>> Power supply system. Engine.
Supply system
Fuel and combustible mixtures
To operate the internal combustion engine, a combustible mixture consisting of finely atomized and evaporated fuel mixed with air enters its cylinder. The fuel used in modern scooter engines is motor gasoline with an octane rating of at least 93 (for scooters with two-stroke engines, oil is added to gasoline; this was discussed in more detail earlier). The octane number of gasoline characterizes the fuel's resistance to detonation - explosive combustion of fuel in the cylinder under high loads.
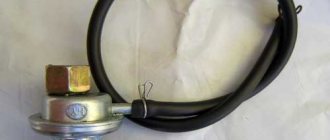
Fuel pump (Honda).
Fuel tank
It stores a supply of fuel; its volume in 50 cc scooters usually does not exceed 5 liters. Fuel tanks are made from plastics, which have almost replaced the steel that was used until recently. The tanks are located in different places. These used to be mounted directly under the front of the seat, but most modern scooters have a helmet storage bin located here. Therefore, the tank is moved to the “tail” part of the scooter, lowered below the luggage capacity or placed in the front part. There is a special hole in the tank cap through which air enters the tank as fuel is consumed. On many scooters, the tank lid is sealed, and the internal volume of the tank communicates with the atmosphere through special tanks with activated carbon, which absorbs gasoline vapors.
Fuel pump
It is not used on all scooters, since on most models the fuel tank is located above the engine and the fuel flows by gravity through a hose into the carburetor.
Automatic fuel tap: 1 - fitting to which vacuum is supplied; 2 — fuel supply fitting; 3 — nut for fastening to the tank; 4 - fuel filter.
On scooters with four-stroke engines, the fuel pump is electrically driven. Scooters with two-stroke engines are equipped with vacuum-driven fuel pumps - similar designs are widely used on outboard boat motors. They use the pressure pulsation that occurs in the crank chamber when the piston moves.
Fuel tap
It is a mandatory part of the power system, since it prevents fuel from leaking through the carburetor when stopping in the event of a leak in its float valve.
On motorcycles and older models of scooters (motor scooters), manually operated fuel taps were used. Such a tap has three positions: “3” or “Off” - closed; “O” or “On” - fuel comes from the main volume of the tank; “P” or “Res” - fuel comes from the reserve volume of the tank. When stopping for a long time (for example, at night), the driver closes the tap. When starting the engine, it turns it to the normal “open” position. If the engine stalls while driving, the driver switches the tap to the “reserve” position and drives to the nearest gas station. Usually the volume of the “reserve” is such that you can drive 20-30 km on it.
Diagram of an automatic fuel valve: 1 - membrane; 2 — valve body; 3 - fuel tank; 4 — fuel supply fitting; 5 - locking needle; 6 — control channel (communicating with the inlet pipe).
The engine power supply system of the vast majority of scooters includes: a fuel tank, a fuel tap, a fuel filter, a carburetor and an air filter. In some cases, the fuel system includes a fuel pump. Modern scooters with large engine displacement use a fuel injection system.
Detonation is an undesirable and dangerous phenomenon; it causes overheating and destruction of parts of the engine cylinder-piston group. The higher the octane number, the higher the compression ratio the engine can have. This means, in accordance with the theory of internal combustion engines, it will work more efficiently, its efficiency and power will be higher.
A fuel pump is required for those scooter models in which the fuel tank is located under the saddle or floor, below the carburetor.
Air filter location (shown by arrow).
Modern scooters are equipped with automatic fuel taps, which, as the name suggests, do not require any action from the driver. This valve opens only when the engine starts, and closes immediately when it stops. On modern scooters, the operation of the valve is controlled by the vacuum in the intake manifold (between the carburetor and the cylinder). When starting and operating the engine, the vacuum acts on the membrane of the fuel valve, which, overcoming the force of the spring, lowers the shut-off needle associated with it and ensures the flow of fuel.
There is usually a strainer in the line in front of or inside the fuel valve that prevents dirt from entering the carburetor. The second fuel filter - a replaceable paper one - is often cut into the hose connecting the tap and the carburetor. For safety reasons, clamps or retaining rings are placed on the ends of the connecting hose.
Air filter with foam filter element: 1 — housing cover; 2 - filter element; 3 - limiter; 4 - body.
Air purifier
Serves to clean the air entering the carburetor from dust and other foreign particles. The air cleaner is an important part of the scooter that ensures the longevity of the engine. In addition, the air cleaner plays the role of a muffler for intake noise. The air cleaner consists of a housing with a cover and an air filter. Modern scooters use two types of filters: paper and polyurethane foam (foam). Until recently, the metal mesh filters that were used, which required regular washing and did not guarantee fine air purification, have fallen out of use. Paper filters are disposable, i.e. they are replaced at every maintenance. Foam filters allow repeated washing and subsequent impregnation with special oil.
Recently, so-called zero-resistance filters, which are a type of mesh metal filters, have become somewhat widespread. However, they are installed only during tuning.
Whatever air filter is used, regular cleaning and monitoring of its condition is necessary, and, if necessary, replacement. If the filter is faulty, solid dust particles enter the engine, causing accelerated wear of the piston, cylinder bore, connecting rod bearings and crankshaft. An excessively dirty filter impedes the flow of air, enriching the fuel mixture, reducing power and increasing fuel consumption.
Main metering system of a spool carburetor: 1 - throttle spool: 2 - mixing chamber; 3 — conical spool needle; 4 — sprayer of the main dosing system; 5 - float chamber; 6 — main fuel jet; 7 - air channel.
Carburetor
This device, as part of the power supply system, prepares and doses the combustible mixture, which then enters the cylinder. Its design is quite complex; it includes several fuel dosing systems.
Float chamber
Its purpose is to maintain the fuel level at a constant level, since the amount of fuel supplied along with the air depends on this. In addition, it is necessary to stop the fuel supply when the engine is stopped.
Detailing of the throttle valve assembly: 1 - valve needle; 2 - throttle valve; 3 — cover gasket; 4 - cover; 5 — spool spring; 6 — needle lock.
A float with a valve attached to it, usually a needle type, maintains a constant fuel level. When the chamber is empty, the float and needle are lowered, and fuel can flow freely into the chamber from the tank. After filling the chamber with fuel to a certain level, the float rises and, acting on the needle (directly or through a lever), raises it, stopping the fuel supply. The fuel level is adjusted by bending the lever that controls the valve or by installing shims under the valve seat. Often such adjustment is not provided at all - it is ensured by precision manufacturing of parts.
