masses of units
masses of units
Post by Nitro » Mon Apr 21, 2008 7:05 pm
There is no data on radiators. Accordingly, most of the data is not available, but you can estimate
Power unit 2101 117 kg Lubrication system 2101 3.75 l Cooling system 2101 9.9 l
Power unit 2108 82 kg Lubrication system 2108 3.5 l Cooling system 2108 7.8 l
Power unit 331.7 128 kg Lubrication system 331.7 4.8 l Radiator 2141 5.5 kg Cooling system 2141 9 l
Power unit 1111 66.5 kg Lubrication system 1111 2.5 l Cooling system 1111 4.8 l
KP 2101 26 kg Carter KP 2101 1.35 l
KP 2108 34 kg Carter KP 2108 3.3 l
KP 2141 40 kg Carter KP 2141 3.4 l
KP 1111 24.5 kg Carter KP 1111 1.8 l
Rear hub 2108 assembled 2.5 kg Brake disc 2108 4 kg Knuckle 2108 4.5 kg Caliper 2108 3 kg
Rear hub 2141 assembled? kg Brake disc 2141 4.2 kg Knuckle 2141 5 kg Caliper 2141 ? kg
Front suspension 2101 assembled? kg Front suspension 2108 assembled 55 kg Front suspension 2121 assembled? kg Front suspension assembly 2141 72.5 kg Front suspension assembly 2410 ? kg OKA stand assembly 14.2 kg
CV joint 2141 standard 6 kg
Gas tank 2101 39.0 l = 28.7 kg Gas tank 2104 45.0 l = 33.1 kg Gas tank 2108 43.0 l = 31.6 kg
Wheel 2108 beskam 13.4 kg Wheel 2410 21 kg
Post by zilbergilzen » Mon Apr 21, 2008 9:57 pm
Post by wat » Tue Apr 22, 2008 1:43 am
Posted by Nitro » Tue Apr 22, 2008 9:12 am
Post by zilbergilzen » Tue Apr 22, 2008 6:40 pm
Weight of units (in kg): Engine assembly - 114; gearbox with clutch housing - 32; transfer case - 27.6, rear axle - 60.5, front axle with front wheel drive - 32; complete body without upholstery - 284; wheel with tire - 21.
Post by ForSash » Tue Nov 18, 2008 10:14 am
Maybe it will help someone (don’t take it as advertising, please - this is serious work that has been going on for more than one year)
Historically, we supply components for various pneumatic manufacturers. First of all - for “Litvina”, as well as for “Trekol”. So, this is not the first year we have been collecting information on the weight of spare parts. They themselves hung about 20 thousand pieces of iron in warehouses. About 30 thousand more were found from other sources.
We don’t yet keep it in the public domain in the form of a complete reference book, but you can look at the characteristics of individual parts. In particular, here on the website https://www.avtoall.ru, in our product cards, the weight is marked for the spare part, if it is known to us. (don't take it as an advertisement)
Post by ilmar » Tue Nov 18, 2008 1:27 pm
Posted by ACD » Tue Nov 18, 2008 1:54 pm
Post by ilmar » Tue Nov 18, 2008 2:36 pm
Post by ForSash » Tue Nov 18, 2008 3:28 pm
I am interested in this weight as an average statistical parameter. For example, if an SPZ bearing weighs 150 grams, then the same SKF bearing will weigh the same, because I will simply copy the weight from one to the other. Therefore, I cannot say that each figure given is 100 percent verified. For example, a reference book on weights of spare parts from the ZIL plant was given to me as a terrible military secret, and only after 135 requests. And you can’t keep track of the number of typos that manufacturers come across, even though we try and hang the hardware in warehouses ourselves. Again, there is the question of the weight of the packaging container, the density of liquids, and completeness. Well, in general, there are a lot of subtleties in this seemingly simple matter.
Therefore, it somehow doesn’t even occur to me to post such data in the form of a DIRECTORY. This is sewn into the internal database, rather as a GUIDELINE by which you can estimate whether the weight of the cargo will fit into a 3-ton container or whether you need to order a 5-ton container. Well, something like this, in general.
