Unlike car batteries, motorcycle batteries have a lower capacity. At the same time, they work better due to kickstarter. No matter how functional the battery is, it needs to be recharged. To charge a motorcycle battery, you do not need to have special knowledge; it is enough to control the voltage and current during the process. If this is not done, the battery will be overcharged, which will negatively affect its condition.
A motorcycle battery has a smaller capacity than a car battery.
Battery charging rules
It is important to remember that batteries of different quality require different charging frequencies.
For example, lead-acid batteries - once every month and a half or a month. Gel ones hold a charge longer, so it’s enough to charge them once or twice during the entire season. Before removal, it is important to write down the terminal connection diagram. This will save a lot of time when you reinstall the battery. Next, you need to wait until the battery warms up to room temperature. The charging itself should be carried out away from sources of fire or sparks. When connecting, observe the polarity.
There is a rule that works effectively for lead batteries: the current should be equal to 10% of the battery capacity. The desired value can be set on the corresponding regulator.
Often beginners do not know how long to charge a moped battery. It can be visually determined by the bubbles that begin to appear on the surface of the electrolyte. After this, the current is reduced by half and the battery is charged for about 2 hours.
Sometimes there are disputes about how to properly charge a dry-charged motorcycle battery. The standard duration of the procedure is up to 9-10 hours. If the battery is new, then 3-4 hours will be enough.
Gel batteries are also charged at a current of no more than 10% of the battery capacity. Even when charging a gel battery, there is no reduction in current for recharging.
When preparing to charge, avoid silly mistakes like incorrectly connected poles. Sometimes the battery becomes overcharged. In such a situation, use a current strength that is two times lower than usual - 5% of the battery capacity.
What do you need to know about battery charge/discharge?
If the voltage on the battery is not lower than 12.5 Volts, it’s okay, but you need to charge it as quickly as possible, otherwise sulfation will develop. Another important thing is that deep discharges shorten the battery life. But if the voltage on the battery is below 12.5 Volts, which indicates an unacceptably deep discharge, then the battery will indeed soon fail, since irreversible processes have begun.
Let's start charging the battery
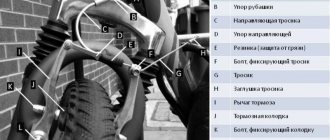
So, the battery is ready to charge. Connect the terminals of the charger to the battery. The red terminal is to the positive terminal of the battery, the black (or blue) terminal is to the negative terminal. Don't mix up the polarity!
Most modern chargers automatically set the charge current and charging time. But if it is possible to set the charging current, it is chosen by dividing the nominal capacity of the battery by ten. For example, with a capacity of 4 Ampere-hours, the charge current should be 0.4A. In this case, the charging time will be approximately 10 hours.
You should not charge a motorcycle battery with a car charger if it cannot charge with a current of less than 1A. High charging currents can damage the battery.
The process of charging the battery of an Alpha moped is shown in this video
Noise when charging battery?
While charging the battery, the electrolyte enters into a chemical reaction with the lead plates, and its constituent acid releases gas (hydrogen) in the form of bubbles. Those. what you hear is the process of slight gas formation in the battery. Visually it looks like boiling.
Tips for proper charging
Make sure the battery is at room temperature before charging. It's also worth checking to see if there are any open flames or sparks nearby. After this, you can connect the charger, observing the polarity.
Lead-acid batteries must be charged at a current equal to 10% of their capacity. Therefore, using the current regulator, set the required value. In this form, charging should be carried out until the voltage reaches a value equal to the number of battery cells multiplied by 2.4 (for a standard battery, respectively, 14.4).
When visually observing the electrolyte, this moment will come when gas bubbles begin to form on the surface of the acid. After this, you need to reduce the current by half and charge for another 2 hours.
The gel battery is charged in a similar way. Here you also need to use a current that does not exceed 10% of the battery capacity. The main feature of this process is that the voltage supplied to it should not exceed the threshold. For most gel batteries, this indicator is in the range of 14.2-14.4 V. Well, the second stage of charging with a decrease in current is not required here. Just continue the process until fully charged. This usually takes about 10 hours.
And one more useful tip. If you have over-discharged your battery (it doesn’t matter whether it’s lead or gel), you need to revive it with a current half as strong as usual. That is, approximately 5% of its capacity. The charging time will also increase noticeably. If this doesn't help, nothing will help.
How often should you charge your motorcycle battery?
A motorcycle battery needs to be charged when it is completely discharged. Lead batteries require this procedure every 2 months. Power supplies used for more than 2 years are charged once a month. Gel batteries have the lowest self-discharge. It is enough to service them once every 3 months.
After storage, a power source that has been discharged over the winter should be charged immediately. Don't wait until your motorcycle won't start. A critical discharge negatively affects the performance of the battery. A voltmeter is used to monitor the condition of the power source.
Testing is done like this:
- The indicator is set to 20. The red probe is connected to the positive current terminal, the black one to the negative one.
- Evaluate the reading appearing on the tester screen. The normal value is 12.3. When you receive the number 11.2, you need to urgently start charging. A critical loss of energy is indicated by an indicator of less than 11. Recharging in this case may not help.
Automatic and non-automatic charger for 12V batteries.