Types of carburetors
The simplest carburetor is capable of preparing the optimal air-fuel mixture in only one engine operating mode, with constant load and speed. For any transport engine, including a scooter, both of these parameters are constantly changing, and there is also the problem of cold start. Therefore, the carburetors used on scooters are much more complex. Modern carburetors have a main metering system, starting, idle and transition systems, as well as mixture correction systems to obtain maximum power. To control the engine operating mode, a throttle valve is installed in the carburetor, connected by a cable to the “gas” handle on the steering wheel. With its help, the amount of air-fuel mixture entering the cylinder is regulated. There are two types of carburetors used on modern scooters: spool-type and so-called constant vacuum (CV). The latter are used primarily on scooters with four-stroke engines.
The conical spool needle has grooves (1) that secure the split washer (2). By moving the washer, the composition of the mixture can be adjusted.
AIR/FUEL MIXTURE
. As was experimentally established at the beginning of the 20th century, the fuel-air mixture burns most efficiently when the weight ratio of the components is 1:15. When the proportion of fuel is higher, the mixture is called rich, less - lean. Running the engine on rich mixtures increases power, while running on lean mixtures increases efficiency. Too rich mixtures do not burn completely in the cylinder, and poor ones lead to engine overheating, flashes and pops in the carburetor.
THE SIMPLE CARBURETOR
. Consists of two chambers: mixing and float. The mixing chamber is formed by a diffuser - this is the name of the channel, the cross-section of which in the middle is smaller than at the ends. As air passes through the diffuser, its speed in the middle increases, and the pressure drops below atmospheric pressure. The mixing and float chambers communicate with each other and the fuel channel (nozzle), in which a part with a calibrated hole is installed - a nozzle. The vacuum formed in the diffuser causes the fuel to flow out of the atomizer in the form of small drops, which are then crushed and evaporated in the air stream, forming a combustible mixture.
Main parts of a spool carburetor: 1 - automatic starting enrichment; 2 — carburetor body; 3 — float; 4 — float chamber cover; 5 — fuel jets of the main metering system; 6 — heating element; 7 - throttle with dosing needle.
The length of the nozzle is chosen such that the fuel level in the float chamber is 1-2 mm below the upper edge of the nozzle. This prevents spontaneous fuel supply when the engine is not running.
Spool carburetor
In it, the throttle valve (spool), moving, changes the cross-section of the diffuser. In this way, the amount of air passing through the carburetor and, consequently, the engine speed are regulated. A cone-shaped needle is rigidly connected to the spool, tapering downwards and entering the sprayer. The main fuel jet is installed on the other side of the atomizer. All these parts form the main metering system of the carburetor.
Main metering system of the CV type carburetor (position corresponds to full load): 1 - diffuser; 2 - membrane; 3 - spring; 4 - spool; 5 - dosing needle; 6 - rotary throttle valve; 7 - sprayer; 8 — main fuel jet; 9 — float; 10 - float shut-off valve.
When you turn the throttle handle, the needle moves along with the spool, and, due to the fact that its diameter at the bottom is smaller than at the top, when the spool and needle are raised, the cross-section of the fuel channel increases. By changing the position of the cone needle relative to the spool, you can slightly adjust the composition of the mixture: enrich it by raising the needle, or, conversely, deplete it by lowering it.
CV type carburetor
In constant vacuum carburetors, the movement of the “gas” handle is transmitted not to the spool connected to the metering needle, but to the rotary throttle valve located closer to the carburetor outlet. This damper, like the spool of the carburetor discussed above, regulates the amount of air passing through the carburetor. The diaphragm chamber above the spool communicates with the carburetor mixing chamber.
Adjusting screws for the idle speed system: 1 — “quantity” screw; 2 - “quality” screw.
Thus, the movement of the spool (and with it the fuel-metering needle) is controlled by the vacuum in the intake tract. At low loads, when the rotary throttle valve is closed, the vacuum in the mixing chamber (and therefore in the cavity above the membrane) is small, and the spool together with the needle is lowered under the action of a spring. Under heavy loads, when the throttle valve is open, increased vacuum is transferred to the cavity above the membrane and raises the spool along with the metering needle. The advantage of this type of carburetor is that the spool maintains a constant vacuum in the sprayer area, ensuring an optimal ratio of fuel and air in the working mixture.
As the throttle valve opens (the spool rises), the main metering system comes into operation, ensuring the required mixture composition throughout the entire range of engine operation.
Idle system of spool carburetor (a) and CV type (b): 1 - throttle valve (spool); 2 - fuel channel; 3 — mixture “quality” screw; 4 — jet of the idle system; 5 - throttle valve stop (spool valve) - “quantity” screw; 6 - air channel.
Idle system
When the scooter is standing still or coasting without a load (the gas is released), the carburetor must ensure that the engine operates at a minimum stable speed. In the simplest carburetor, this task is difficult to complete, since the vacuum with the spool almost completely closed in the area of the fuel supply channel is so small that it is not able to ensure the flow of fuel required for engine operation through the nozzle. However, in another place of the carburetor, behind the spool, closer to the cylinder, the vacuum is higher, and there is a small channel to which air and fuel are supplied. Several of these channels form the idle system that all carburetors have. It includes idle air and fuel channels, a fuel jet and adjusting screws for the optimal amount and composition of the fuel mixture at idle. One screw, called the mixture “quantity” screw, rests its end against the spool, preventing it from completely lowering. The other screw, called the mixture “quality” screw, with its conical end partially blocks the air supply channel to the idle system. Since fuel comes from the float chamber through a different channel, when the “quality” screw is tightened, the proportion of air decreases and the mixture entering through the idle system becomes slightly richer. To fix the adjusting screws from spontaneous rotation, springs or plastic bushings are used.
Cold start system
When starting a cold engine, a rich mixture is required for normal combustion. This is due to the fact that in this case most of the fuel settles in the form of drops on the cold walls of the cylinders and intake channels and the combustible mixture turns out to be too lean to ignite. Another carburetor system enriches the mixture when starting a cold engine - the cold start system.
Design of the injection system of Ditech two-stroke engines. GASOLINE, FUEL PUMP, PRESSURE REGULATOR, INJECTORS, COMPRESSOR, MICROPROCESSOR.
In the simplest scooter carburetors of yesteryear, a float stopper was located in the float chamber cover. When its rod was pressed, the float was forcibly lowered (recessed) and the fuel level in the float chamber became higher than permissible. This resulted in forced fuel supply from the atomizer into the intake manifold. Some of the gasoline flowed out through the drainage hole in the float chamber.