Source
The weight of the Ural motorcycle engine determines the weight of the motorcycle
For decades now, the Irbit plant has been producing Ural motorcycles - reliable and durable units. Not only our compatriots, but also foreign vehicle users are interested in them. A heavy “Ural” - three decades ago it sounded proud and honorable; even then every second person wanted to become its owner.
The plant produces not only the motorcycles themselves, but also spare parts for them. You can look at the spare parts you need in the catalogue, including engines. When choosing, you must definitely pay attention to the engine, they are:
Before buying a motorcycle, each of us will want to study the technical characteristics of the Ural motorcycle engine. The engine is four-stroke, two-cylinder. The engine capacity is 750 cubic centimeters. If we talk about the gearbox, it is a four-speed one and has a reverse gear. The rear wheel has a cardan drive.
The weight of the Ural motorcycle engine determines the weight of the entire machine; on average, motorcycles weigh 300 kg. The service life of a Ural motorcycle engine depends on many factors, but the most important among them is the service life and rules of operation. Reliability and durability largely depend on operating conditions. Only with good knowledge of the structure of motor vehicles, proper care and timely maintenance can you count on reliable and trouble-free operation of the machine.
Peculiarities
Some models have hydraulic brakes. It is located at the rear of the wheel on the hub and provides confident braking even at high speed. The style of the bike is adjusted to wartime, especially the mirrors and fuel tank.
The engine of the Ural, a motorcycle whose characteristics do not differ only in power, has a number of advantages. Good cross-country ability due to the force commensurate with the mass allows you to easily move on loose or even wet soil. Therefore, movement in forested areas will not be difficult. Moreover, the Irbit plant provided excellent resistance to climatic conditions. The engine starts even at -30 degrees. However, in hot weather, prolonged use may cause overheating. In such cases, motorcyclists install forced cooling of the motorcycle engine.
Specifications
In the Urals, the technical characteristics depend on the specific model, of which there were many. Being, according to the official classification, a heavy motorcycle, this model was equipped with a side trailer and had a solid length of the frame and chassis as a whole.
Engine
On early models, the engine capacity of the Ural motorcycle reached 750 cubic meters. cm, but on the M67 it was reduced to 650cc . Power is 36 horsepower on later versions and 32 on early versions . boxer motor weighs a lot, and dismantling it requires considerable force, so this operation is definitely not possible to cope with alone.
Transmission
All Urals were equipped with a 4-speed gearbox with reverse gear , which was activated by a separate lever. The mediocre reliability of the gearbox led to the fact that many owners replaced it with one from the Dnepr, which was distinguished by a less reliable engine, prone to cranking of the liners, but at the same time a less problematic transmission.
Chassis and brakes
The recipe for the Soviet monster is simple - more iron! A steel frame , spoked tube wheels, toothy tires for dirt roads, a primitive but extremely reliable suspension - this is a completely comprehensive characteristic of the Ural chassis. The brakes were mechanical, drum , so their efficiency cannot be called high. There is no fuss with spring-oil shock absorbers either; even without maintenance, they can feel great for years.
Electronics
There are a minimum of wires in the Urals; 12-volt battery is used . It is worth immediately replacing the armored wires and spark plug caps with better ones, since the caps, exposed to bad weather, heat up from the cylinders, and after driving through a puddle they cool down sharply and therefore often crack. Rubber models instead of plastic ones have proven themselves well.
Weight and dimensions
The weight of the Ural motorcycle without a sidecar is about 220 kg , and a hundred kilograms more with it. By modern standards, its mass cannot be called large; many cruisers weigh one and a half times more. And it’s worth remembering that, due to the presence of a side trailer, the Ural is comparable in width to a small car, so you can’t fit it between the rows.
Controllability
The Ural M 67 with a side trailer is extremely difficult , and it is not recommended . When turning, you need to slow down, as a three-wheeled motorcycle has a tendency to tip over. And without a side trailer, it can reach speeds of up to 110 km/h , and in this case it is much easier to control.
Fuel consumption
The refueling volumes on all modifications of the Urals are almost the same, the M67 was no exception. The tank capacity is 19 liters , which provides about 200 km of travel without refueling . The engine was originally designed for AI-76, so you can safely fill it with the cheapest gasoline.