How to charge a gel battery for a moped without special charging
A couple of years after purchasing a moped, it becomes necessary to recharge the battery. And then it turns out that the battery belongs to the category of gel batteries, for which not all chargers are suitable. How to restore battery capacity if a special charger is not at hand?
Is there an alternative to special memory devices? The gel battery does not tolerate overdischarge, as a result of which the gel melts and turns into liquid. For this reason, devices capable of charging a lead or AKB battery for a moped are not suitable for recharging. These options have too high current and voltage ratings.
You need special chargers with automatic adjustment of the charging current, which are quite difficult to find on sale. The voltage of a suitable charger does not exceed 14 V, and the upper current threshold corresponds to 1/10 of the battery capacity (for 5 Ah - 0.5 A, for 7 Ah - 0.7 A). In this case, the device determines the charging time and turns off automatically when the battery is fully charged.
As an alternative to special chargers, you can use conventional chargers with a low charge current (for example, 0.5 A) and an output voltage of 12 V, which are suitable for recharging batteries with a capacity of 5 Ah or more. In this case, it is important to turn off charging in time to prevent the battery from heating up.
To determine the duration of the procedure, it is worth dividing the battery capacity by the current strength (for a 5 Ah battery and a 0.5 A charger, the charging time will be 10 hours). It is also important to periodically check the voltage on the gel battery using a tester: it should not exceed 14 V.
Which factors shorten and which extend battery life?
The following factors can reduce battery life:
- Frequent full discharges and charges. The first sign of element failure is a light coating.
- Overheat. If the case temperature reaches 50°C, the likelihood of failure increases.
- Operation in frosty weather.
- Long-term storage in a discharged state. When the voltage drops to 10 V, the battery can be disposed of.
The service life is extended by reducing the output voltage to 0.3 A. The charging duration increases to 24 hours, but the loss of capacity is reduced.
Types of chargers
To restore the charge of moped batteries, the following types of devices are used:
- Simple. The required characteristics of the electricity supplied by the devices are specified by the user. It is necessary to constantly monitor the condition of the product using a universal tester. If a multimeter is not available, remove the plugs and measure the density of the acid solution. Other characteristics of a simple charger are not much different from the properties of more expensive models.
- Automatic. In this case, the device independently controls the process, choosing the appropriate parameters. Automatic devices are well suited for restoring the power of motorcycle batteries at home.
- Automotive. They are rarely used, which is explained by the difference in battery capacities for cars and motorcycles. An automobile charger produces high current, which leads to boiling of the electrolyte and destruction of the plates. Batteries charged with such devices often become unusable. Car chargers can be used if they have a parameter adjustment function.
Moto AGM battery: commissioning
Hello, Habr! Today we will put into operation a dry-charged motorcycle AGM battery
. This manual can also be used for conventional dry-charged calcium batteries with liquid electrolyte.
At the same time, we will discuss how different types of lead-acid batteries differ, and how this affects their use. As always, there will be videos and instrument readings.
Such small batteries are used in motorcycles, scooters, ATVs, jet skis, snowmobiles, cultivators, mini-tractors and even sprayers.
The main difference between a motorcycle AGM battery and conventional backup batteries (for uninterruptible power supplies, UPS) and traction batteries is the purpose, according to which key parameters are standardized. Batteries intended for different purposes and conditions of use have different parameters.
The voltages in this article will be given for the most common 12-volt batteries, which includes the experimental one.
For a starter or low-power backup battery, the title is the useful capacity of a 20-hour, sometimes 10-hour discharge to 10.5 or 10.8 volts under load. Example
- GS-12-12 L: 12 volts, 12 amp hours.
For traction (deep cycle) as the main parameter
the capacity of a 2-hour discharge is normalized (6-DZM-12: 6 cans, that is, 12V, 12 A*h), for a powerful backup - the power of a 15-minute discharge (HR-W 12-34: 12V, 34 watts per can ). Here is the answer to the question why a traction or premium UPS battery of the same voltage, the same title capacity has a weight, price and sometimes size noticeably higher than that of a budget UPS line.
, Peukert's law comes into force
, according to which the useful delivered capacity will be lower than at lower currents.
The reasons for this phenomenon
are polarization and clogging of the pores of the active masses with reaction products, in the case of a lead battery - with lead sulfate crystals. The way out is to add more active masses, which, along with a more durable design of current leads, plates and separators that prevent their destruction, will also be useful for improving the following characteristics.
The second and third most important parameters
are the number of charge-discharge cycles and service life with constant buffer charging until the capacity is reduced by 20-40 percent. In addition, in the information sheet (datasheet) for the battery, manufacturers usually provide tables and graphs of capacity at different currents and discharge power to different voltages, taking into account temperature.
Unlike traction and reserve batteries, after capacity, the starter battery has the second, most key parameter
- starting current, normalized as cold cranking current according to one or another measurement standard.
It is this that determines the ability to start the engine with a starter, which is the primary task of a car or motorcycle battery. Therefore, the main property
of a starter battery is to produce a very significant current for a short time, and then promptly replenish the expended charge from the generator.