Recently, mixture fortifiers of various designs have been used. They represent an additional fuel channel, which opens only on a cold engine, or (less often) an air damper, which creates a higher vacuum at the nozzle and increases the amount of fuel supplied through the nozzle. The operation of the manual mixture enricher is controlled by the driver: to do this, when starting the engine, he presses the lever located on the left of the steering wheel, which, through a cable, controls the enricher damper. The most common are automatic starting enrichment units with a heating element. In such designs, when starting a cold engine, the enricher shut-off needle is retracted, the cross-section of the fuel nozzle is completely open, and the air-fuel mixture is enriched. After starting the engine, current from the generator flows to the heating thermoelement. After a certain time, sufficient to warm up the engine, the working fluid of the element expands and, acting on the enrichment needle, closes the fuel channel.
Scooters are often equipped with an electric heater, activated by a temperature sensor at a temperature of about +5 ° C and below. In addition, some scooters (for example, Yamaha BW's) are equipped with the non-automatic enricher described above in addition to the automatic one. In this case, the driver himself decides which enrichment system to use.
On modern scooters, manual enrichment is rare. Typically, automatic devices are used that allow the driver not to think about what to do when starting a cold engine.
Fuel injection systems
Carburetors of modern scooters are quite complex and sophisticated devices. However, today they are being replaced by electronically controlled fuel injection systems. Such systems include an electrically driven fuel pump (usually submerged in the fuel tank), a fuel accumulator, a check valve and drain line into the tank, a distribution pipeline (for two-cylinder engines), an electromagnetic injector, an electronic control unit connected to a number of sensors (opening throttle valve, coolant temperature, crankshaft speed, oxygen content in the exhaust pipe, detonation, etc.).
Injection system: a - general view; b - location of the nozzle; 1 — electromagnetic injectors; 2 — fuel manifold; 3 - pressure regulator; 4 — electronic control block; 5 - fuel pump; 6 — fuel tank; 7 - fuel filter; 8 — inlet valve; 9 — intake manifold.
Recently, Italian scooters have appeared with the Ditech fuel injection system into the cylinder of a two-stroke engine. Only air with atomized oil added to it in the inlet pipe to lubricate the parts of the cylinder-piston group and the crankshaft bearings enters the crankcase of engines with this system through the reed valve. Next, the oil-air mixture enters the cylinder and combustion chamber through the purge windows. Some of the air is compressed by a mechanically driven supercharger and supplied to an additional injector. A fuel pump located in the tank supplies gasoline to the injector, which is no different in design from those used in conventional four-stroke engine injection systems. The jet of injected fuel is picked up by compressed air in an additional injector and directed into the combustion chamber. The injection system provides a very fine atomization of fuel. The chamber is filled at such a speed that the engine can operate without interruption up to a crankshaft speed of 12,000 rpm. In addition, an engine equipped with the Ditech system is 40% more economical than a two-stroke engine of comparable power and even outperforms a four-stroke engine in this parameter, while meeting the most stringent exhaust gas emissions standards.
A lubrication system for engine parts is needed to reduce friction between them (and therefore reduce wear) and remove heat. Lubrication is carried out with motor oils, the thin film of which formed between the rubbing parts separates them from each other. A lack of oil in any place can cause local overheating, scuffing, and even welding of parts together.
Mineral oils (obtained from petroleum by distillation), synthetic and semi-synthetic are used to lubricate engine parts of Nexus scooters.
A gear-type oil pump driven from the engine crankshaft circulates oil in four-stroke engines. In addition to the pump, the lubrication system contains an oil filter, valves (return and safety) and lines in the form of channels (tubes and drillings in parts).
Lubrication system of four-stroke scooter engine:
- pallet;
- oil intake;
- oil pump;
- oil filter;
- safety valve;
- front disc brake;
During operation, the oil becomes contaminated with wear products from engine parts and soot particles that have penetrated into the crank chamber through the gap between the piston and cylinder. To capture these particles, an oil filter located in the discharge line is used.
Lubrication system elements:
- filler neck with dipstick;
- oil filter housing
Gasoline quality.
Low-quality gasoline not only worsens the dynamics of the scooter, sometimes it can literally destroy the engine in a matter of minutes.
Therefore, the use of fuel additives (despite the fact that no one can guarantee the quality of gasoline) is not only justified, but necessary. It would also be good to fill the fuel not at a gas station, but in your garage through a special filter nozzle that does not allow water and debris to pass through. Such a watering can can be purchased at a car store. The use of high-quality fuel additives not only eliminates scooter engine problems, but also allows you to significantly save fuel. A good additive keeps the combustion chamber and entire fuel system clean. A clean carburetor provides a mixture of optimal composition and allows you to save on adjustments to the scooter’s carburetor. It is convenient to purchase additives that come in packaging with a dispenser.
Design and connection of a Yamaha scooter carburetor
The Yamaha Jog scooter is one of the most popular on the Russian market: this is explained by the simplicity and reliability of the model, and its affordable price. The carburetor design of this scooter is standard, so you can figure it out using the description given above. However, when installing it, inexperienced owners may encounter some difficulties, which we will help you sort out.
Carburetor of a Japanese scooter Yamaha Jog
The device is worth considering in more detail. This will help you understand not only how to adjust the carburetor and use it correctly, but also how to connect it correctly.
- A starter enricher is attached to the carburetor body: it is small in size and housed in a plastic case. It has two bolts with rubber seals. The enricher is powered via a 12 V battery. This device is used to start the engine when cold, as it allows you to automatically enrich the mixture with oxygen.
- The fitting is connected to the fuel supply hose coming from the gas tank tap.
- If the enrichment unit needs to be removed, you will need to not only unscrew the bolts, but also disconnect the electric valve, to which there are only two wires.
- The mixing chamber has a special cover to which a bolt is attached. If you unscrew it, you can get to the throttle valve. This allows you to check whether the throttle cable is connected, and also to get to the needle that regulates the level of fuel and air supply. If the carburetor needs cleaning, you will definitely need to remove the throttle.
- The enrichment connector has two wire outputs, the yellow one is connected to the generator, the green one goes to ground. In principle, if you reverse the polarity, nothing will happen and the device will still work.
- For the enricher to operate, voltage must come from the battery. When the element inside the device heats up, the needle will extend.
- A special fitting is connected to the air filter, and there is a rubber elbow between them.
- There are several screws on the carburetor body with which you can adjust the idle speed and mixture quality.
- The float chamber is screwed from below and has 4 mounting bolts.
- There is an additional fitting for oil supply: it is the smallest.