Characteristics:
Overall dimensions, mm
Motorcycle base (distance between wheel axles), mm 1100
Ground clearance at full load and normal tire pressure, mm 150
Maximum speed, km/h 95
Maximum load, kg 255
Average operating fuel consumption per 100 km when driving in various road conditions with variable load, l 6
Type Four-stroke, carburetor, two-cylinder, opposed cylinder, air-cooled
Working volume, cm3 650
Cylinder diameter, mm 78
Piston stroke, mm 78
Compression ratio 7
Maximum power, hp 32
Maximum power, kW 23.5
Crankshaft rotation speed at maximum power, rpm. 5000-5200
Maximum torque. Nm 47
Carburetor K-301 G
Air cleaner Combined inertial contact-oil filter with two-stage cleaning
Transmission
Clutch Dry double-disc, driven discs with linings on both sides
Cardan drive Cardan shaft with elastic coupling and joint on needle bearings
Final drive Pair of bevel wheels with spiral teeth, gear ratio - 4.62
Gearbox Four-speed, with gear ratios in 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th gears 3.6; 2.28; 1.7; 1.3, respectively
Electrical equipment
Ignition system Battery
Battery 3MT-12
Ignition coil B201
Chassis
Frame Tubular double closed type
Front wheel suspension Telescopic fork with double-acting hydraulic shock absorbers
Rear wheel suspension Lever on double-acting spring-hydraulic shock absorbers, adjustable in height
Front wheel travel, mm 140
Rear wheel travel, mm 90
Tire size, inch 3.75-19
Brakes: Shoe brakes, with friction linings on the front and rear wheels
Transmission
On the M 61 and M 62 a clutch is installed, similar in design to the K 750 clutch, but the K 750 clutch is adjusted by one adjusting screw screwed into the clutch release lever, and the M 61 and M 62 clutches by two screws: an adjusting screw in the release lever and a shell stop screw cable screwed into the crankcase bracket.
Cardan and final drive diagram.
The power transmission gearbox of the Ural M 61 and M 62 motorcycles is the same in design as the M 72. True, there is not much difference, the M 62 differs from the M 61 only in the design of the shift couplings, the secondary shaft and its gears.
The cardan transmission is identical in design to the K750. The rear gears of the M 61, M 62 and K 750 are the same, with the exception of the crankcase covers: for the M 61 and M 62 motorcycles, the crankcase cover is made integral with the right suspension bracket, and the cover has an oil filler hole.
History of the development of the model design
The Ural M 62 motorcycle, 650 cm cubed, was created in 1961 by the Irbit Motorcycle Plant on the basis of the M 72M motorcycle.
After the Irbit plant created a new forced overhead valve engine and began installing it on the M 72 motorcycle, a transitional model appeared - the M 61.
The M62 motorcycle is a modernized model of the M 61 and differs from it in the design of the power transmission, chassis and ignition system devices. The main technical parameters of the engine remained unchanged.
The engines are overhead valve and were manufactured on the basis of the M 72M engine, therefore only their distinctive features are described in comparison with the design of the M 72M engine.
The crank with connecting rods is an integral unit, which differs from the corresponding unit of the M 72M engine in the length of the connecting rod and the distance from the axis of the axle to the axis of the crank pin.
A second oil scraper ring is installed on the lower part of the piston skirt.
The cylinders are interchangeable and in the upper part have four holes for the head mounting studs and two holes into which the pusher rod tubes are pressed.
To drain oil from the valve box into the crankcase, there is a tube passing through the cylinder ribs.
Diagram of the gas distribution mechanism of the M 62 engine.
The gas distribution mechanism of the described engine is an overhead valve mechanism, which is its fundamental difference from the M 72M engine.
The valve disc diameter is 35mm, the stem diameter is 7.5mm and the overall valve length is 91mm. The valves move in guides pressed into the body of the cylinder head. The gap between the bushing and the valve stem is 0.05-0.1 mm.
The camshaft has four camshafts, which differ from the cams of the M72M engine shaft in their shape and location, which makes the camshafts not interchangeable.
Tips with a hemispherical recess are pressed into the body of the pushers.
The thermal gap (0.1 mm) between the valve stem and the rocker arm is adjusted with the valve box cover removed.
