Moto battery. How to choose and serve
Choosing a battery for a motorcycle is not an easy task. Each type, from lead-acid with a liquid electrolyte, to lithium-ion, has its own pros and cons, and there are also a number of urban legends associated with each type.
I have been working as a motor electrician for several years, and before that I was mainly involved in the development and repair of small electronic devices, and I am ready to claim that I understand this topic well enough to tell you about it.
Let's start with the simplest thing.
Numbers on the battery
The battery has two important parameters (except for the on-board voltage). The first is volume or capacity. It is measured in ampere-hours (Ah, Ah, Ah), and it is very simple to understand: capacity means the ability to produce a certain current (in other words, a certain power or a certain amount of heat, for example) for a certain time. For example, a 10Ah battery has a capacity that allows it to deliver 1 ampere for 10 hours, or a current of 10 amperes for 1 hour. And so on. The more ampere-hours in the battery, the longer it can work under a certain load - be it light, music, or cranking the starter of a poorly starting engine.
The second important parameter is the cold cranking current (aka CCA). It characterizes the battery's ability to deliver high currents. The fact is that no battery is capable of delivering an infinite number of amperes, especially in cold weather. And if your big V-twin with thick oil barely turns over in the cold and does not want to start, the battery with its small CCA is to blame, not being able to provide enough current for the electric starter to crank the engine at high speed. On the fingers, cold start current means the current that the battery is capable of delivering for 30 seconds at a temperature of -18 degrees Celsius, without dropping the voltage below 7.2 volts. The larger the engine capacity, the heavier it is, the colder, thicker the oil, the higher the compression ratio, the smaller the thermal clearances, and so on, the more cold start current is required from the battery. Sometimes even the depressed clutch plays an important role in how difficult it is for the starter to turn the engine, however, this has little to do with motorcycles, because we rarely drive in weather when engine oil turns into engine grease.
There are three problems with this important parameter. Firstly, manufacturers of motorcycle batteries do not always indicate it at all. Secondly, it may be greatly overestimated, since it is impossible to check it at home. And thirdly, and this is the most important thing, the value of the maximum cold start current inevitably decreases during the operation of the battery due to its wear.
Numbers on a motorcycle battery
A detailed guide to the capacity of motorcycle batteries. Everything you need to know in one article
General information and answers to the most important questions about motorcycle battery capacity.
Content:
1. What is the capacity of a motorcycle battery and how is it measured 2. Typical capacities of motorcycle batteries 3. How to find out the capacity of your motorcycle battery 4. The importance of selecting a battery with the correct capacity 5. Can the battery capacity change? 6. Is it worth buying a large capacity battery?
7. What affects the battery capacity?
What is the capacity of a motorcycle battery and how is it measured?
Battery capacity (or “useful charge”) is the amount of electricity stored by the device. The larger the capacity, the longer the battery can supply the engine with electricity in autonomous mode.
Capacity is one of the main parameters by which the selection of a battery for a motorcycle should be made. It is measured in ampere-hours (the designations Ah or Ah are also acceptable), which fully reflects its essence. For example, a capacity of 12 ampere-hours means that the battery is capable of delivering an operating current of 1 ampere for 12 hours. Accordingly, if a current of 0.5 amperes is sufficient for normal operation of your motorcycle for an hour, the same battery will be enough to operate for 24 hours. This works the other way too. If the engine requires a charge of 2 amps per hour, the capacity will last for 6 hours. All this does not mean that the battery will need to be charged every day. We are talking specifically about battery life. After all, while driving, the battery is recharged automatically. With proper operation, you will have to use a special charger no more than once every 2-3 months.
Sometimes the unit of capacity is called "ampere per hour" (rather than ampere-hour). This is not entirely correct. Developing our example with a 12 Ah battery, we can say that the vast majority of motorcycles per hour require a current strength much less than 12 amperes.
Another point that depends on the capacity of the motorcycle battery is the current strength1 when charging it (it is the current strength, not the charging speed; we’ll talk about speed a little lower). In order for the process to occur without damage to the battery itself, it is recommended to set the current on the charger to the equivalent of ten percent of its capacity. That is, our battery with a capacity of 12 Ah needs to be charged with a current of no more than 1.2 amperes.
1. Current strength is the amount of electricity passing through the cross-section of a conductor in one second. Ampere is the strength of electric current at which an amount of electricity equal to one coulomb passes through the cross-section of the conductor every second: 1 ampere = 1 coulomb/1 second.
Typical capacities of motor batteries
The category of motor batteries includes not only batteries directly for bikes, but also devices for a wide range of motor vehicles: scooters, mopeds, ATVs, snowmobiles, jet skis and even lawn mowers. Therefore, the range of capacities of such batteries is very wide: from 2.3 to 30 ampere-hours. If we take into account only batteries directly for motorcycles, then a rare bike is designed for a battery with a capacity of less than 6 Ah.
The table below shows typical battery capacities. For clarity, here are additional data about them. Using these data, you can trace the influence of battery capacity on its other parameters.