- The second fitting is needed for communication with the atmosphere; you do not need to put anything on it.
- The third one is connected to a gas hose. It goes to the gas tank vacuum valve.
Adjusting the fuel level
The final step in considering the topic of how to adjust the carburetor on a scooter is adjusting the fuel in the float chamber. This is a simple but important procedure. You can check the fuel level using a transparent tube. It is located at the bottom of the carburetor.
The drain screw must be unscrewed. The tube rises up. It allows you to estimate the fuel level in the tank. The engine must be running. The tube should be higher than the carburetor. The gasoline level should be detected slightly lower than the cap curb.
If there is little or much fuel, you need to remove the cap and adjust the timing of the needle. In this case, the holder's tendril needs to be bent, but in very small ranges. Such adjustment should be carried out in stages, otherwise the result will be temporary and the adjustment will not have the desired effect.
Having considered the technology of how to adjust the carburetor on a scooter, each owner of such a vehicle can carry out the procedure independently. By following the recommendations of professional auto mechanics, as well as carrying out maintenance on time, you can significantly extend the life of the carburetor and engine. Therefore, due attention must be paid to regulation issues.
Why adjust the carburetor?
Carburetor adjustment may be required in the following cases:
- The spark plugs are serviceable, but do not work very well; their color has changed to black or yellowish.
- The engine does not provide the required power
- Scooter won't start
- Fuel consumption has increased excessively.
All these problems in most cases are caused by an insufficiently enriched or, conversely, overly enriched mixture with oxygen, and they can be corrected by correctly adjusting the carburetor.
The settings, regardless of whether you have a 2t or 4t scooter, have three phases and are made as follows:
- Idle speed adjustment
- Setting the fuel level
- Adjusting the quality of the mixture.
On some carburetor models there is no screw that adjusts the fuel quality, so you have to disassemble the carburetor to change the position of the needle.
The idle speed adjustment is carried out after the engine has warmed up: this takes no more than 15 minutes. For this purpose, the design provides an idle screw. It allows you to make the engine stable by selecting the desired idle speed. When the screw is tightened, the speed will increase, and when it is rotated counterclockwise, it will decrease.
It is important to adjust the quality of the mixture. If it is too lean, the scooter will ride with difficulty, the engine will noticeably lack power
If the mixture is too rich, the spark plugs will turn black and quickly fail. Fuel quality adjustment is usually carried out using a screw located on the carburetor body. To enrich it you need to turn it clockwise, to lean it counterclockwise. If there is no screw, the carburetor is opened, the locking ring on the needle moves up for a richer mixture, down for a leaner one.
Adjustments are made as follows:
- Start the engine and warm it up for 10 minutes, after which you need to turn it off
- The screw must be tightened clockwise until it stops, but without force.
- After this, it is unscrewed counterclockwise 1.5 turns
- The engine needs to be started and the screw turned an additional 1/3 turn in the same direction. Wait 2 minutes
- As the speed increases, you need to unscrew the screw an additional 1/4 turn and observe the reaction for about 2 minutes. If the speed does not drop, repeat the steps
- If the speed begins to decrease, the screw must be turned clockwise 1/4 turn.
Ideally, the engine will operate exactly at 1.5-2 propeller revolutions, but its position depends on the quality of the fuel. In the case of a needle, the quality of the mixture will vary depending on the position of the needle locking ring. The disadvantage of such a carburetor is the small number of needle positions and the need to disassemble it each time to make adjustments.
You can adjust the fuel level in the chamber as follows:
- Unscrew the drain screw
- The phone is lifted up
- You need to check the fuel level while the engine is running. The melting level is slightly below the skirt located on the float chamber cover
- Most often, the level rises above normal and the carburetor overflows, so you need to adjust the float so that it fires earlier. To do this, the needle holder is usually bent. A lot of force is not required, only a few mm are needed.
World of scooters.
Models, selection, tuning, repair and driving. >> Power system. Engine. Contents :: Next >>
Supply system
Fuel and combustible mixtures
To operate the internal combustion engine, a combustible mixture consisting of finely atomized and evaporated fuel mixed with air enters its cylinder. The fuel used in modern scooter engines is motor gasoline with an octane rating of at least 93 (for scooters with two-stroke engines, oil is added to gasoline; this was discussed in more detail earlier). The octane number of gasoline characterizes the fuel's resistance to detonation - explosive combustion of fuel in the cylinder under high loads.
Fuel pump (Honda).
Fuel tank
It stores a supply of fuel; its volume in 50 cc scooters usually does not exceed 5 liters. Fuel tanks are made from plastics, which have almost replaced the steel that was used until recently. The tanks are located in different places. These used to be mounted directly under the front of the seat, but most modern scooters have a helmet storage bin located here. Therefore, the tank is moved to the “tail” part of the scooter, lowered below the luggage capacity or placed in the front part. There is a special hole in the tank cap through which air enters the tank as fuel is consumed. On many scooters, the tank lid is sealed, and the internal volume of the tank communicates with the atmosphere through special tanks with activated carbon, which absorbs gasoline vapors.
Fuel pump
It is not used on all scooters, since on most models the fuel tank is located above the engine and the fuel flows by gravity through a hose into the carburetor.
Automatic fuel tap: 1 - fitting to which vacuum is supplied; 2 — fuel supply fitting; 3 — nut for fastening to the tank; 4 - fuel filter.
On scooters with four-stroke engines, the fuel pump is electrically driven. Scooters with two-stroke engines are equipped with vacuum-driven fuel pumps - similar designs are widely used on outboard boat motors. They use the pressure pulsation that occurs in the crank chamber when the piston moves.
Fuel tap
It is a mandatory part of the power system, since it prevents fuel from leaking through the carburetor when stopping in the event of a leak in its float valve.
On motorcycles and older models of scooters (motor scooters), manually operated fuel taps were used. Such a tap has three positions: “3” or “Off” - closed; “O” or “On” - fuel comes from the main volume of the tank; “P” or “Res” - fuel comes from the reserve volume of the tank. When stopping for a long time (for example, at night), the driver closes the tap. When starting the engine, it turns it to the normal “open” position. If the engine stalls while driving, the driver switches the tap to the “reserve” position and drives to the nearest gas station. Usually the volume of the “reserve” is such that you can drive 20-30 km on it.
Diagram of an automatic fuel valve: 1 - membrane; 2 — valve body; 3 - fuel tank; 4 — fuel supply fitting; 5 - locking needle; 6 — control channel (communicating with the inlet pipe).