Lubrication system
Valves and rocker arms are splash lubricated. Through holes located at the end of the pushrod guide bushings and the rod casing, oil enters the cylinder heads and is sprayed there by the valve springs.
Supply system
The M 61 engine has two K-52 carburetors, and the M 62 engine has two K-38 carburetors. Two K-37 carburetors can be installed on the M61 motorcycle engine.
Return to contents — ↑
Repair and tuning
Close to 100% maintainability and huge scope for tuning are the strengths of the Urals . But all this will require a garage, a lot of tools and even more free time.
Repair
The Ural motorcycle requires attention often, and breakdowns happen from time to time. To avoid them, the bike needs to be given the closest attention, often servicing the cardan, adjusting valve clearances, setting the ignition correctly and performing other service operations.
Spare parts
They are available and inexpensive, but the quality varies from acceptable to extremely poor. The mediocre quality of spare parts is one of the reasons for frequently occurring problems.
Controlling a motorcycle Ural M 72
The Ural M 72 motorcycle is controlled by mechanisms located on the steering wheel and having a manual drive.
In addition, there are a pair of brake pedals and a gear shift lever.
Manual control mechanisms include: throttle handle, front brake lever, clutch lever, combination shifter.
The gas handle, located on the right half of the steering wheel, is connected to the carburetors using flexible cables. To increase the engine speed, you need to turn the throttle towards yourself, and to decrease it away from you.
The front brake lever is hinged on a bracket on the right side of the steering wheel and connected to lever 24 by a flexible cable. To brake the front wheel, the front brake lever must be pressed against the steering wheel handle.
The clutch lever is located on the left handlebar and is connected to the clutch lever 19 using a flexible cable. To disengage the clutch, the clutch lever should be pressed against the steering wheel handle.
The combined shifter is designed to force the ignition advance, switch the headlight light and turn on the electric signal.
Repair, disassembly, assembly and video of gearboxes of heavy Ural motorcycles
In 2022, the Ural company offers motorists only two models for purchase - Ural Gear Up 2022 2WD and Ural City. This is a rather expensive equipment that has found the bulk of buyers in the USA and Canada. In the CIS, few fans of two-wheeled “iron” horses buy new motorcycles from IMZ. The main reason is high cost. The price tag starts at 798 thousand rubles. It is justified by the manufacturer’s widespread use of imported components and the small number of units produced. Plus, many consider Ural motorcycles to be morally and structurally obsolete. However, the manufacturer is constantly improving its developments, improving the characteristics of the engine, gearbox and other important components. In this article we will talk in detail about the Ural gearbox.
Chassis
The M62 is equipped with a telescopic fork with hydraulic shock absorbers and internal springs. The difference between this fork and the M72 fork is a different spring arrangement and a slightly different design of the fork leg shock absorber.
Each shock absorber consists of a housing, a rod 11 with a piston 17, a lower guide and a housing nut. The shock absorber body is placed inside the fork leg tube. Holes for oil passage are drilled in the lower part of the housing.
The piston has a disc-shaped shape. The edges of the piston fit tightly to the inner surface of the shock absorber body.
The shock absorber tube nut is a cup with a calibrated hole in the center. A rubber buffer is installed inside the nut to protect the piston from sudden impacts.
The shock absorber body moves along with the tips of the fork stays, and the rod and the lower guide rod with the piston are stationary
A fork spring is screwed onto the spiral groove of the shock absorber body nut, the upper end of which is screwed onto the spring tip mounted on the rod and clamped between two nuts.
When assembling the front fork, you must ensure that there is a gap of 0.2-0.5 mm between the upper tip of the spring and the nut locking the tightening nut of the fork leg tube, ensuring free rotation of the tightening nut with the rod.
M 62 front fork diagram
The rear suspension of the chassis consists of two identical units, does not have hydraulic shock absorbers and is installed in the rear frame brackets.
Advantages and disadvantages
The strengths and weaknesses of the model are obvious, and they are inextricably interrelated. The archaic and outdated design half a century ago is unreliable, but thanks to its simplicity bordering on primitivism, it is easy to maintain and repair.
Advantages
- Quite high power compared to most other Soviet motorcycles.