The starter battery of a modern vehicle, in which there are many consumers of electricity, including such powerful ones as heating devices and winches, which is often operated in the “urban” mode for short trips, in addition to decent capacity, must have a third important property
- the ability to withstand cycling and long-term stay in a state of partial charge -
PSoC, partial state of charge
. That is why AGM or EFB (SFB, etc.) are increasingly being installed under the hood - starter batteries that have some features of traction batteries.
In AGM - absorbent glass mat
- the liquid electrolyte does not splash freely, but impregnates fiberglass separators - glass mats. Similar glass mats, along with envelopes protecting the plates, can be used in the EFB design, where the electrolyte splashes freely. Also, these premium-segment batteries are equipped with reinforced grids and thicker active masses compared to conventional starter and cheap reserve ones. All this increases reliability and durability, but most often complicates the diffusion of ions and mixing of the electrolyte, therefore, when operating advanced batteries, their features should be taken into account.
So, we have a new AGM battery Siltech DC MF 1205 12 V 5 Ah. The kit includes a passport with instructions in Russian, the battery itself, screws with nuts for the terminals, a convenient battery of capsules with dosed electrolyte and valve plugs for the filler necks, structurally combined with the top cover.
Containers with electrolyte should not be opened; the films on the necks of the capsules are pierced by the needles of the filler necks when installing the container on the battery. But we will still pierce one of the films to measure the density with a refractometer. (Don't repeat this!)
The density is slightly higher than 1.31. Once again we are convinced that high-density electrolyte is poured into the AGM.
Forming of dry-charged batteries is carried out at the factory, then the plates are dried, and the battery is assembled from the dry molded plates. We tear off the sticker that protects from oxygen, moisture and dust, we see the filler necks with needles.
Before filling the electrolyte, connect a voltmeter with a recorder to the battery terminals to see how the chemical current source is activated. The initial battery temperature is 24.3 degrees Celsius.
Carefully turn the dispenser container over, place it on top of the battery and push it down, piercing the films on the necks. This had to be done with both hands. it was necessary to apply force evenly on the left and right sides.
Not all the electrolyte has yet reached the battery banks, and its temperature has already risen by almost 2 degrees, to 26.2.
After making sure that all the electrolyte has leaked out, remove the dispenser container. Temperature 31 degrees.
Activation is in full swing, with heat being released. The reaction is exothermic.
Since the electrolyte entered the jars unevenly, the voltage increase during activation was also uneven. In one minute, the open circuit voltage (OCV) rose from 10.72 to 12.55 volts, then for two minutes it rose to 12.7 and continues to rise.
Half an hour has passed, 12.78 V at the terminals. The temperature drops, activation can be considered complete.
Motorcycle batteries are marked according to the Japanese industrial standard JIS. The manufacturer labeled our battery with its own code DC MF 1205, but in JIS this size is designated UT5L-BS. We select this item in the tester menu.
Internal resistance 18.18 mOhm, cold cranking current 165 A, NRC 12.72 V. The battery is working.
The tester shows that the battery is fully charged, but the instructions prescribe that before installing the battery on the vehicle after activation, it must be charged, otherwise the battery loses up to 20% of its capacity.
The instructions recommend charging with a current of 1/10 of the capacity (in our case, 500 mA), and stopping the charge when the voltage reaches 16 volts. It is recommended to fully charge on a stationary charger at least once every 3 months.
In the Vector auto electrics laboratory, when charging with direct current, before high-voltage additional charging, we prefer to carry out the main charge stage with a current of 10% of the capacity to a voltage of 14.1 to 14.8 volts, depending on the type of battery, (usually 14.4-14.7), wait for the current to decrease at this voltage , and then charge at higher voltage with a lower current, usually 2% of capacity.
However, the one-stage profile from the Siltech instructions instructs not to keep the battery at 16 volts, but to immediately turn off the charge when this voltage is reached. Since this is a starter AGM, this profile can be considered suitable for a safe charge, but in this case it is important not to miss the moment it reaches 16 volts and immediately turn off the current.
You can charge either with a stabilized source of current and voltage in the form of a charger (charger) or power supply, or with a charger with automatic adjustment of charge parameters with microprocessor control in real time. There are many such advanced machines today, for example, foreign STEC, Optimate, NOCO and domestic products from LB-Electro, Avtoelektro, Balsat. We will use the Berezhok-V device based on the Vympel-30 charger manufactured by Orion St. Petersburg.
When starting the charge, the machine supplied a current to our 5 A*h battery, which increased in about a second from the 0.5 to 5 amperes recommended in the instructions, that is, 1C, 100% of the capacity, a seemingly tenfold increase. What is this, a glitch, a glitch, an error or a flaw in the algorithm?
In fact, there is no excess.
According to Woodbridge, the current at the start of constant voltage charging is exactly 100% of the capacity. And such a beginning of the first stage is far from uncommon in the world of ultra-fast charging methods and useful models that implement them. On the contrary, it happens every day - under the hood of a car. A car's generator often supplies 60 amps, or even more, 60 Ah to the battery. But this does not mean that this way you can charge the battery in an hour, or that this current can be kept up to 16 volts. As soon as the terminal voltage reaches the voltage regulator setting, the charging current is reduced.