The first line is typical battery capacities (when you click on the link, you will be taken to a page with a full range of batteries of the corresponding capacity). Next - indicators of voltage, size, weight and starting current level of batteries from Yuasa, Skyrich and Kyoto brands
6Ah 9Ah 12Ah 14Ah 18Ah Yuasa Yuasa YTX7L-BS Voltage: 12 V Dimensions: 114 mm x 71 mm x 131 mm Weight: 2.3 kg Starting current: 100 CAA Yuasa YB9-B Voltage: 12 V Dimensions: 135 mm x 75 mm x 139 mm Weight: 2.4 kg Yuasa YB12A-A Voltage: 12 V Dimensions: 134 mm x 80 mm x 160 mm Weight: 3.1 kg Yuasa YB14-A2 Voltage: 12 V Dimensions: 134 mm x 89 mm x 166 mm Weight: 3.4 kg Yuasa YB18-A Voltage: 12 V Dimensions: 180 mm x 90 mm x 162 mm Weight: 4.3 kg Skyrich Skyrich YTZ7S Voltage: 12 V Dimensions: 113 mm x 70 mm x 105 mm Weight: 1.55 kg Starting current: 100 CAA Skyrich YB9-B Voltage: 12 V Dimensions: 135 mm x 75 mm x 139 mm Weight: 2.1 kg Starting current: 100 CAA Skyrich YB12A-A Voltage: 12 V Dimensions: 134 mm x 80 mm x 160 mm Weight: 3.1 kg Starting current: 165 A. Skyrich YB14-A2 Voltage: 12 V Dimensions: 134 mm x 89 mm x 166 mm Weight: 3.4 kg Starting current: 190 A. Skyrich YTX20L -BS Voltage: 12 V Dimensions: 175 mm x 87 mm x 155 mm Weight: 4.5 kg Starting current: 310 A. Kyoto Kyoto YB9L-A2 Voltage: 12 V Dimensions: 135 mm x 75 mm x 139 mm Weight: 2 .4 kg Kyoto YB12A-B Voltage: 12 V Dimensions: 134 mm x 80 mm x 160 mm Weight: 3.1 kg Kyoto YB14L-A2 Voltage: 12 V Dimensions: 134 mm x 89 mm x 166 mm Weight: 3.4 kg Kyoto YTX20L-BS Voltage: 12 V Dimensions: 175 mm x 87 mm x 155 mm Weight: 5.1 kg
The table shows typical capacities that are used to produce most modern batteries. But you can find a battery with any other capacity in the range from 2.3 to 30 ampere-hours. It is also worth noting that all of the above models are designed for a voltage of 2 V 12 V. There are batteries with other voltage ratings (for example, 6 V).
The starting (or cranking) current that the battery is capable of providing directly depends on the battery capacity. This is the amount of electricity that the motorcycle needs to start and run all the electrical mechanisms. Pay attention to the table row dedicated to Skyrich batteries. The larger the battery capacity, the greater the starting current. According to this indicator, all batteries can be divided into 3 classes:
1. Batteries with a capacity of less than 12 Ah. They are capable of powering the lighting, ignition and speakers of medium and large motorcycles (if used as an additional battery). In addition, such batteries are used to start the engine and ensure the operation of all electrical circuits of some models of small-capacity motorcycles. The engine capacity of such bikes rarely exceeds 500 cubic centimeters. They are often used on ATVs, snowmobiles, etc.
2. Batteries with a capacity of 12 Ah. They are used to provide current to all systems and start the engine of medium-sized motorcycles, of which the majority are on the market. The engine capacity of a significant part of these bikes is within 900 cc. see. But there are exceptions. Thus, the Skyrich YT14B-BS battery can be installed on some Yamaha motorcycle models (XV17P Road Star Warrior and Silverado). But this is precisely an exception to the general rule.
3. Batteries with a capacity of more than 12 Ah. Used for installation on heavy motorcycles (with an engine capacity of 900 cc).
2. Battery voltage is the potential difference immersed in the electrolyte and acting on the positive and negative electrodes. Battery voltage is not constant. It changes depending on the battery charge level.
How to find out the battery capacity of your motorcycle
Each battery is marked with all the necessary data.
Sometimes the marking is in a continuous format and looks something like this: 12V12Ah. Explanation: voltage – 12 volts, capacity – 12 ampere-hours.
There are several other types of less common markings, which are shown in the diagram below.
If for some reason this parameter is not indicated on your battery, you can look at the data sheet. It usually lists not only the capacity of the battery installed at the factory, but also the range of battery capacities that can be installed on the bike. This is done in case a specific factory battery model cannot be found. Well, or if you think that you need a higher starting current than provided by the manufacturer (we’ll talk about why such situations can arise a little lower).
If this option does not work (the registration certificate is far away or lost), you can use the services of one of the online services, which will not only tell you the battery capacity, but also select the right battery according to the model of your motorcycle.
The importance of choosing a battery with the correct capacity
If you purchase a battery with insufficient capacity, it may not have enough cranking current to start your motorcycle engine. Or for the normal operation of headlights, lighting and other electrical equipment, which is becoming more and more common on modern bikes. In addition, it is worth considering that in the cold season, starting the engine is even more difficult due to low temperatures. And in such a situation, it is extremely useful to have some reserve battery capacity.
You can buy a battery with a slightly larger capacity than was installed at the factory. Many manufacturers try to save money and do not equip their products with the most powerful available options. But before you take this step, make sure that a battery with a higher capacity will fit in the space allocated to it. In the table above, you can see that the larger the battery capacity, the more space it takes up in all three parameters. In addition, do not forget that buying a battery with a larger capacity means an additional overpayment, which is most often unjustified. And this overpayment can be avoided if you correctly select the battery capacity.
Can the battery capacity change?
During operation, the battery capacity will steadily decrease due to natural wear and tear. But if the battery is used correctly, the decrease in capacity will become obvious only a few years after the battery starts to be used. Typically towards the end of the warranty period.
There are factors that can speed up the decline in battery capacity.
1. Deep discharge. If you let a lead acid battery discharge to below 10.5 volts, its capacity will be greatly reduced when it comes back to life.
2. Excessive charging. If the battery does not yet require recharging, it is better not to connect it to the charger again. As a rule, the procedure is required once every two to three months.
3. Electrolyte contamination. This item applies only to serviceable batteries. The electrolyte is the liquid that allows current to flow inside the battery. During operation, this liquid gradually evaporates. Therefore, the electrolyte volume must be regularly replenished (which is why such batteries are called serviceable). If the levels of iron or chlorine in the electrolyte exceed the permissible values, the battery will quickly lose its capacity. Therefore, you need to replenish the electrolyte level only with distilled water.
4. Incorrect storage conditions when unplugged. Leaving a disconnected battery for a long time at sub-zero temperatures or in conditions above 15-20 degrees will also negatively affect its capacity. The ideal temperature is ten to fifteen degrees above zero.
5. Low driving speed. Some motorcycle models, when driven at too low a speed, do not charge the battery sufficiently, resulting in loss of capacity. But this is an extremely rare case, and the speeds must be very low indeed. This does not happen when driving in normal city traffic.