- Huge scope for tuning . What craftsmen don’t install on Urals, from the injector to the fifth gear!
- Total maintainability . The bike can be repaired no matter what happens to it. Always.
- Undemanding to the quality of gasoline.
- Short service intervals . Valves require frequent adjustment.
Flaws
- The deplorable technical condition of most copies.
- Low quality components , which leads to frequent minor breakdowns.
- High fuel consumption .
Dismantling and assembling the gearbox of a Ural motorcycle
To disassemble the gearbox, proceed as follows:
Complete disassembly of the clutch mechanism, gear selection mechanism and kickstarter is allowed only when repairing them - otherwise there is no need to disassemble them.
The Ural motorcycle gearbox is assembled with reverse gear in reverse order. After assembly, the gear shift mechanism must be adjusted, otherwise problems may arise when choosing them.
The gearbox of a Ural motorcycle with reverse speed begins to be adjusted by placing the motorcycle on the stand. Then the 2nd speed is turned on and the pedal is pressed to the 3rd gear. If the ball coincides with the well, adjustment of the lower adjustment screw is not required. After moving from 3rd speed, you need to return to the second and check the alignment of the ball, tighten the upper screw if it does not match. This completes the gear selection adjustment.
The Ural motorcycle allows you to repair the gearbox with minimal effort, thanks to the simplicity of its design, which distinguishes this model from other two-wheeled vehicles.
Electrical equipment of the motorcycle Ural M 72
The electrical equipment of the Ural M 72 motorcycle consists of the following devices and units: a G-11A generator; battery Z-MT-7 or Z-MT-14; relay-regulator RR-31; ignition coils IG-4085-B; breaker-distributor PM-05; spark plugs NA11/11AU; FG-6 headlights, lighting lamps, signal, switches and warning lamp.
The spark plug NA11/11AU is a collapsible type, consisting of: uralite insulator 1; central electrode 4; steel body 2; side electrode 5; insulator nuts 3; two copper gaskets 6; one copper-asbestos gasket 7. The central electrode is covered on top with a carbolite tip 5. The spark gap between the central and side electrodes should be 0.7 mm.
The FG-6 headlight consists of a housing 1, a rim 2 with a lens, a reflector 3 with a double-filament lamp 4 and a parking light lamp 5. The headlight housing contains a central switch 6, a high and low beam switch 7, a speedometer 8, a warning lamp 9 and a fuse 10 The various positions of the central switch are switched on using key 11. There are wire holders on the sides of the headlight housing.
Electrical diagram of the M 72 motorcycle.
1 – double-filament lamp; 2 – ignition key; 3 – fuse; 4 – headlight; 5 – central switch; 6 – reflector wire to ground; 7 – high voltage wire; 8 – candle; 9 – high voltage wire; 10 – ignition coil; 11 – side lamp; 12 – signal; 13 – wire for the rear light of the stroller; 14 – lamps for the rear light of the stroller; 15 – motorcycle taillight lamps; 16 – brake light sensor; 17 – relay regulator; 18 – generator; 19 – battery; 20 – low voltage wires; 21 – battery ground wire; 22 – breaker; 23 – distributor; 24 – high voltage wire; 25 – connecting wires of the breaker with the ignition coil; 26 – signal button; 27 – signal wire; 28 – ignition timing lever; 29 – light switch cable; 30 – light switch; 31 – control lamp; 32 – parking light lamp; 33 – speedometer lighting lamp; 34 – motorcycle-sidecar wire connector; 35 – wire for the rear light of the stroller; 36 – wire for the rear light of the stroller; 37 – Sh, Z and B – relay-regulator terminals.
Owner reviews
A powerful unit with decent performance characteristics, in the right hands can live forever, or as long as there are spare parts. Considering how many opposition pieces were riveted in the USSR, there is every chance of passing it on to one’s grandchildren as an inheritance. Anyone who says that this is a bad spender simply does not know how to handle it. Igor, Smolensk.
I started my two-wheeled life with a stroller, like many, and rode until I earned money for an old Honda Steed. When I sold the stroller and switched to a Japanese one, I drove it once and realized that when I go to hell, part of the torment will be credited to me there))) Ivan, Tver.