The condition of the battery does not always allow it to accept such a high current after starting the engine with the starter; a progressive imbalance due to undercharging and sulfation often interferes. And alas, a full equalizing restoration charge can never be carried out at the voltages of the car’s on-board network (if we don’t talk about hypothetical complex microprocessor systems, where the on-board network has a charge controller, a battery current sensor, and so on). Therefore, at least once every 3 months, the battery needs a stationary charge. Stationary - that is, not from a standard generator, but from a specialized charger or power source, adequately controlled manually or automatically.
There were 5 amps at 13.5 volts, and after 5 minutes at 14.1 V there were only 4 amps. Further, the voltages will increase, and the maximum currents will decrease; this is a general rule for almost all methods and charge profiles. The exception is special modes for effective mixing of the electrolyte, when significant currents are supplied during overvoltages for a standardized time, as well as buffer and periodic recharging modes in storage. The stage parameters also depend on the battery temperature, which can change in one direction or another for internal and external reasons several times during the charge.
The next morning the charger is in storage mode and the charge is complete. There are 13 volts at the terminals.
The tester shows 16.38 mOhm, 184 A, 12.88 V. The battery parameters have improved compared to those before charging: 18.18 mOhm, 165 A, NRC 12.72 V.
We will configure the electronic load for a 20-hour discharge current according to GOST up to 10.5 volts. For a 5 Ah battery, this current is 250 mA.
The battery delivered 5.461 Ah. Excellent result.
On a discharged battery, the tester shows 129.87 mOhm, TCP 24 A, health 16%, NRC 11.03 V, and instructs to charge and recheck.
The degree of charge is 0%, therefore the internal resistance is high, health and current output are low. We'll charge.
2 hours have passed after charging, you can close the lid and use the battery for its intended purpose. It has been put into operation.
The tester readings after the discharge are 15.27 mOhm, 196 A, 12.92 V. Thanks to the control and training cycle (CTC), they have improved even more from the previous 16.38 mOhm, 184 A, 12.88 V. Battery health is 100%.
Based on the results of measurements
, both the starting current and the capacity of this battery correspond to the declared ones, the manufacturer is not deceiving, this dry-charged battery can be recommended for purchase.
So, after filling a dry-charged lead-acid battery, it really needs to be charged so as not to lose capacity and current output, which we saw from the instrument readings in this experiment.
The article was compiled in collaboration with battery engineer Victor VECTOR.
Why do you need to maintain electrolyte levels?
Maintenance-free or low-maintenance lead-acid batteries use an electrolyte that is a solution of sulfuric acid and distilled water. During operation, water evaporates and the concentration of sulfuric acid increases. Concentrated acid can cause accelerated corrosion of the internal elements of the battery, which leads to the formation of sediment, which can subsequently lead to short-circuiting of the oppositely polarized plates.
What to do if the electrolyte level in the battery has dropped?
You need to purchase distilled water and add it to the battery. The electrolyte is dilute sulfuric acid. During the operation of the battery, only a slight evaporation of water occurs, which needs to be topped up. Under no circumstances should you add new electrolyte, only distilled water!
How to check electrolyte level
There are lines on the wall of the battery that indicate the maximum and minimum level in each bank. Take the battery carefully in your hands and hold it up to the light. This way you can see how much electrolyte is in each jar. It should be between the minimum and maximum lines.
Pros of lithium-ion batteries
The fact is that they lack one of the main disadvantages of lead-acid. The capacity of lead-acid batteries seems quite large, for example 10 amp hours implies that this battery can hold a load of 10 amps for an hour, or 20 amps continuously for half an hour, or 40 amps for 15 minutes at a time. Yes, but not so. 40 amperes is a current quite sufficient to turn over a medium-sized motorcycle engine, and 15 minutes of such work seems like a lot. But in fact, lead-acid batteries are not capable of delivering really high current at any state of charge.
That is, a half-empty lead-acid battery will no longer be able to produce 40 amperes, but the same 10 amperes will be sufficient. Therefore, formally its capacity is large, but its useful capacity (for the operation of the electric starter) is half, or even four times less.
Lithium-ion batteries are capable of delivering powerful currents up to the deepest discharge. Therefore, a 4-amp-hour lithium battery can start the engine more times than a 10-amp-hour lead battery. Plus, lithium batteries are lighter and more compact, even with comparable capacities. But they also have disadvantages, in particular the price.
Why does a new battery drain?
There can be several reasons for rapid battery discharge. Below we list the most common ones:
- The security alarm is faulty or the alarm has been on for a long time. Any current leakage reduces the battery charge.
- A faulty charge relay can result in the battery simply not being recharged from the generator during a trip. You can check the functionality of this device by turning on the headlight and increasing the engine speed - the brightness should increase. If the brightness decreases, your regulator most likely needs to be replaced.
- Faulty generator. To check its performance, it is enough to measure the voltage on the battery; with the relay-regulator and generator running, it should be at least 13.8 Volts, at 2-3 thousand rpm and the headlights are on low beam.
Types of Lithium Ion Batteries
There is some confusion with the term "lithium-ion" - it describes the technology rather than the specific chemistry of the battery. To make matters worse, different lithium-ion batteries have different cell voltages, but this information can help you understand what type of battery is used in a particular device (including a motorcycle).