The engine power supply system of the vast majority of scooters includes: a fuel tank, a fuel tap, a fuel filter, a carburetor and an air filter. In some cases, the fuel system includes a fuel pump. Modern scooters with large engine displacement use a fuel injection system.
Detonation is an undesirable and dangerous phenomenon; it causes overheating and destruction of parts of the engine cylinder-piston group. The higher the octane number, the higher the compression ratio the engine can have. This means, in accordance with the theory of internal combustion engines, it will work more efficiently, its efficiency and power will be higher.
A fuel pump is required for those scooter models in which the fuel tank is located under the saddle or floor, below the carburetor.
Air filter location (shown by arrow).
Modern scooters are equipped with automatic fuel taps, which, as the name suggests, do not require any action from the driver. This valve opens only when the engine starts, and closes immediately when it stops. On modern scooters, the operation of the valve is controlled by the vacuum in the intake manifold (between the carburetor and the cylinder). When starting and operating the engine, the vacuum acts on the membrane of the fuel valve, which, overcoming the force of the spring, lowers the shut-off needle associated with it and ensures the flow of fuel.
There is usually a strainer in the line in front of or inside the fuel valve that prevents dirt from entering the carburetor. The second fuel filter - a replaceable paper one - is often cut into the hose connecting the tap and the carburetor. For safety reasons, clamps or retaining rings are placed on the ends of the connecting hose.
Air filter with foam filter element: 1 — housing cover; 2 - filter element; 3 - limiter; 4 - body.
Air purifier
Serves to clean the air entering the carburetor from dust and other foreign particles. The air cleaner is an important part of the scooter that ensures the longevity of the engine. In addition, the air cleaner plays the role of a muffler for intake noise. The air cleaner consists of a housing with a cover and an air filter. Modern scooters use two types of filters: paper and polyurethane foam (foam). Until recently, the metal mesh filters that were used, which required regular washing and did not guarantee fine air purification, have fallen out of use. Paper filters are disposable, i.e. they are replaced at every maintenance. Foam filters allow repeated washing and subsequent impregnation with special oil.
Recently, so-called zero-resistance filters, which are a type of mesh metal filters, have become somewhat widespread. However, they are installed only during tuning.
Whatever air filter is used, regular cleaning and monitoring of its condition is necessary, and, if necessary, replacement. If the filter is faulty, solid dust particles enter the engine, causing accelerated wear of the piston, cylinder bore, connecting rod bearings and crankshaft. An excessively dirty filter impedes the flow of air, enriching the fuel mixture, reducing power and increasing fuel consumption.
Main metering system of a spool carburetor: 1 - throttle spool: 2 - mixing chamber; 3 — conical spool needle; 4 — sprayer of the main dosing system; 5 - float chamber; 6 — main fuel jet; 7 - air channel.
Carburetor
This device, as part of the power supply system, prepares and doses the combustible mixture, which then enters the cylinder. Its design is quite complex; it includes several fuel dosing systems.
Float chamber
Its purpose is to maintain the fuel level at a constant level, since the amount of fuel supplied along with the air depends on this. In addition, it is necessary to stop the fuel supply when the engine is stopped.
Detailing of the throttle valve assembly: 1 - valve needle; 2 - throttle valve; 3 — cover gasket; 4 - cover; 5 — spool spring; 6 — needle lock.
A float with a valve attached to it, usually a needle type, maintains a constant fuel level. When the chamber is empty, the float and needle are lowered, and fuel can flow freely into the chamber from the tank. After filling the chamber with fuel to a certain level, the float rises and, acting on the needle (directly or through a lever), raises it, stopping the fuel supply. The fuel level is adjusted by bending the lever that controls the valve or by installing shims under the valve seat. Often such adjustment is not provided at all - it is ensured by precision manufacturing of parts.
Types of carburetors
The simplest carburetor is capable of preparing the optimal air-fuel mixture in only one engine operating mode, with constant load and speed. For any transport engine, including a scooter, both of these parameters are constantly changing, and there is also the problem of cold start. Therefore, the carburetors used on scooters are much more complex. Modern carburetors have a main metering system, starting, idle and transition systems, as well as mixture correction systems to obtain maximum power. To control the engine operating mode, a throttle valve is installed in the carburetor, connected by a cable to the “gas” handle on the steering wheel. With its help, the amount of air-fuel mixture entering the cylinder is regulated. There are two types of carburetors used on modern scooters: spool-type and so-called constant vacuum (CV). The latter are used primarily on scooters with four-stroke engines.
The conical spool needle has grooves (1) that secure the split washer (2). By moving the washer, the composition of the mixture can be adjusted.
AIR/FUEL MIXTURE
. As was experimentally established at the beginning of the 20th century, the fuel-air mixture burns most efficiently when the weight ratio of the components is 1:15. When the proportion of fuel is higher, the mixture is called rich, less - lean. Running the engine on rich mixtures increases power, while running on lean mixtures increases efficiency. Too rich mixtures do not burn completely in the cylinder, and poor ones lead to engine overheating, flashes and pops in the carburetor.
THE SIMPLE CARBURETOR
. Consists of two chambers: mixing and float. The mixing chamber is formed by a diffuser - this is the name of the channel, the cross-section of which in the middle is smaller than at the ends. As air passes through the diffuser, its speed in the middle increases, and the pressure drops below atmospheric pressure. The mixing and float chambers communicate with each other and the fuel channel (nozzle), in which a part with a calibrated hole is installed - a nozzle. The vacuum formed in the diffuser causes the fuel to flow out of the atomizer in the form of small drops, which are then crushed and evaporated in the air stream, forming a combustible mixture.
Main parts of a spool carburetor: 1 - automatic starting enrichment; 2 — carburetor body; 3 — float; 4 — float chamber cover; 5 — fuel jets of the main metering system; 6 — heating element; 7 - throttle with dosing needle.
The length of the nozzle is chosen such that the fuel level in the float chamber is 1-2 mm below the upper edge of the nozzle. This prevents spontaneous fuel supply when the engine is not running.
Spool carburetor
In it, the throttle valve (spool), moving, changes the cross-section of the diffuser. In this way, the amount of air passing through the carburetor and, consequently, the engine speed are regulated. A cone-shaped needle is rigidly connected to the spool, tapering downwards and entering the sprayer. The main fuel jet is installed on the other side of the atomizer. All these parts form the main metering system of the carburetor.
Main metering system of the CV type carburetor (position corresponds to full load): 1 - diffuser; 2 - membrane; 3 - spring; 4 - spool; 5 - dosing needle; 6 - rotary throttle valve; 7 - sprayer; 8 — main fuel jet; 9 — float; 10 - float shut-off valve.