In stock condition, it’s trash, killed by a disregard for it. With the right approach, the motorcycle is reliable and durable, it will go anywhere, there are enough horses and torque, it can be repaired with a hammer and a screwdriver, and it will eat any gasoline. If you put survivability at the forefront, then Uralei has no competitors except old Harleys, but here the price of the issue is completely different. Anton, Murom.
ATTENTION. Update your browser! Our site does not work correctly with IE 8 and older versions.
I read reviews about the motor from the Urals - they are not very good. Now I went outside, tripped over the engine from my previous motorcycle and started thinking. After all, many people made it so that it would be reliable and powerful, but no one tried to make it light. I read somewhere that more than 130 kilograms of force were removed from the snow, albeit with a 170 propeller. Having looked at the spare parts, of which I also still have quite a few, I came to the conclusion that quite a lot of excess weight can be removed from the engine. The first thing you can safely throw away is the flywheel with the clutch, and this is more than 5 kilograms. The second is a heavy and weak generator. Third, replace the heavy lids with fiberglass ones. You can also cut off excess, unnecessary pieces of a thick engine crankcase, plugging the resulting holes, such as the place where the generator is attached, for example, and the partition of the oil pan. (In the last place of the engine, we see the aviation tendencies of BMW - a separate pan in which oil accumulates - there is an oil pump, there is also a second oil scraper ring - between them a certain amount of oil is stored, which lubricates the cylinder walls of some kind time, preventing oil starvation of the piston, in extreme moments.) In general, you can! I'm throwing it away anyway, so I now have a great opportunity to work with a hacksaw and grinder at my leisure. Of course, if someone has already done this, and it turned out to be a mess, then I won’t waste my energy. It is possible to provide a photo report and the weight of individual pieces of iron.
Malfunctions
One of the features of the power units of Ural motorcycles is the relatively frequent occurrence of minor faults, which must be eliminated quite quickly. Delaying repairs can, and usually does, lead to more serious damage and a significant increase in the cost of repairing them. The main malfunctions and the reasons for their occurrence are summarized in the table.
| FAULT | REASON FOR APPEARANCE |
| The motor does not start. | 1. The fuel supply system is clogged. |
| 2. The spark plugs are out of order (carbon deposits, etc.). | |
| 3. Insufficient compression in the cylinders (valve clearances, rings, etc.). | |
| The power unit operates intermittently. | 1. Uneven fuel supply. |
| 2. Water in the engine or fuel. | |
| 3. The injector jets or nozzles are clogged. | |
| 4. Spark plugs are faulty. | |
| 5. The integrity of the electrical wiring is broken. | |
| 6. Excessively enriched fuel-air mixture. | |
| Extraneous knocking noise in the engine. | 1. Early ignition is set. |
| 2. Motor overheating. | |
| 3. Problems with pistons and rings (loose fit, etc.). |
Description
The Ural motorcycle engine is a two-cylinder, four-stroke, air-cooled power unit.
It is equipped with an electronic fuel injection system (injector) developed by the engineering company ElectroJet Inc. The main power element of the motor housing is the crankcase. Structurally, it consists of:
- the crankcase itself;
- distribution box covers;
- front and rear bearing housings;
- pallet;
- front cover.
The crankcase is cast from high-strength aluminum alloy. Pistons and the junction box cover are also made from it. The cylinders that are installed in the crankcase are cast from special cast iron, which has increased strength. Their internal surfaces are honed before installation, bringing the surface cleanliness to almost a “mirror state”. The materials from which the pistons and cylinders are made during operation form a good anti-friction pair that is not subject to severe wear.
In addition to the parts of the cylinder-piston group, a crank mechanism, a gas distribution mechanism, etc. are installed inside the crankcase and on its outer walls. In this case:
- the camshaft is installed in the upper part of the crankcase on bearing supports, and the pushers are located on its two sides;
- the junction box cover is attached to the front wall;
- the oil filler neck with a plug equipped with a dipstick is located on the left wall;
- the crankshaft is mounted on main bearings installed in the walls;
- From below, the crankcase is closed with a special steel pan, which is used as a reservoir with engine oil.
The assembled engine is installed on the motorcycle frame and secured to it with two studs.