How to avoid rapid loss of battery capacity and extend its service life? It is enough to avoid everything described in the five points above. It is only worth adding that during the wintering process of the battery at your home, it is also worth recharging it 1-2 times to avoid excessive discharge. Otherwise, go ahead and don’t worry, the battery will last as long as it should.
Is it worth buying a large capacity battery?
A battery with a larger capacity than was installed by the manufacturer may be needed in two cases.
1. For driving in winter. It is in cold weather that a few extra ampere-hours can provide the necessary starting current to start the engine.
2. To install additional equipment. A larger battery may be needed if you are going to outfit your bike with various electrical gadgets: a powerful sound system, lighting not provided for by the design, additional alarm, etc. The standard battery capacity may not be designed for all this and you will have to choose a more expensive model.
Before purchasing a larger battery, make sure you have space for it. The larger the battery, the more space it takes up.
What does battery capacity affect?
Battery capacity AFFECTS:
1. Its size. The larger the capacity, the more space the battery takes up. This does not mean that batteries with the same capacity will all be the same size. Sometimes they differ in height or width, but this is already due to different manufacturer standards (see table above).
2. His weight. Same situation. How much the weight of the battery increases, depending on its capacity, can also be seen in the table.
3. Starting current strength. The larger the battery capacity, the greater the starting current it can provide. The stronger the starting current, the larger the engine size that the battery can serve. And the more different additional devices you can place on it.
4. Battery life. If your motorcycle's electricity consumption is 1 amp per hour, then a battery with a capacity of 12 amp-hours will last 12 hours in off-line mode. But the relationship here is not entirely linear. The same battery, if your motorcycle consumes 12 amps, will last not an hour, but only 35 minutes, so be more vigilant. And remember about the gradual decrease in capacity during operation. The examples we give only work with new batteries.
5. Battery cost. Yes, where would we be without it? The larger the capacity (and, accordingly, the weight, size, etc.), the more expensive the battery.
6. Current strength when charging the battery. It is considered normal to charge the battery with a current equal to 10% of its capacity. If the discharge is higher than normal, it is recommended to reduce this figure to 5%.
Battery capacity DOES NOT AFFECT:
1. Battery charging speed. Since charging occurs at a current of 10% of the battery capacity, the process will take about 10 hours in any case.
Thank you for reading this article to the end. We hope that with its help you began to better understand the principle of operation of motorcycle batteries and now you can accurately select a battery with the capacity you need.
www.le-parts.ru
Lead acid batteries
The oldest type of starting battery is still relevant today because it has an excellent price-quality ratio. This type of battery was developed back in the mid-19th century, and since then work has been ongoing to improve the quality and ease of use of these batteries.
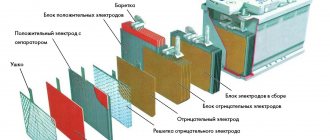
I suggest not turning this article into a chemistry lesson, so I’ll keep it short. A typical 12-volt lead-acid battery consists of six cells in a plastic case.
Actually, the word “battery” here meant “a string, a series, a series of elements of the same type” - it was only later that we began to call any current sources, including those consisting of a single cell, batteries.
So, the cells of lead-acid batteries consist of lead plates with various additives and coatings for strength and increased current output. Sometimes the plus and minus plates have identical composition and design, but more often they are designed slightly differently, but this does not affect the essence. The plates are immersed in a solution of sulfuric acid in water, called an electrolyte. In a charged battery, there is some lead dioxide present on the plate. During the current transfer process, lead dioxide in the presence of acid is converted into lead sulfate and water, and metal lead with a sulfate ion at the second pole is converted into lead sulfate. When charging, a reverse reaction occurs, consuming lead sulfate, reducing it to metallic lead at one pole and converting it to lead oxide at the other, consuming water in the process.
It is important for us to remember this: sulfuric acid converts a certain amount of lead metal into sulfate immediately after filling the battery, so after filling the electrolyte, the battery is capable of delivering some current, but it cannot be considered fully charged. A fully charged battery has almost no lead sulfate in the electrolyte, and on one of the plates there is a layer of lead dioxide, while the second remains purely metal.
Another important nuance: if the battery, in which all the lead sulfate has turned into metallic lead and lead dioxide, is not disconnected from the current source, then the water in its electrolyte will begin to decompose into oxygen and hydrogen. There is one interesting feature here: the intensity of water decomposition depends on the voltage applied to the cell, because if it does not exceed a certain level, then oxygen and hydrogen do not fly away from the electrolyte, but combine back into the water, releasing a little heat. This is what ideally should be the maximum voltage in the on-board network of a car and motorcycle - at which the battery can be fully charged, i.e. to exhaust the supply of lead sulfate in the electrolyte, but at which water does not yet begin to evaporate in the form of detonating gas.
And here's where the fun part begins: the ideal voltage for different types of lead-acid batteries varies. Moreover, this is influenced not only and not so much by the type of battery design itself, but by additives to the plates. But more on that later.
Lead acid batteries
Types of Lead Acid Batteries
Depending on the form in which this acid is between the plates, batteries are divided into several types.
Standard wet batteries are the oldest type. In them, a solution of sulfuric acid in water literally splashes inside, and when charging such a battery, the solution mixes quite poorly, and although lead sulfate still remains in it, a certain amount of water necessarily decomposes into oxygen and hydrogen, regardless of the applied voltage. This is why such batteries require the addition of distilled water. The advantage of such batteries is their simplicity of design, and therefore their low cost. The downside is that liquid electrolyte can spill out of the battery if it is tilted at a certain angle, and it cannot be sealed due to the release of gases.