When you turn the throttle handle, the needle moves along with the spool, and, due to the fact that its diameter at the bottom is smaller than at the top, when the spool and needle are raised, the cross-section of the fuel channel increases. By changing the position of the cone needle relative to the spool, you can slightly adjust the composition of the mixture: enrich it by raising the needle, or, conversely, deplete it by lowering it.
CV type carburetor
In constant vacuum carburetors, the movement of the “gas” handle is transmitted not to the spool connected to the metering needle, but to the rotary throttle valve located closer to the carburetor outlet. This damper, like the spool of the carburetor discussed above, regulates the amount of air passing through the carburetor. The diaphragm chamber above the spool communicates with the carburetor mixing chamber.
Adjusting screws for the idle speed system: 1 — “quantity” screw; 2 - “quality” screw.
Thus, the movement of the spool (and with it the fuel-metering needle) is controlled by the vacuum in the intake tract. At low loads, when the rotary throttle valve is closed, the vacuum in the mixing chamber (and therefore in the cavity above the membrane) is small, and the spool together with the needle is lowered under the action of a spring. Under heavy loads, when the throttle valve is open, increased vacuum is transferred to the cavity above the membrane and raises the spool along with the metering needle. The advantage of this type of carburetor is that the spool maintains a constant vacuum in the sprayer area, ensuring an optimal ratio of fuel and air in the working mixture.
As the throttle valve opens (the spool rises), the main metering system comes into operation, ensuring the required mixture composition throughout the entire range of engine operation.
Idle system of spool carburetor (a) and CV type (b): 1 - throttle valve (spool); 2 - fuel channel; 3 — mixture “quality” screw; 4 — jet of the idle system; 5 - throttle valve stop (spool valve) - “quantity” screw; 6 - air channel.
Idle system
When the scooter is standing still or coasting without a load (the gas is released), the carburetor must ensure that the engine operates at a minimum stable speed. In the simplest carburetor, this task is difficult to complete, since the vacuum with the spool almost completely closed in the area of the fuel supply channel is so small that it is not able to ensure the flow of fuel required for engine operation through the nozzle. However, in another place of the carburetor, behind the spool, closer to the cylinder, the vacuum is higher, and there is a small channel to which air and fuel are supplied. Several of these channels form the idle system that all carburetors have. It includes idle air and fuel channels, a fuel jet and adjusting screws for the optimal amount and composition of the fuel mixture at idle. One screw, called the mixture “quantity” screw, rests its end against the spool, preventing it from completely lowering. The other screw, called the mixture “quality” screw, with its conical end partially blocks the air supply channel to the idle system. Since fuel comes from the float chamber through a different channel, when the “quality” screw is tightened, the proportion of air decreases and the mixture entering through the idle system becomes slightly richer. To fix the adjusting screws from spontaneous rotation, springs or plastic bushings are used.
Cold start system
When starting a cold engine, a rich mixture is required for normal combustion. This is due to the fact that in this case most of the fuel settles in the form of drops on the cold walls of the cylinders and intake channels and the combustible mixture turns out to be too lean to ignite. Another carburetor system enriches the mixture when starting a cold engine - the cold start system.
Design of the injection system of Ditech two-stroke engines. GASOLINE, FUEL PUMP, PRESSURE REGULATOR, INJECTORS, COMPRESSOR, MICROPROCESSOR.
In the simplest scooter carburetors of yesteryear, a float stopper was located in the float chamber cover. When its rod was pressed, the float was forcibly lowered (recessed) and the fuel level in the float chamber became higher than permissible. This resulted in forced fuel supply from the atomizer into the intake manifold. Some of the gasoline flowed out through the drainage hole in the float chamber.
Recently, mixture fortifiers of various designs have been used. They represent an additional fuel channel, which opens only on a cold engine, or (less often) an air damper, which creates a higher vacuum at the nozzle and increases the amount of fuel supplied through the nozzle. The operation of the manual mixture enricher is controlled by the driver: to do this, when starting the engine, he presses the lever located on the left of the steering wheel, which, through a cable, controls the enricher damper. The most common are automatic starting enrichment units with a heating element. In such designs, when starting a cold engine, the enricher shut-off needle is retracted, the cross-section of the fuel nozzle is completely open, and the air-fuel mixture is enriched. After starting the engine, current from the generator flows to the heating thermoelement. After a certain time, sufficient to warm up the engine, the working fluid of the element expands and, acting on the enrichment needle, closes the fuel channel.
Injection system: a - general view; b - location of the nozzle; 1 — electromagnetic injectors; 2 — fuel manifold; 3 - pressure regulator; 4 — electronic control block; 5 - fuel pump; 6 — fuel tank; 7 - fuel filter; 8 — inlet valve; 9 — intake manifold.
Scooters are often equipped with an electric heater, activated by a temperature sensor at a temperature of about +5 ° C and below. In addition, some scooters (for example, BW's Yamaha) are equipped with the manual enricher described above in addition to the automatic one. In this case, the driver himself decides which enrichment system to use.
On modern scooters, manual enrichment is rare. Typically, automatic devices are used that allow the driver not to think about what to do when starting a cold engine.
Fuel injection systems
Carburetors of modern scooters are quite complex and sophisticated devices. However, today they are being replaced by electronically controlled fuel injection systems. Such systems include an electrically driven fuel pump (usually submerged in the fuel tank), a fuel accumulator, a check valve and drain line into the tank, a distribution pipeline (for two-cylinder engines), an electromagnetic injector, an electronic control unit connected to a number of sensors (opening throttle valve, coolant temperature, crankshaft speed, oxygen content in the exhaust pipe, detonation, etc.).
Injection system: a - general view; b - location of the nozzle; 1 — electromagnetic injectors; 2 — fuel manifold; 3 - pressure regulator; 4 — electronic control block; 5 - fuel pump; 6 — fuel tank; 7 - fuel filter; 8 — inlet valve; 9 — intake manifold.
Recently, Italian scooters have appeared with the Ditech fuel injection system into the cylinder of a two-stroke engine. Only air with atomized oil added to it in the inlet pipe to lubricate the parts of the cylinder-piston group and the crankshaft bearings enters the crankcase of engines with this system through the reed valve. Next, the oil-air mixture enters the cylinder and combustion chamber through the purge windows. Some of the air is compressed by a mechanically driven supercharger and supplied to an additional injector. A fuel pump located in the tank supplies gasoline to the injector, which is no different in design from those used in conventional four-stroke engine injection systems. The jet of injected fuel is picked up by compressed air in an additional injector and directed into the combustion chamber. The injection system provides a very fine atomization of fuel. The chamber is filled at such a speed that the engine can operate without interruption up to a crankshaft speed of 12,000 rpm. In addition, an engine equipped with the Ditech system is 40% more economical than a two-stroke engine of comparable power and even outperforms a four-stroke engine in this parameter, while meeting the most stringent exhaust gas emissions standards.