FAQ
- How much does a Ural motorcycle weigh without a sidecar? Not much - about 220 kg. But many owners dismantle the cradle permanently, removing some components and thereby making the bike lighter.
- How many cubes are there in a Ural motorcycle? In older models - 650. In modern ones - 750.
- How much does a Ural motorcycle with sidecar weigh? Weight varies depending on the specific modification, but on average it is about 320 kg.
- Is it comfortable to drive around the city? Not very much, given the solid overall dimensions.
- How much does he really eat? A bike without a sidecar consumes about 6 liters when riding leisurely on the road. But if you drive aggressively, the consumption will be higher, up to 8 liters or more.
Motorcycle Ural M 72
The Ural M 72 motorcycle, in terms of its design and performance qualities, belongs to the category of heavy road motorcycles of the 750 cm cube class.
Produced since 1942 by the Irbitsky and since 1952 by the Kyiv motorcycle factories.
Over the many years of its existence, it has shown itself at its best. A large reserve of engine power in all gears, a large permissible load, significant speed, ease of control, ease of care and maintenance, great wear resistance - all this attracts motorsports enthusiasts to it.
Valuable qualities are due to its successful layout and thoughtful design.
Shock absorption of sprung wheels provides comfort and significantly reduces driver fatigue during long driving.
Reliable lighting allows for fast driving in the dark.
Currently, the M 72 motorcycle has been discontinued, but more advanced models have been created on its basis.
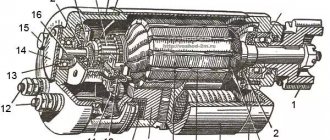
Motorcycle gearbox design
Over the long history of its existence, the Ural gearbox has undergone several global upgrades. Today it is a modern transmission with reverse gear. Ural is equipped with a 2-shaft four-speed gearbox model 6204. Due to the introduction of the second shaft, the dimensions of the unit have been significantly reduced, and productivity has also increased significantly. In this gearbox, the gears are constantly meshed, and due to the fact that it uses fewer gears when transmitting torque, it is characterized by increased efficiency. There are three initial speed gears located on the input shaft, forming a single whole with the shaft. The gears are rigidly fixed on the secondary shaft and its main purpose is to select the desired speed.
The design includes the following parts:
The gearbox with reverse gear is very convenient to operate and repair. She received manual and foot methods of switching gears. Unlike many modern motorcycle gearboxes, the gearbox in the Urals is detachable from the engine, which greatly facilitates motorcycle repairs. The crankcase of the unit is made of aluminum alloy; on the latest models of motorcycles, the crankcase additionally received a removable rear cover, which simplifies the disassembly and assembly of the gearbox. Such a transmission can also be installed on previous Ural models, but this will require installation of the latest modification of the air filter.
Conclusion
Many bikers started out as boxer road veterans found in grandpa's garage. Ural M 67 is an excellent learning desk that will teach you not only how to ride, but also how to maintain a motorcycle, and of course, how to repair it. And after this fiend of the Soviet motorcycle industry, you will be able to handle any other bike! This is the case when starting with a structurally simple motorcycle would be a good idea, especially since a fair number of them can always be found on the secondary market, and for very modest money.
Specifications
| Power: | 36 HP |
| Engine type (cylinder arrangement): | Opposed |
| Number of cylinders: | 2 |
| Engine capacity: | 649 cm3 |
| Cooling type: | Air cooling |
| Transmission: | 4-speed, manual |
| Drive unit: | Cardan |
| Frame: | Steel tubular |
| Weight: | 330 with stroller kg |
| Tank capacity: | 19 l. |
| Maximum speed: | 105 km/h |
Speed indicators
The maximum speed of the Ural Gear Up 2022 2WD is 110 km/h, fuel consumption remains at 7.5 liters per 100 kilometers in the combined cycle.
Ural City 2022 is not inferior in terms of dynamic characteristics: the maximum speed is also 110 km/h, fuel consumption is 7 liters for every “hundred” of kilometers traveled. Riding comfort at high speed is ensured by a front wheel suspension with two spring-hydraulic shock absorbers and a pendulum-type rear wheel suspension with two spring-hydraulic shock absorbers. Both are load adjustable.