AGM batteries with absorbent glass mats are the most popular on modern motorcycles. Here, the liquid electrolyte is absorbed into a layer of glass wool placed between the plates, so it does not spill out of them under any conditions. However, the volume of electrolyte here is smaller, and therefore there is less water in it, so such batteries die especially easily when overcharged. But the acid concentration here is higher, so they produce more current, and at the top of the cells there is a recombination chamber in which the oxygen and hydrogen released when the cell is charged combine back into water, and its drops fall back into the cell and are absorbed into the glass wool. This is in an ideal world. But in fact, if overcharged too much, such a battery can turn into a bomb, so a valve is installed in the cell that releases detonating gas when a certain pressure is exceeded. Such batteries are also called by the abbreviation VRLA (which translates as valve-regulated lead-acid). Their advantages are the ability to work in a supine position, the absence of liquid electrolyte that can leak, good capacity and current output. Another advantage is the low tendency to form sulfation (which will be discussed below). One of the disadvantages is the small volume of water, as a result of which such batteries quickly deteriorate when overcharged.
There are also gel batteries, under which unscrupulous manufacturers often disguise batteries made using AGM technology. In real gel batteries, the electrolyte is thickened with a gelling agent, which prevents it from leaking out, but at the same time slows down the flow of ions, so such batteries do not have a very high current output, and they also need to be charged with a low current. Their use as starter batteries is extremely limited by these factors, and at least now I have not seen real gel models on sale. Anything marked with the words GEL or iGel are regular AGM batteries. The main thing that surprises is why the respected public decided that gel batteries in a motorcycle are something good. The best type of lead-acid starter battery is, without a doubt, AGM.
How does a motorcycle battery work?
The battery installed in the electrical circuit of a motorcycle is one of the sources of electromotive force and currents flowing in the electrical circuit. In the battery itself, current flows due to the transfer of electrical charge by ions that give or take away electrons, and the main thing that is important for us to understand here is that chemical reactions in the battery cannot be stopped, unlike, for example, the rotation of an engine.
While the battery is disconnected, the electrons in it move from one pole to the other, and very little energy is spent on this, but when an external consumer is connected, everything speeds up: the electrons have the opportunity to go a different way, transferring the energy of chemical reactions with their movement. A large load, such as starting the engine with an electric starter, leads to the fact that a large flow of charge carriers - electrons - leaves the battery and the same large flow returns to the second terminal from the electrical network, and under the influence of such powerful dynamics of the exchange of charge carriers, chemical processes in the battery are significantly accelerated. Sulfate ions of sulfuric acid combine with the lead atoms of the plates, emit “extra” electrons, giving them additional energy, and they transfer it to where it is spent - to the electric starter, to power the switch or ECU, and so on, until the battery is exhausted. chemical energy for these reactions to occur. This occurs at the point when all the sulfuric acid (H2SO4) has not been converted into lead sulfate covering the surfaces of the plates, and the electrolyte in this state is water. Roughly speaking, lead sulfate is a waste product from the reaction in a battery that produces electricity, but unlike most waste, this type of waste can be reused.
When the battery is charged, the process of lead sulfate formation is reversed: lead oxide, sulfuric acid and metallic lead are formed in the battery, and thus chemical energy is returned to this system, which the system again becomes capable of delivering.
The motorcycle electrical network works on the following principle: to start the engine, the electric starter and other consumers take a fairly large portion of energy from the battery, and when the engine is started and running, the generator, which is usually located on the engine shaft, begins to generate electricity. This energy enters the relay-regulator, which is a rectifier and stabilizer: it rectifies alternating current from the generator into direct current and supplies a stable (if possible) voltage to the on-board network. At idle speed, it is usually only enough to operate the main systems of the motorcycle (lights, ECU, dashboard, ignition, etc.), but as soon as the engine starts operating at higher speeds, the battery connected to the on-board network begins to charge.
Here's where the catch lies: a perfectly manufactured lead-acid battery that, once the engine starts, is fully charged (i.e. it depletes the supply of lead sulfate on the plates, turning into metallic lead and lead oxide), but is not recharged (i.e. in it, water does not decompose or is completely returned to the cells), it can work almost forever. But if, after starting the engine, the lead sulfate on the plates is not allowed to completely dissolve and turn into oxide and metallic lead, then it forms lead sulfate crystals, which turn into a dielectric film on the surface of the plate, through which ions do not pass, which reduces the operating plate area, and therefore current output and capacity. This process is called sulfation (and the battery that has undergone it becomes sulfated), and only a special form of current issued by smart chargers in desulfation mode can remove this film from the plate. In this mode, a battery whose plates are not too heavily sulfated can be restored to almost its full condition.
Three more unpleasant effects associated with lead sulfate are that the plates of conventional lead-acid batteries with liquid electrolyte are made porous in order to increase their effective ion exchange area. When lead sulfate crystals begin to grow in these pores, over time they grow to such a size that they destroy the metal lead around them, making the plate loose and increasing its volume. Such crystals are even more difficult to dissolve because the metal area of the plate around them decreases and its ability to conduct current deteriorates.
The second effect is that the crumbled plates can form a bridge at the bottom of the cell, and then it (the cell) stops producing current altogether. And the third effect of sulfation is that it is very undesirable to leave an undercharged battery in the cold, since lead sulfate much more readily forms a dense insoluble layer in the cold, and water (which the electrolyte of a discharged battery turns into) freezes in the cold, swelling the battery and damaging its plates .
Battery in a car - what is it?
In the world of cars, the abbreviation AKB means nothing more than a rechargeable battery, or, more simply, a battery.
The battery is one of the most important elements in the design of any car, the very part of the car without which it will not start and, accordingly, will not move.
In the current market conditions for automotive spare parts and components, the most common are three main types of batteries.
The first type is low-antimony batteries, which are the most common lead-type battery, without any additives in the lead plates inside.
The second type is hybrid batteries, which use plates with different compositions. Plus low-antimony and minus calcium-lead or with the addition of silver alternate.
The third type is calcium batteries.
Each of the three types has its own pros and cons. Thus, low-antimony batteries are characterized by the greatest tendency to self-discharge or boiling away of water from the electrolyte solution present inside. But these batteries are not at all afraid of crude charging methods.
Calcium batteries, on the contrary, practically do not self-discharge and do not boil over, but at the same time it is easy to ruin such a battery with several rough charges.
That is why hybrid batteries are considered to be a kind of “golden mean”, which are quite resistant to the phenomenon of self-discharge, practically do not self-boil, and withstand deep charging quite reliably. Accordingly, the average price for such universal batteries is higher than for the previous two types of batteries.