All lithium-ion cells are divided into two groups. The nominal voltage in the first is 3.2-3.3 volts, and in the second - 3.6-3.7 volts.
Motorcycle batteries built on lithium ferrophosphate (LiFePO4) technology, also known as iron phosphate or nanophosphate, consist of four cells with a nominal value of 3.2 volts, giving a total of 12.8 volts and charging up to 14.4 volts (maximum - 14.6 volts).
Some manufacturers, for marketing reasons, state that their batteries have a nominal cell voltage of 3.3 volts (and together they then give 13.2 volts), but the LFP or LiFe marking will tell an understanding person that this is still the same 12.8- volt LiFePO4.
There are other lithium-ion battery chemistries, such as lithium cobalt oxide, lithium manganese, or even a combination of the two known as lithium polymer (the cells in these batteries are soft and can be molded into different shapes in the factory), but they all have a nominal cell voltage equal to 3.6-3.7 volts. Nowadays, 3.6-volt cells are almost never found, but high-voltage lithium-polymer cells with a nominal value of 3.85 volts can be found. Cells with a voltage of 3.7 volts should be charged with a voltage no higher than 4.2 volts, and at 3.85 V - no higher than 4.35 V.
However, these are not used in motorcycles. Mainly because three of these cells provide 11.1 volts (such a battery can be charged up to 12.6 volts, higher is dangerous), and four - 14.8 volts, which is outside the permissible voltage range for standard 12-volt motorcycle electrics . However, three- and four-cell batteries are used in jump starters, and three-cell batteries have a protective board built into the positive wire that prevents the flow of current from the on-board network to the jump starter to avoid overcharging and overheating.
No lithium-ion technology can withstand overcharging and can ignite if overheated.
What is sulfation and what causes sulfation?
Sulfation is an electrochemical process that occurs in a battery during discharge. The discharge can be different, starter and long-term, with low current. In case of prolonged discharge with low current (current leakage during inactivity) or undercharging from the generator, the plates are coated with lead sulfate. This process is reversible, called desulfation (occurs during the charging process). There are a number of reasons leading to sulfation:
- Frequent or constant undercharging, battery operation in negative balance (gives out more than it receives).
- Long-term storage of the battery in an undercharged state. The voltage is below 12.5 Volts.
- Deep discharge. A discharge below 10.5 Volts is especially dangerous. Then sulfation becomes irreversible. The battery loses a lot of its capacity and cannot be charged.
Many people mistakenly believe that sulfation occurs during overcharging, overheating and high loads at low or high ambient temperatures. But that's not true. Under these conditions, the active mass of the plates floats into slurry and the gratings warp.
How to prevent sulfation?
First of all, you need to keep your motorcycle's electrical system in good working order. The battery must renew the charge lost when starting the motorcycle. If you do not plan to use the moped for a long time, you must disconnect the negative (-) terminal from the battery.
In case of irregular use of the moped, charge the battery with a special charger. Elimination of sulfation is possible by charging the battery for a long time with a low current. In the best case, sulfation can be dealt with by a charger that has a pulse current charging function. There is also irreversible sulfation, in which the battery cannot be charged. The case of such batteries usually has swelling and gets very hot when trying to charge.
If I disconnect the battery, will it discharge?
Disconnected from the electrical circuit, even in good condition, the battery will still lose charge, although this will happen much more slowly than when it is connected to the moped. This process is called self-discharge. And the older the battery, the faster the self-discharge occurs.
Precautions when working with batteries
Batteries constantly produce explosive hydrogen, especially while charging. To avoid the potential risk of fire when working near a battery, the following guidelines should be followed:
- Do not smoke near batteries.
- Keep sparks, short circuits, or other sources of ignition away from the battery.
- When disconnecting/connecting current-carrying cables, be sure to first turn off the consumers, turn off the ignition, and turn the key to the off position.
- Ensure proper ventilation of the battery charging area.
The charger must be turned off in the following cases:
- when connected to a battery;
- when disconnected from the battery.
The ground wire (-) must be disconnected from the battery first and connected last.
Is lithium safe?
Of course, these batteries are certified and tested under adequate conditions. The main thing is that their operation occurs in normal modes.
For example, overcharging a lithium-ion battery can cause it to catch fire, so if you're thinking of replacing your stock lead-acid battery with a lithium one, check to see if your motorcycle's electrical system is compatible with lithium. For example, if the voltage in it can exceed 14.6 volts, it’s better not to, since this is the upper safe limit for a lithium-ion motor battery. Once again, the worst thing that can happen to a lithium-ion battery is overcharging.
Such batteries have a much lower self-discharge than lead-acid ones, but in most modern motorcycles there is bound to be some leakage to power the ECU, immobilizer and the like, even when the key is removed from the ignition. This is not to mention the alarm system, which can use up the charge of even a full lead battery in a couple of days if it is noisy or windy outside, or the feedback signal is unstable, and so on. Here we come to another point: lithium motorcycle batteries do not tolerate deep discharge and also become dangerous. The third nuance is that it is highly advisable to purchase a special charger for such a battery.
How to restore the battery
First, you need to thoroughly rinse the damaged battery with distilled water several times and pour the prepared electrolyte into it. We check the density of the electrolyte - normally it should be 1.27 g/cm³. Now you need to charge the battery for 10-12 hours.