Contents :: Next >>
Equipment, etc.
Various insects cause quite a lot of inconvenience when riding a scooter. They constantly strive to break on the visor of the helmet and dry on it for a long time. In this case, as well as to protect the helmet glass from water, dirt and fogging, a helmet cleaner can be used. For leather lovers, there are leather care products. These are lotions that make the skin softer, prevent it from drying out and cracking, protect the skin from water and improve its appearance. Skin treated with this lotion is cleansed and looks like new.
For lovers of fabric clothing, there are various means of impregnating clothing and tents. They will save you from getting wet and dirty in bad weather, maintain the breathability and softness of the fabric, and prevent the formation of oil and grease stains. Such aerosols are suitable not only for fabric, but also for impregnating suede.
Signs of deviation in mixture preparation
When studying the technology of how to adjust the carburetor on a 2t, 4t scooter, the driver must know what factors indicate deviations in the process of preparing the fuel mixture. If it is lean, a popping noise will be heard from the system when the vehicle reaches high speed. In this case, the carburetor spark plug will be white. Electrodes may in some cases melt due to operating at too high temperatures. Also, the scooter will react poorly to turning the throttle when reaching the upper limit.
If the mixture is rich, a large excess of fuel will be detected. There will be black carbon deposits on the spark plugs. Black smoke and popping noises will come out of the muffler.
But if configured correctly, such phenomena will not appear. The engine will operate evenly at all speeds. There is no excessive consumption of gasoline. At any speed, the throttle will be informative, and when examining the spark plug, soot and soot will not be detected. Its color is slightly brownish (not white).
Problems when paying with bank cards
Sometimes difficulties may arise when paying with Visa/MasterCard bank cards. The most common of them:
- There is a restriction on the card for paying for online purchases
- A plastic card is not intended for making payments online.
- The plastic card is not activated for making payments online.
- There are not enough funds on the plastic card.
In order to solve these problems, you need to call or write to the technical support of the bank where you are served. Bank specialists will help you resolve them and make payments.
That's basically it. The entire process of paying for a book in PDF format on car repair on our website takes 1-2 minutes.
If you still have any questions, you can ask them using the feedback form, or write us an email at [email protected]
When to check your work?
Let's figure out in what cases it is necessary to check the operation of the scooter. For this you need:
periodic checks, cleaning, replacement of parts
With them, attention is directed to brittle, fragile parts; regular – parts sensitive to blockages. Dirt on them can lead to engine failure, overheating or jamming;
Maintenance leads to an extension of the life of motorcycle equipment
- current - when a violation is detected: rupture of connecting tubes, leakage of oil and the presence of stains from it, as well as cracks due to the influence of precipitation and temperature on the plastic;
- Preventive checks when changing oil, refueling, cleaning from dirt. Ignition and braking systems are also checked.
Preventive inspections and measures taken to replace unsuitable parts are important:
- fuel pump,
- gas tank,
- gasoline tap,
- fuel filter,
- air filter,
- carburetor,
- connecting tubes.
You can check the functionality of the fuel pump yourself.
Cooling system
All Nexus scooters are equipped with a forced air cooling system. It is needed to prevent jamming and damage to parts due to overheating, which causes excessive expansion of the piston, as well as disruption of lubrication conditions. Since the motor of all scooters is covered with a casing and is located under the seat in the rear, the flow of oncoming air cannot effectively cool it. Therefore, a fan impeller is used, mounted on the right side of the engine on the generator rotor. This centrifugal fan forces air under a casing that covers the outside of the cylinder and cylinder head.
Cooling system details:
- fan impeller;
- casings
Downloading a book
After successfully completing the payment (by any method) and returning to the KrutilVertel store from the payment system website, you will be taken to the successful payment page:
The book you purchased will be in your personal account, from where you can always download it.
Please note that after making the payment, you need to return back from the payment system website to the KrutilVertel website. If for some reason you did not return back to the site and closed the payment system tab with a message about the successful completion of the payment, please let us know - we will send you a letter indicating access to download the book
If for some reason you did not return back to the site and closed the payment system tab with a message about the successful completion of the payment, please let us know - we will send you a letter indicating access to download the book.
Features of operation and spare parts
Gasoline is poured into one of the holes in the tank. The fuel pump automatically opens when the engine starts, and closes its second hole when it stops. In this case, a vacuum occurs, affecting the opening of the gas tap to supply fuel to the pipeline. Then, through the gasoline filter, the fuel enters the carburetor, where it is mixed with the air that has passed through the air filter. At the same time, the filters clean gasoline and air from foreign impurities, respectively, protecting scooter parts from damage.
How do they use a fuel pump on Chinese scooters? On Chinese technology, instead of a pump, there is a vacuum valve. Here, fuel is supplied from the tank by gravity, since the tank is located above the carburetor
When servicing and repairing, it is necessary to pay attention to breakdowns and contamination of hoses from the carburetor and filters in the tap.
Signs of necessary adjustment
There are several main signs that let the driver know that it is time to have their vehicle serviced. They cannot be ignored. Otherwise, repairs will cost much more. In this case, you should learn how to properly adjust the carburetor on a scooter as soon as possible.
First of all, engine power drops. This can also be observed due to wear and tear of the engine systems. The cylinder piston group may require replacement. However, an incorrectly configured carburetor can also affect the power of the engine. If it introduces more air into the mixture than required, the fuel becomes lean. This leads to overheating and reduced power.
If the engine refuses to work at all, this may also be evidence of improper carburetor operation. However, to find the cause of the breakdown, you will need to check several major systems.
If the engine starts but stalls, this may be due to a clog in the carburetor. In any case, the driver must responsibly approach the issue of solving any problem related to his vehicle.
Scooter oil
Modern scooters usually use 2 types of oil - motor and transmission, for the engine and transmission, respectively. For the normal operation of these components, the oil, of course, should be changed regularly, using the oil class recommended by the manufacturer (Read more about scooter oils). Engine oil change intervals
The scooter is also installed by the manufacturer, but on average every 3000 km (when using really high-quality oil). During the break-in period of a scooter (or a new engine), the oil is changed more often. That is, for a new scooter, the frequency of replacing the motor (and, by the way, the transmission too) is approximately the following:
after the 300 km mark after the 1000 km mark after the 2000 km mark then every 2-4 thousand km.