Another quite important consumer characteristic of a battery is the ability to service it. There are serviceable batteries, where it is possible to remove the cover, unscrew the plugs, and, accordingly, get more opportunities for various charging methods, and maintenance-free ones, where the closed design does not imply any consumer intervention in the inside of the battery.
The advantage of maintenance-free batteries is a much smaller percentage of evaporated liquid; the disadvantage is the inability to add liquid to the battery if it does evaporate. At the same time, as a rule, maintenance-free batteries are more expensive than serviced ones, despite the fact that this is not reflected in the service life.
As for the principle of operation of rechargeable batteries, as a rule, the battery contains six working components of 2 volts each, which provide a total current voltage of 12 volts necessary for the operation of the car. The battery has negative electrodes, which are lead sponge, and positive electrodes, which are lead dioxide. When a load is connected to the battery, that is, the electrical circuit is closed, a certain reaction begins between the active substance and the electrolyte. Next, lead sulfate appears on the electrodes. In this case, reduction occurs on the positive electrodes, while on the negative electrodes there is an oxidation reaction of lead or the release of electrons. As a result of these reactions, an electric current arises in the circuit. During battery operation, lead sulfate settles on the plates, and the electrolyte, on the contrary, is depleted.
Another nuance in the operation of the battery, which it is advisable to understand, is the fact that the battery does not produce electricity, but only accumulates it in itself, after which it releases it.
During charging, the electrical form of energy is converted back into a chemical form. This process can be represented by a fairly simple chemical formula, but absolutely all the details of the reactions occurring during charging and discharging have not been sufficiently studied.
The process of charging a car battery occurs with a car electric generator in the car itself. In order to ensure the safest possible mode for charging the battery, a relay regulator is installed between the generator and the battery charged from it, which controls the charging voltage at a level of no more than 14.1±0.2V. However, to fully charge the battery, a voltage of 14.5 volts is required. That is, for a 100% charge, the charging system in the car itself is not enough, therefore, the battery loses its charge after a certain time, and in order to restore it, external chargers will be required.
It is worth considering that in the warm season, the engine of almost any car starts from a 50% charged battery, while during negative temperatures outside, the battery capacity itself is usually halved. At the same time, starting currents also increase during engine starting, which usually occurs due to lubricant thickening in the cold. Thus, with the onset of frost, the probability of not starting the car engine increases significantly if the battery charge level is far from 100%.
Capacitor-type devices are used as external battery chargers.
avtoexperts.ru
Why do batteries die?
As I already mentioned, from too much lead sulfate, that is, from operation in an undercharged state. Or from long-term storage in an undercharged state in the cold - do you hear where I’m going with this? That's right. It is necessary to charge the battery in the winter, and if you want to keep it longer, it makes sense to connect a so-called standby or maintenance charger to it. This device connects to the battery and monitors its condition, maintaining a constant charge level in it, but without causing water decomposition. Sounds risky? Don’t want to leave the charger on in a garage that you don’t visit for six months? Then alas.
Which battery to buy
Primary and probably most serious: beware of purchasing a counterfeit battery . In the markets, they may even give you a partially empty battery - with a reduced number of plates! To prevent this, you don’t need to pay money for the first cheap battery you see, but it is advisable to spend a little time before purchasing on the Internet searching for official battery sellers who provide them with a warranty of at least 1 year and documents, or resort to recommendations professionals from the same web. Of course, someone may say that the best solution is to come to the official service center of the brand and buy the battery recommended by the scooter manufacturer. This is quite accurate, but not the most accessible solution.
If the model of your scooter is more or less common and was produced exclusively for one market (European, American or Japanese), then the trading organization has a chance to look at the price list and choose a battery based on the scooter modification or battery encryption. It is perfectly. But if you are the owner of something unusual, domestic, or the model was sold in different markets in various configurations, then the ruler will help you! Measure the seat, secure the placement and shape of the terminals, and only then look through catalogs on websites or call stores. If the battery you found fits perfectly into place, but has small deviations in capacity, it’s not a disaster; differences of 1-2 Ah are not fatal.
What kills batteries
Undercharging leading to sulfation, which leads to a decrease in capacity and a decrease in current output. But the worst thing is to let the battery run out, and then smoke the motorcycle from the car - it will greedily and gladly take current from the powerful on-board network of the car, but will not be able to cope with it. This is especially true for lithium batteries (more on that below). Frost is also fatal for a discharged battery. Overcharging (from a low-quality, faulty charger or on-board network relay regulator) first of all dries out the battery, and too high a voltage can even decompose the acid (in this case, the battery smells like rotten eggs). But this smell cannot be ignored, and I personally recommend adding water even to supposedly maintenance-free AGM batteries - therefore, I still consider undercharging to be the main enemy of the battery.
Buy a cheap 12V battery
You need to take the purchase of a battery very seriously, since a good battery is a guarantee that you will start the vehicle engine without any problems. But where can I buy a good battery ? We recommend purchasing spare parts only from well-known suppliers, among which the online spare parts store “Chinese” //chery-parts.com.ua/Akkumulyatory certainly stands out.
Why you should buy a battery or other spare parts in this store:
- purchase of spare parts to order
- large range of auto parts and components
- flexible pricing policy
- delivery anywhere in Ukraine
- free consultation
Against the backdrop of all that has been written above, almost everyone chooses the path of minimal resistance, purchasing the most affordable batteries “for one season.” Any battery will be enough for this very “season”, and you will not be disturbed by either winter temperature conditions or electrolyte levels and density. You just need to prepare a little money to buy a new one in the spring. True, there is no guarantee of reliability, but there are a lot of propositions in the lower price sector. Chinese, Polish, and even ours, domestic!
How to check the battery
How to check the battery
Very simple. But you need to understand that checking it in idle mode is not enough. We are interested in its operating parameters.
Set your multimeter to 20V DC (i.e., measure DC voltage between 0 and 20 volts), make sure the probes are in the voltage sockets (there are often other sockets for measuring current, and you don't want to see how your multimeter will burn when it is shorted with the motorcycle battery probes), and connect the black probe to the negative and the red probe to the positive of the battery.