After charging, connect any high-power power source to it and discharge it completely. We repeat the process at least ten, maximum fifteen times. This is exactly how it is recommended to “bring to life” an old acid battery. It is important to remember that you cannot leave it completely discharged for a long time between charge and discharge cycles.
Owners of mopeds, who thus save on buying new batteries, claim that after the battery has been restored, it can work for about a month and holds a stable charge. In some cases this can be quite useful.
Restoring a gel battery is often a thankless task. Most likely, you will not achieve a positive result.
In order for your scooter or moped to last as long as possible, you should not constantly ride it without a battery. It is better to purchase a suitable power source and provide it with proper care from time to time, thereby saving both the vehicle and its battery. It never hurts to know how to start a moped in emergency situations, but in order to avoid unpleasant consequences, this should not be abused.
And of course, for those who are limited in financial resources, we can recommend purchasing an inexpensive liquid-acid battery: it will require care, but it is not as complicated as it might seem at first. In addition, it is much more realistic and easier to restore such a battery on occasion than an expensive gel battery, which places higher demands on its owner.
Is it possible to charge a motorcycle battery with a car charger?
Complex issue. Manufacturers of smart motorcycle battery chargers want you to trust them and be afraid to use products from other brands. But they forget that most motorcyclists are thinking people.
On the one hand, car batteries are much larger than motorcycle batteries and are capable of both delivering and taking much higher currents. Therefore, chargers for them are made more powerful. If the charge tracking circuit of such a charger is implemented clumsily, it is quite capable of overlooking the fact that the motorcycle battery has already been charged and boiling it.
On the other hand, a battery installed in the on-board network of a motorcycle is charged according to the Spartan principle: it is supplied with a voltage higher than its output, and it takes as much current from the on-board network as it can take. Approximately the same process occurs when charging a motorcycle battery from a car charger. If the battery is not completely empty, that is, it is used in normal mode, then the car charger will not do anything particularly new with it.
The main thing is to disconnect the positive terminal from the battery if you charge it with a powerful charger right on the motorcycle. This is because some of them implement desulfation algorithms that try to “break through” the sulfate film with pulses of increased voltage. The on-board network (in particular, the ECU) is often not completely de-energized when the key is removed, and may not evaluate pulses with an amplitude of 18-20 volts.
Is it possible to ride a moped without a battery?
Experienced owners of scooters and mopeds can start them in any way - from kickstarter to using the most ordinary drill. There are amateurs who even write about this on their forums: “I’ve been driving without a battery for a month now and don’t bother about it.”
However, the consequences of constantly driving without a battery can be very disastrous for a moped. First of all, this concerns lighting devices: the bulbs in the turn signals burn out, the headlights do not burn well, the backlight begins to act up.
Why does this happen? Let's find out the reason.
If the moped has a battery, it is regularly recharged from the generator. But when it is not there, the current generated by the generator begins to flow into all devices: it simply cannot evaporate or dissolve in the air. As the driving speed increases, the voltage begins to increase, and the entire lighting system of the moped can “fly” at any moment. And the lamps themselves, in the absence of a battery, work much worse, because they simply do not have enough energy. They can shine dimly, blink, or even burn out due to uneven distribution of energy.
Based on this, we can conclude: driving for a long time without a battery can lead to the failure of all lighting. And not only him. For example, in this situation the generator is also forced to work in increased mode, which leads to its breakdown. You should think carefully before constantly driving in this manner.
It is best to purchase a suitable battery for your scooter - despite the fact that for some lovers of “trouble-free” riding, caring for the battery seems cumbersome. However, it is precisely to such people that we owe the fact that we now have at least several ways to start a moped without a battery in an emergency.
How does a LiFePO4 motorbattery work?
Each cell contains an anode made of carbon, a cathode made of lithium ferrophosphate, and between them is an electrolyte made of lithium perchloride. In a discharged state, all the lithium is in the cathode and electrolyte, and in a charged battery, lithium ions move to the carbon anode. It's porous, so lithium ions fill those pores, and the battery is charged when they're all filled.
When the battery discharges, lithium ions leave the anode and are directed to the cathode, simultaneously creating an electromotive force between them and transferring energy through the flow of electrons through the connected load. Looks simple? But there are nuances.
When discharging, you should not completely empty the carbon anode, and when charging, you should not direct more lithium ions to it than enters it, and it is also undesirable to dissolve the lithium cathode. During overdischarge, when a deficiency of lithium ions occurs in the carbon anode, it begins to collapse as the walls of its pores become brittle. When overcharging, two troubles occur at once: at the cathode, pores capable of emitting lithium ions close, and at the anode, excess ions collide with carbon and heat it, which can cause it to ignite.
Unlike lead-acid batteries, it is better to keep lithium-ion batteries undercharged (since a fully charged battery is vulnerable to overcharging), but it should not be allowed to overdischarge below 30% - 13 volts, in other words.
Helpful information
To protect the terminals from oxidation and the appearance of a white coating, they need to be cleaned, securely fastened and only then lubricated with grease (technical Vaseline, Litol, Solidol, etc.) or protected with a special acid-resistant mastic. The battery being serviced must have a special tube for removing gases; it must be taken outside the motorcycle and not closed; it serves to remove gases and condensate during operation. You can insert the battery into a rubber or plastic box that is slightly higher than the battery. Then, if the electrolyte suddenly spills out, it will not get on the frame and other parts of the motorcycle.
