 and M 62 clutches by two screws: an adjusting screw in the release lever and a shell stop screw cable screwed into the crankcase bracket.
Cardan and final drive diagram.
The power transmission gearbox of the Ural M 61 and M 62 motorcycles is the same in design as the M 72. True, there is not much difference, the M 62 differs from the M 61 only in the design of the shift couplings, the secondary shaft and its gears.
The cardan transmission is identical in design to the K750. The rear gears of the M 61, M 62 and K 750 are the same, with the exception of the crankcase covers: for the M 61 and M 62 motorcycles, the crankcase cover is made integral with the right suspension bracket, and the cover has an oil filler hole.
Return to contents — ↑
Engine
Engine type – four-stroke two-cylinder. Brand – M-72M. Cylinder diameter, mm – 78. Piston stroke, mm – 78. Working volume, cm³ – 746. Compression ratio – 5.5 ± 0.2. Maximum power, l. With. – 22. Maximum torque, kg m – 4.0. The block head material is aluminum alloy. Head gasket – asbestos metal 0.6 mm. The piston material is aluminum alloy.
Valve distribution phases (according to the angle of rotation of the crank), degrees: – beginning of intake to c. m.t. – 76; – end of inlet after n. m.t. – 92; – beginning of release BC m.t. – 116; – end of release after c. m.t. – 52.
Carburetor – Two K-37.