A live battery will show from 12.5 to 12.9 volts, it depends on the technology and additives. For example, for AGM, plates alloyed with calcium are most often used - such batteries boil away less and withstand a slightly higher charging voltage, and therefore their no-load voltage is slightly higher). But don’t worry too much about this, because your motorcycle’s relay-regulator still doesn’t have the slightest idea about what kind of battery is in the on-board network.
A voltage below 12.5 volts indicates that the battery is either undercharged or already dying. Above 12.9 means that the engine has recently been started and the battery has had time to charge and warm up. You need to wait half an hour and measure the voltage again.
Next we start the motorcycle. During startup, the voltage should not drop too much. Here I won’t give true numbers, because they depend on the speed of the multimeter and a whole bunch of other factors, but the guideline is this: if when starting the engine the voltage in the on-board network does not drop below 9 volts, then everything is most likely in order.
Now let's spin the engine up to 3-4 thousand rpm. Here the voltage in the on-board network (that is, at the battery terminals) should be in the range from 13.5 to 14.5 volts. More than 15 is definitely not good, but in the range from 14.5 to 15 it is acceptable, but usually indicates that the battery does not take current well, and therefore is not able to drain the on-board network. If you have access to a service manual for your motorcycle, it may indicate a procedure for checking the battery. There can be indicated two values of engine rotation speed and the corresponding nominal voltage values in the on-board network - for example, at idle and at 5000 rpm.
Some modern motorcycles have smart relay regulators that first allow the battery to restore charge as quickly as possible, and then reduce the voltage to 14 volts to reduce water breakdown.
How to determine that the battery is not being charged in the on-board network? Honestly, the best way is to drive for a couple of hours outside the city, let it cool down for an hour, and then plug the charger into it and see how much charge it takes. Normally it shouldn’t, but if it takes a lot and greedily, it means it’s not charging enough.
Choosing a scooter battery
When choosing a battery for a scooter or moped, you need to consider the following points:
- electrical characteristics;
- form factor and design (dimensions, type of terminals, etc.);
- battery type;
- the presence of additional functions that simplify operation (charge indicator);
- brand.
About the types of scooter batteries, suffice it to say here that they are WET, AGM and GEL. In electric scooters you can find lithium-ion batteries, which act as traction batteries rather than starter batteries. Although starter Li-Ion models can sometimes be found on scooters with internal combustion engines (ICE). More details about the types of batteries for scooters will be discussed in a separate section. Examples of battery lines for scooters from various brands will also be given below. Here we will look at the main parameters of batteries.
Electrical characteristics
One of the key parameters for choosing a battery is its capacity. The other two electrical specifications are rated voltage and inrush current.
The vast majority of scooter models are equipped with a battery with a nominal voltage of 12 volts and a capacity of 4 to 9 Ah. On sale you can find motorcycle batteries with a capacity of up to 30 Ah. However, models over 15 Ah are usually installed on motorcycles and ATVs with a large engine capacity. The starting current ranges from 20 to 90 amperes. In the case of lithium-ion starter batteries, this value can reach 180 amperes. However, in most cases, this current is not required to start the scooter engine.
The capacity of the scooter battery should be greater, the higher the engine capacity. A similar relationship can be seen between the magnitude of the starting current and the volume of the motor.
Dimensions and terminals
In the case of scooter batteries, there are significantly more form factors and types of terminals than for car starter batteries. Therefore, the choice here must be made in accordance with the recommendations of the scooter manufacturer or purchase a battery completely similar to the old one. In most cases, the larger the battery's dimensions, the greater its rated capacity. Common sizes include the following:
- 114×39×87, 115×50×86, 120×61×129, 150×86×94, 151×71×107 mm (models with a capacity of up to 9 Ah);
- 150×87×131, 151×71×130, 151×88×147, 207×71.5×164, 151×88×164, 177×88×154 mm (models with a capacity of 10─20 Ah);
- 181×77×167, 176×87×154, 168×126×175, 165×125×175, 205×85×162, 166×130×175 mm (models with a capacity of 20─30 Ah).
The polarity of the batteries can be either direct or reverse. Scooter batteries also have a wide variety of terminals. Some manufacturers may adhere to accepted standards, while others produce batteries with their own type of mounts. At the following links you can read more information about battery polarity and terminals.
Other
Some manufacturers produce battery models with additional capabilities. For example, this could be a charge indicator.
On car batteries, similar indicators have an “eye” that changes color depending on the state of charge. On scooter batteries, similar indicators can be found in the form of a liquid crystal display.
Below you can see what this looks like using Red Energy batteries as an example.
Is it possible to charge a motorcycle battery with a car charger?
Complex issue. Manufacturers of smart motorcycle battery chargers want you to trust them and be afraid to use products from other brands. But they forget that most motorcyclists are thinking people.
On the one hand, car batteries are much larger than motorcycle batteries and are capable of both delivering and taking much higher currents. Therefore, chargers for them are made more powerful. If the charge tracking circuit of such a charger is implemented clumsily, it is quite capable of overlooking the fact that the motorcycle battery has already been charged and boiling it.
On the other hand, a battery installed in the on-board network of a motorcycle is charged according to the Spartan principle: it is supplied with a voltage higher than its output, and it takes as much current from the on-board network as it can take. Approximately the same process occurs when charging a motorcycle battery from a car charger. If the battery is not completely empty, that is, it is used in normal mode, then the car charger will not do anything particularly new with it.
The main thing is to disconnect the positive terminal from the battery if you charge it with a powerful charger right on the motorcycle. This is because some of them implement desulfation algorithms that try to “break through” the sulfate film with pulses of increased voltage. The on-board network (in particular, the ECU) is often not completely de-energized when the key is removed, and may not evaluate pulses with an amplitude of 18-20 volts.