Limitations of Li-ion Batteries
With a lot of advantages, lithium-ion batteries for a motorcycle are not an absolute blessing. Usually you need a good reason to replace lead with lithium: they have excellent starting current, but they really don't like to work in the cold, they are light and good for sports driving, but have either a small volume or a significant price tag. And they are also not at all suitable for motorcycles in which small consumers operate with the ignition off - for example, trackers or alarms. For tourism, when weight and volume do not impose critical restrictions, it is better to choose a high-quality AGM battery.
The importance of choosing a battery with the correct capacity
If you purchase a battery with insufficient capacity, it may not have enough cranking current to start your motorcycle engine. Or for the normal operation of headlights, lighting and other electrical equipment, which is becoming more and more common on modern bikes. In addition, it is worth considering that in the cold season, starting the engine is even more difficult due to low temperatures. And in such a situation, it is extremely useful to have some reserve battery capacity.
You can buy a battery with a slightly larger capacity than was installed at the factory. Many manufacturers try to save money and do not equip their products with the most powerful available options. But before you take this step, make sure that a battery with a higher capacity will fit in the space allocated to it. In the table above, you can see that the larger the battery capacity, the more space it takes up in all three parameters. In addition, do not forget that buying a battery with a larger capacity means an additional overpayment, which is most often unjustified. And this overpayment can be avoided if you correctly select the battery capacity.
If there is no charge
To fix this problem, let’s first figure out how the battery is charged in general. While the engine is running (over 2 thousand revolutions), the generator is switched on, creating current (alternating current). To convert alternating current into direct current, a converter is provided in the scooter's electrical system. In this case, the stabilizer. The stabilizer also serves to prevent the scooter's battery from overcharging. If there is a problem in this system (generator-stabilizer-battery), the battery will not receive charging.
In order for charging to be constant, it is necessary to do the following:
- Check contacts and fuse. Clean the contacts and replace the fuse if broken.
- You should also pay attention to the battery terminals. They must be properly stripped and tightly attached.
- Inspect all plugs and connections (wires).
- Check for ground (wire connected to the equipment frame and battery negative.)
In most cases, the operations performed are enough to correct the problem in question. But there are other, more advanced cases. Let’s go even deeper and consider a number of actions that will certainly help.
First, let's install a working, fully charged battery on the scooter. Next, connect the multimeter to the installed battery. The multimeter scale should show 13.1 V. Then you need to start the engine, add gas so that the engine speed increases to 3 thousand per minute. We connect the multimeter back, it should output 14.5 V. If this is true, then the problem is in the battery itself. It needs to be replaced. For reference: the best battery for a scooter is considered to be acid-based.
Video
Examples of motorcycle battery models from various manufacturers
Exide
A well-known manufacturer has in its product line “Bike” batteries for motorcycles, scooters and other motorcycle equipment:
- Standard WET (6 and 12 volts);
- Maintenance free AGM (12V);
- Sealed GEL (12 V).
Banner
This Austrian manufacturer has in its arsenal the Bike Bull series, which includes classic lead-acid batteries, as well as Bike Bull AGM and GEL, which are recommended for motorcycle equipment operating in difficult conditions.
- Bike Bull WET. 6 V, 4 Ah;
- Bike Bull AGM. 12 V, 3 Ah;
- Bike Bull AGM PROfessional. 12V, 8 Ah;
- Bike Bull GEL. 12V, 3 Ah.
Varta
Varta offers a line of Powersports batteries for motorcycles and scooters. There are about 60 different models.
- Powersports Freshpack. Dry-charged batteries supplied with electrolyte;
- Powersports AGM. Maintenance-free batteries;
- Powersports GEL. Varta recommend using them in various tourist equipment;
- Powersports Gardening. Designed for garden equipment such as lawn mowers.
Bosch
This manufacturer's line also includes a category of motorcycle batteries. It includes:
- Bosch M4 Fresh Pack. The battery is sold dry-charged with electrolyte for filling;
- Bosch M6 AGM. Bosch notes the tightness and vibration resistance of AGM models;
- Bosch M6 Gel. M6 Gel motorcycle batteries are recommended for use on motorcycle equipment operating in difficult conditions.
This is only a small part of the batteries that are offered for motorcycles on the market. Almost all manufacturers of car batteries have their own solutions for motorcycles.
Main characteristics of rechargeable batteries
In order not to make a mistake when choosing a battery for a motorcycle, you need to understand the technical characteristics:
- Capacity
The parameter is measured in Ampere-hours (Ah) and indicates the ability of the unit to produce a certain power for 1 hour. If the label indicates 20 Ah, it means that the battery can produce a current of 20 A for an hour.
The larger the volume of the internal combustion engine of a motorcycle or ATV, the higher the capacity should be. Here you need to follow the recommendations of the manufacturer, who indicates the capacity for each specific model of equipment.
If the capacity is less than that recommended by the manufacturer, the engine may not start.