After break-in, the transmission oil is changed a little less frequently than the engine oil, approximately every 4-6 thousand km. The process of changing the engine and transmission oils of a scooter.
The condition of the air filter is very important for a scooter.
The air filter is an important element in the scooter's power system. The filter must always be clean, not have even a little dirt, especially not be clogged with dirt, dust, poplar fluff and other evil spirits. Otherwise, this dirt will prevent the free flow of fresh air into the carburetor, which will change the air/gasoline ratio in the combustible mixture (making it richer); also, this dirt will certainly penetrate into the carburetor, clog the jets, tubes, etc., which in turn will also change the air/gasoline ratio in the combustible mixture (make it lean); and finally, in the worst case scenario, foreign small particles will penetrate into the combustion chamber, which can damage the cylinder walls and reduce compression; in other words, the engine will grunt. So, clean your air filter more often.
Scooters often use “zero” resistance filters made of special foam rubber. Such a filter requires very regular maintenance: washing and impregnation of the foam rubber with a special oil that can gel.
Oil for impregnating filters is produced according to a special recipe, although it is quite normal to use regular engine or transmission oil. Oil prevents water, dust and dirt from entering the engine. The due date for the next scooter filter service can be determined by the “fading” of the filter color. Learn more about cleaning your scooter's air filter.
Fuel filter - replacement
SERVICE FREQUENCY
On most models of modern scooters with a four-stroke engine or a two-stroke engine with a separate lubrication system, a fuel filter is installed in the power system. It is needed in order to protect the carburetor and cylinder-piston group of the engine from fine dust and other particles that have entered the fuel. It is recommended to replace the filter once every 10 thousand km, or after parking the scooter for a long time. The fuel filter is located in the gap in the gas tank-carburetor line and is often dismountable, which allows it to be cleaned without replacing the filter element.
REMOVAL
1. Loosen the fastening clamps on the fuel hoses. To avoid fuel spilling from the line, place a rag under the filter and remove it
INSTALLATION
We install a new fuel filter in the fuel line.
ATTENTION:
There is an arrow on the filter housing indicating the direction of fuel flow. When installing, observe the direction “towards the carburetor”.
How to properly check?
How to check the fuel pump on a scooter? This question worries many fans of this vehicle when the vehicle does not start. There could be several reasons for this, one of them is that there is something wrong with this part. You can carefully check the performance of the fuel pump yourself.
First, let's try to configure the fuel pump:
- It has two screws: the first is for idle speed, the second is responsible for the quality of the fuel mixture. We tighten both screws, then release the second screw two turns, the first two and a half turns. We start the scooter, listen to the engine: smooth - no adjustment required, intermittent - continue.
- We fix the equipment with a step, slowly tighten the idle screw until the clutch engages - the wheel begins to rotate. Unscrew it a quarter turn. We check while driving: if acceleration is difficult, then tighten the screw a quarter turn. Acceleration is normal - the screw should be turned a quarter counterclockwise. Then we adjust the idle speed screw again.
Let's take a closer look at how to check the vacuum fuel pump on a scooter if the adjustment fails:
- Unscrew the four screws using the hexagonal star handle;
- carefully pull out the fuel pump cover, remove the rubber gasket, membrane, see the valve;
One of the important parts is the fuel pump for the scooter.
- due to the vacuum, gasoline passes through the valve from the tank into the upper chamber of the carburetor, we clean it;
- close it in the same sequence: gasket, membrane, gasket, screw it on, install it on the scooter and ride. It is necessary that there is always gasoline, otherwise these parts in the gasoline pump may dry out;
- You must tighten it carefully so that gasoline does not spill out.
Maintenance Procedure
Carburetor failure is the most common problem with a vehicle such as a scooter. Four-stroke (4t) and two-stroke (2t) engines are available for sale. Engines are produced in volumes of 50 and 150 cubic meters. The differences in them are insignificant, so the adjustment in all systems is almost identical.
It is much easier to adjust the carburetor of a Honda Dio scooter. Therefore, many auto mechanics use this technique as an example when training inexperienced drivers. During the setup process, you need to perform a number of manipulations.
First of all, the carburetor is adjusted at idle speed. Next, using a special screw, the ratio of air and gasoline in the fuel mixture is equalized. It is possible to perform this operation by moving the needle. The final stage is to control the fuel level in the float chamber.
Before tuning, the carburetor must be removed and washed. Only after this can the settings be made.
What is the carburetor of a Chinese scooter and its capabilities, disadvantages, tuning
The carburetor circuit of a Chinese scooter is, in principle, standard and suitable for both 2t and 4t engines. The design of the carburetor allows certain actions to be taken to improve its performance, however, if the engine is two-stroke, the efforts will not make sense.
The simplest approach is to replace the carburetor with a more advanced one, for example, with an accelerator motor, if you have a fairly old version without it. Most often, simple tuning is limited to replacing the main fuel jet, this is especially true for engines with low power. Replacing the nozzle helps to increase the fuel channel and, due to this, add a little power to the engine.
Quite often, more serious tuning involves the use of a 150 cc scooter carburetor. Interesting models with a diffuser diameter of 17.5 mm. It is great for 70cc piston. Less often you come across a large diameter of 19-24 mm, it is just ideal for a bored 150 cc piston engine. However, the diameter must be selected correctly, otherwise the motor will begin to choke.
On what models is it installed?
The fuel pump is installed on various models of scooters. The most common ones are presented below.
The scooter's fuel pump plays a role in the proper functioning of gasoline in the engine operating system.
On Japanese models:
- Honda Dio - easy to use, with a glove compartment that allows you to store a helmet and other things on the go, tank capacity is 4-6 liters;
- Vamaha Jog – has great maneuverability, the volume of the power unit is 49 cubic centimeters.
On Chinese scooters:
- Suzuki Address V110 is a two-stroke with a medium speed engine, its wheelbase is designed for movement around the city and beyond;
- Viper Storm 150 is a two-seater, reliable, comfortable model.
Gasoline pumps are installed on equipment from Russia - a manufacturer in Yoshkar-Ola, an official dealer of Polaris and the Russian brand of several companies Irbis:
- Lifan LF 125T-27 - it has a four-stroke engine, 125 cubic centimeters, speed 80 kilometers per hour, gas tank capacity 5 liters;
- Irbis Z50R is a high-speed scooter for driving outside the city with wide tires.
A fuel pump is installed on various scooter models