Charging algorithms
The simplest charger works like this: it supplies current to the battery until the voltage across it reaches the ceiling, then turns off until the terminal is disconnected from the battery. However, this is a very “gentle” mode, which essentially does not allow the battery to be fully charged. The fact is that the maximum voltage on the battery is reached long before it runs out of lead sulfate. Therefore, if the charger stops pouring current into the battery (that is, turns off the voltage supply to it), then under no circumstances will it be able to recharge this battery. One way to get around this problem is to reconnect the battery to it half an hour to an hour after it shows a full charge.
More advanced chargers use various smart and patented algorithms that allow you to use up the entire supply of lead sulfate without boiling the electrolyte - for example, we charge for half an hour, wait for half an hour, then check whether the voltage has dropped, and if so, then add more current, and so on. Duty chargers work in much the same way - they constantly monitor the voltage on the connected battery and recharge it when it drops below a certain level. Note that simply connecting the battery to a constant voltage source is not the best solution, because the ions in the electrolyte do not migrate to the plates very quickly, and it is possible that the electrolyte has already decomposed at the plates, but still contains lead sulfate somewhere in between.
By the way, most standby chargers are directly designed for use with a connected battery. Many are equipped with a special connector that can be brought out somewhere convenient and a charger can be connected to it without the need to attach additional terminals or clamps to the battery terminals. And some on-duty chargers generally recommend connecting it to the battery and leaving it like that, if necessary, simply plugging the charger into a 220V network. There are options for connecting via the cigarette lighter socket, however, it depends on its implementation: if it is connected via a relay, then when the ignition is turned off, the cigarette lighter is disconnected from the battery.
Predicted battery wear
Those who use uninterruptible power supplies know that the batteries in them last 2-3 years, after which they dry out completely. Conspiracy theorists will talk about predictable wear and tear, and Occam's razor supporters will talk about the not-so-smart designer. The truth is that both of these options only work when the main stupid link is the user: in a UPS, the batteries are constantly under voltage, so even a very small evaporation of water over a couple of years leads to complete failure of the battery. By adding water to the battery, you will definitely extend its life. This also applies to motorcycle batteries.
Pros of lithium-ion batteries
The fact is that they lack one of the main disadvantages of lead-acid. The capacity of lead-acid batteries seems quite large, for example 10 amp hours implies that this battery can hold a load of 10 amps for an hour, or 20 amps continuously for half an hour, or 40 amps for 15 minutes at a time. Yes, but not so. 40 amperes is a current quite sufficient to turn over a medium-sized motorcycle engine, and 15 minutes of such work seems like a lot. But in fact, lead-acid batteries are not capable of delivering really high current at any state of charge.
That is, a half-empty lead-acid battery will no longer be able to produce 40 amperes, but the same 10 amperes will be sufficient. Therefore, formally its capacity is large, but its useful capacity (for the operation of the electric starter) is half, or even four times less.
Lithium-ion batteries are capable of delivering powerful currents up to the deepest discharge. Therefore, a 4-amp-hour lithium battery can start the engine more times than a 10-amp-hour lead battery. Plus, lithium batteries are lighter and more compact, even with comparable capacities. But they also have disadvantages, in particular the price.
Is lithium safe?
Of course, these batteries are certified and tested under adequate conditions. The main thing is that their operation occurs in normal modes.
For example, overcharging a lithium-ion battery can cause it to catch fire, so if you're thinking of replacing your stock lead-acid battery with a lithium one, check to see if your motorcycle's electrical system is compatible with lithium. For example, if the voltage in it can exceed 14.6 volts, it’s better not to, since this is the upper safe limit for a lithium-ion motor battery. Once again, the worst thing that can happen to a lithium-ion battery is overcharging.
Such batteries have a much lower self-discharge than lead-acid ones, but in most modern motorcycles there is bound to be some leakage to power the ECU, immobilizer and the like, even when the key is removed from the ignition. This is not to mention the alarm system, which can use up the charge of even a full lead battery in a couple of days if it is noisy or windy outside, or the feedback signal is unstable, and so on. Here we come to another point: lithium motorcycle batteries do not tolerate deep discharge and also become dangerous. The third nuance is that it is highly advisable to purchase a special charger for such a battery.
Exploitation
And in conclusion, a few words about the operation of batteries for scooters.
Selecting a memory
To charge the batteries of scooters belonging to the WET category with liquid electrolyte, it is quite possible to use charger models for car batteries. If you have an AGM or GEL type battery, then you need to use specialized devices to charge them.
The problem is that when overcharged (usually at 14.4 volts), gases begin to be released. This is the result of hydrolysis, which releases hydrogen and oxygen. In the case of liquid electrolyte, the gas is gradually released outside or recombined inside using a special system of channels in the lids.
In AGM and GEL batteries, when overcharged, gas will be released directly at the electrode plates, causing the fiberglass or gel to peel off from them. This will quickly lead to battery failure.
The charger (charger) must be able to charge the battery with a current of 10% of the rated capacity. In the case of AGM and GEL batteries, the charger must conduct the charging process according to a special algorithm that does not allow the release of gases on the electrodes. Typically, recommendations for a charger can be obtained from the manufacturers of batteries or vehicles of this type of battery.
Below are examples of scooter battery chargers.
Types of Lithium Ion Batteries
There is some confusion with the term "lithium-ion" - it describes the technology rather than the specific chemistry of the battery. To make matters worse, different lithium-ion batteries have different cell voltages, but this information can help you understand what type of battery is used in a particular device (including a motorcycle).
All lithium-ion cells are divided into two groups. The nominal voltage in the first is 3.2-3.3 volts, and in the second - 3.6-3.7 volts.
Motorcycle batteries built on lithium ferrophosphate (LiFePO4) technology, also known as iron phosphate or nanophosphate, consist of four cells with a nominal value of 3.2 volts, giving a total of 12.8 volts and charging up to 14.4 volts (maximum - 14.6 volts).
Some manufacturers, for marketing reasons, state that their batteries have a nominal cell voltage of 3.3 volts (and together they then give 13.2 volts), but the LFP or LiFe marking will tell an understanding person that this is still the same 12.8- volt LiFePO4.
