000_moto_0511_076
Let experienced motorcyclists and motor repair professionals not be surprised that I write about well-known truths.
It is also useful for experts to refresh their memory, but the main thing is to protect beginners from misunderstanding the processes occurring with a motorcycle, and as a result, from costly mistakes. Let experienced motorcyclists and motor repair professionals not be surprised that I write about well-known truths. It is also useful for experts to refresh their memory, but the main thing is to protect beginners from misunderstanding the processes occurring with a motorcycle, and as a result, from costly mistakes.
The abundance of design variations on the theme of friction between a pair of disks sometimes causes confusion in the minds of those who are just discovering the principles of operation of this unit. The purpose of our material is to protect your heads from this strange condition, and your clutch from its consequences. A properly functioning clutch gives the driver the opportunity to accurately dose the engine torque when transmitting it to the gearbox shaft and further to the wheels. On road motorcycles this is important at the start, when turning on a narrow road and, especially, when driving in city traffic jams. On enduro, the work of the clutch is absolutely invaluable when driving through difficult obstacles.
Clutch wear may be indicated by noise in the crankcase, tight lever squeezing, or vibrations. But none of these symptoms alone is a death sentence. For example, noise may be normal for a given model of motorcycle; moreover, as a rule, it is produced by gearbox gears rotating without load. Vibrations at the moment of start are more common on completely new motorcycles, when the clutch discs have not yet gotten used to it.
A more serious symptom is clutch slipping: the lever is released, but there is no rigid connection between the engine and the wheels. The motorcycle can move, but as soon as you add gas, the engine speed begins to increase faster than the speed, as if instead of a manual gearbox you have a hydromechanical “automatic”. In the initial stage, slipping appears only in higher gears, but after half a day of active driving the clutch comes to an end. Therefore, at the first sign of slipping, you need to stop. If the drive is cable, check the free play and ease of movement of the cable. Is the cable tension when the lever is released? Tighten the adjusting nut to loosen the cable. It is better to check the free play of the lever on the drive shaft (1-2 mm at the end of the lever) - this way we will at the same time make sure that the cable is not overtightened and does not get stuck in the sheath. The cable cannot go out of adjustment on its own; there must be some reason. If it gets caught on something, such as in the woods, the shell stop may pop out of its recess, creating tension. Therefore, pay attention to how the cable is installed.
catalogue of articles
Today we will talk about the principle of operation of a motorcycle clutch.
One way or another, the principle of operation of a motorcycle clutch remains virtually unchanged on all motorcycles. If you want to troll major Ducati owners, ask why their clutch rattles))) A small excerpt from Wikipedia:
Clutch is a mechanism whose operation is based on the action of sliding friction (friction clutch); designed to transmit torque, smooth gear shifts, dampen torsional vibrations, and briefly disconnect the transmission from the engine flywheel.
Generally, the term "clutch" refers to the component of a vehicle's transmission designed to engage or disengage the connection between the internal combustion engine and the transmission. The invention of the clutch is credited to Karl Benz.
note
The clutch serves to temporarily disconnect the engine crankshaft from the vehicle’s power transmission, which is necessary when switching gears in the gearbox and when braking the vehicle until it comes to a complete stop. In addition, the clutch makes it possible to move away smoothly (without jerking).
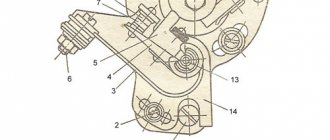
In Figure A we see 1 crankshaft (blue) 2 clutch basket (yellow) 3 gearbox input shaft (green) 4 box secondary shaft (red)
5 stars with chain (purple)
Also, the markings are marked with numbers