- Cold start current
The parameter indicates the battery’s ability to deliver the maximum current, the volume of which would be sufficient to start the electric starter at sub-zero temperatures. The current supply time is within half a minute.
In the labeling, this parameter is designated by the abbreviation SSA.
- Voltage
For motor vehicles, batteries with a voltage of 12 V are mainly installed. For small-capacity equipment (scooters, scooters), units with a voltage of 6 V are installed.
- Dimensions
The unit must fit the size of the site where it will be installed. If the dimensions match, the battery will be level. Therefore, it is necessary to find out in advance the value of this parameter, which is indicated in the operating instructions for the motorcycle and on the body of the old battery.
- Terminals and Polarity
To select the correct type of terminals, use the standard size specified by the manufacturer.
When selecting polarity, take into account the location of the positive and negative terminals. If the plus is located on the right - reverse, on the left - straight.
- Frame
In the production of cases, impact-resistant plastic is mainly used. The main requirement for the housing is tightness. The equipment must be protected from mechanical influences, vibrations, and overturning.
When to charge the battery
Before charging the battery, you must ensure that it is truly discharged. There are several ways to do this:
- Measuring voltage at terminals . This can be done using a constant voltage voltmeter, in other words, an electronic multimeter or a pointer tester. For standard batteries used in most passenger cars, the standard voltage value is 12 V. In practice, it differs slightly from the nominal value. So, a value equal to 12.7 V tells the car owner that the battery charge level is 100%, and accordingly, there is no need to charge it. If the measured voltage is 12.2 V, then this indicates that the charge level is approximately 50%. And if the voltage drops to 11.6...11.7 V, it means that the battery is almost completely discharged and it needs additional charging.
- Measuring the electrolyte density value . However, this verification method is only possible for so-called serviceable batteries, that is, in which it is possible to reach containers with electrolyte (and add it, if necessary). To measure density, a special device is used - a hydrometer. The electrolyte density should be around 1.27 g/cm³. If it is significantly less, it means that the battery should be charged with a charger. In unattended ones there is a special window where 3 stages of density will be displayed.
- Problems starting the engine . One of the reasons why the starter does not turn, and problems arise with starting the engine, is precisely the battery discharge. This is usually accompanied by problems in the operation of other consumers of electricity in the car - lighting, operation of the audio system, and so on.
In a discharged battery, sulfation of its lead plates occurs, which leads to a sharp decrease in its service life, that is, durability.
Recovery
In order to revive such a battery, you need to remove the covers from the battery compartments and start pouring distilled water into each jar. Despite the fact that these batteries are classified as maintenance-free, it is always possible to remove their covers. Add water using a syringe, two milliliters into each “jar.” After half an hour, remove excess water with a rubber bulb - it should slightly cover the plates. Close the battery, place a weight on top (to prevent the caps from being knocked out by high pressure) and start charging.
You can revive the battery by applying a voltage of more than 14 volts. To restore it, at the beginning of charging you will need a voltage of at least 15 volts. It is necessary to keep it on charge for about 14 hours, first waiting for the moment when it begins to consume current. If the battery does not respond to a voltage of 15 volts, it can be raised to 30. When the battery finally “swings”, after two or three such cycles, charge it in the usual way - with a current of 10 percent of its capacity, reducing the voltage to 14 volts.
However, many experts do not recommend reconditioning batteries of this type. Often the effect is only temporary.
How to maintain the battery?
To extend the life of the battery, high-quality and timely maintenance is required:
- It is recommended to check the operation of the electrical circuit before traveling. Short circuits and other emergency situations lead to increased load on the battery. The higher the load, the faster the sulfation process will start.
- It is necessary to ensure the cleanliness and tightness of the battery. If metal shavings or dirt gets into the electrolyte, a rapid discharge occurs. In such cases, recharging will be required every 2-3 days. If a crack or chip is found on the case, the battery must be replaced with a new one. Such damage leads to electrolyte leakage. In GEL batteries, it is possible to replace the case.
- Deep discharge is the main danger to the battery. After the trip, you must turn off the power plant. You should also carry out regular checks of the motorcycle's electrical system and the voltage at the terminals. When using acid batteries with liquid electrolyte, it is necessary to monitor its level.
- If the simplest acid battery is installed, experienced users recommend flushing the housing once a year. To do this, pour out the electrolyte and pour in the distillate, and clean the dirt.
- To clean the terminals from oxide, use regular sandpaper. It not only relieves oxidation, but also helps improve contact.
- It is also necessary to purchase a multimeter that will allow you to measure voltages and determine current leakage.
Particular attention is paid to storing batteries. The Russian climate does not allow year-round use of motor vehicles. Therefore, at the end of the season, motorcycle owners put the equipment in the garage after removing the battery. To store the battery correctly, adhere to the following algorithm:
- Before “preservation,” the battery is recharged and left in a dry place. Storage temperature should be room temperature. In cold weather, the electrolyte will freeze, which will lead to a discharge.
- The terminals are cleaned of oxide.
- The housing should not be exposed to water or dirt.
- Before the start of the season, exercises are carried out.
Important.
The battery should not remain discharged for a long time.
At low storage temperatures, the unit is discharged by more than 1% per day. The problem can be solved by connecting an automatic charger or periodic manual charging.