There are other lithium-ion battery chemistries, such as lithium cobalt oxide, lithium manganese, or even a combination of the two known as lithium polymer (the cells in these batteries are soft and can be molded into different shapes in the factory), but they all have a nominal cell voltage equal to 3.6-3.7 volts. Nowadays, 3.6-volt cells are almost never found, but high-voltage lithium-polymer cells with a nominal value of 3.85 volts can be found. Cells with a voltage of 3.7 volts should be charged with a voltage no higher than 4.2 volts, and at 3.85 V - no higher than 4.35 V.
However, these are not used in motorcycles. Mainly because three of these cells provide 11.1 volts (such a battery can be charged up to 12.6 volts, higher is dangerous), and four - 14.8 volts, which is outside the permissible voltage range for standard 12-volt motorcycle electrics . However, three- and four-cell batteries are used in jump starters, and three-cell batteries have a protective board built into the positive wire that prevents the flow of current from the on-board network to the jump starter to avoid overcharging and overheating.
No lithium-ion technology can withstand overcharging and can ignite if overheated.
Lines of scooter batteries from some manufacturers
Below is a brief look at the range of batteries for scooters from well-known global brands.
Varta
Varta's scooter battery offerings include AGM, GEL and WET models.
- Powersports AGM;
- Powersports Freshpack;
- Powersports GEL.
Bosch
Bosch offers two lines of batteries for scooters.
Exide
The Tab company presents various models for motorcycle equipment in the Moto line.
- Standard Conventional;
- High Performance;
- Maintenance Free;
- Factory Sealed Activated (AGM);
- Gel (GEL).
Mutlu
The Turkish manufacturer offers batteries for scooters and other motorcycles under the Golden brand. They are supplied dry-charged and with a kit for filling electrolyte.
How does a LiFePO4 motorbattery work?
Each cell contains an anode made of carbon, a cathode made of lithium ferrophosphate, and between them is an electrolyte made of lithium perchloride. In a discharged state, all the lithium is in the cathode and electrolyte, and in a charged battery, lithium ions move to the carbon anode. It's porous, so lithium ions fill those pores, and the battery is charged when they're all filled.
When the battery discharges, lithium ions leave the anode and are directed to the cathode, simultaneously creating an electromotive force between them and transferring energy through the flow of electrons through the connected load. Looks simple? But there are nuances.
When discharging, you should not completely empty the carbon anode, and when charging, you should not direct more lithium ions to it than enters it, and it is also undesirable to dissolve the lithium cathode. During overdischarge, when a deficiency of lithium ions occurs in the carbon anode, it begins to collapse as the walls of its pores become brittle. When overcharging, two troubles occur at once: at the cathode, pores capable of emitting lithium ions close, and at the anode, excess ions collide with carbon and heat it, which can cause it to ignite.
Unlike lead-acid batteries, it is better to keep lithium-ion batteries undercharged (since a fully charged battery is vulnerable to overcharging), but it should not be allowed to overdischarge below 30% - 13 volts, in other words.
Limitations of Li-ion Batteries
With a lot of advantages, lithium-ion batteries for a motorcycle are not an absolute blessing. Usually you need a good reason to replace lead with lithium: they have excellent starting current, but they really don't like to work in the cold, they are light and good for sports driving, but have either a small volume or a significant price tag. And they are also not at all suitable for motorcycles in which small consumers operate with the ignition off - for example, trackers or alarms. For tourism, when weight and volume do not impose critical restrictions, it is better to choose a high-quality AGM battery.
Which memory is better to use?
When purchasing a scooter or moped, it is strongly recommended to read the operating instructions. It describes which batteries are suitable for the selected model and which chargers to use.
Do not try to charge the battery of a charger that is not suitable for this type of battery.
Do you have a scooter or moped? Tell us in the comments what kind of battery you use and how much you like it. This will help make the site content more complete and useful.
Source
How to charge a lithium battery
Only with a special charger for lithium batteries. If the battery can be recharged safely from the on-board network (the voltage of which does not exceed 14.6 volts), then in chargers for lead batteries there may well be voltage peaks that can explode a lithium battery. Moreover, its charge level must be carefully monitored to prevent it from falling below a critical value. If this does happen and the voltage drops below 12 volts, then the initial restoration of the anode should occur with a very low current until the battery begins to take a charge normally, reaching a voltage of 12.8 volts. Conventional lead chargers cannot provide anything similar.
Some (but not all) lithium batteries have a built-in protection board. Such boards are called BMS (battery management system) and provide protection against overcharge and overdischarge by turning off the battery output when unsuitable conditions are detected, and BMS also provide cell balancing (equalizing the voltage across them for a more uniform charge and current output). If the BMS has disconnected the battery output, then you can reset it using a special lithium charger - it determines that the correct voltage source is connected to it and connects the battery back.
So, after spending on a new high-tech battery, don't forget about a charger for it. It will be unprofitable and even dangerous to manage with just the on-board network of a motorcycle.
How to extend the life of a gel battery
To extend the service life of your gel battery, it is enough to reduce the output voltage on the charger to 0.3 A. Because of this, the full charge period will increase to 24 hours, but the loss of battery volume will be kept to an absolute minimum. It is important that the electrical voltage during the process does not exceed 15 volts (otherwise the gel battery will simply swell from the inside). The same method can be used to resuscitate and restore a scooter’s gel battery after it has been completely discharged (which, as we wrote above, should be avoided at all costs).
The battery weakens over time, meaning its efficiency decreases and wear increases significantly. Thus, the time it takes to fully charge a battery is directly proportional to the age of the battery itself. A sign that the battery is fully charged is the release of gases in the form of bubbles. You can see this on batteries whose casing is made of transparent plastic. If the so-called “boiling” begins to occur during the first minutes of charging, the battery is faulty. In this case, it is better not to “reinvent the wheel” and buy a new battery.
Let's move directly to the situation when it is necessary to charge the scooter battery from a car charger. Basically, car chargers provide too much current, which is not suitable for a scooter battery. And in most cases it is not possible to adjust the required voltage. What to do in this case? – as an option, you can connect a light bulb to the circuit between the charger and the scooter’s battery. The light bulb should be 12 V, and its power should be 5 Watts. Thus, the question “can a scooter battery be charged with a car charger” becomes clear.