Among all the maintenance work on two-wheeled vehicles, adjusting the motorcycle suspension occupies a special place. It allows you to ensure maximum safety for the rider and improve the capabilities of the equipment, since the stability of the motorcycle depends on the correct settings of the chassis. In theory, adjusting the suspension should take a minimum of time and effort, since it only allows you to change six basic parameters. However, practice shows that such work requires long hours and even days spent studying instructions, expert recommendations and test runs. We will tell you how to properly adjust the suspension of a two-wheeled vehicle so as not to encounter problems in any driving mode.
Basic adjustments
The main parameter that you have to change when setting up the suspension is spring preload. It is installed based on the sagging of the motorcycle in two positions - under its own weight and under the weight of the rider. It is worth understanding that the amount of sag directly depends on the length of suspension travel - for a road motorcycle it should be equal to 20–30% of this figure. The sagging of a motorcycle under its own weight should be in the range of 5–10% of the suspension travel. Therefore, for a sportbike with suspension travel of 120–130 mm, the sag value under its own weight will be 7–15 mm, and under the driver’s weight – 25–40 mm.
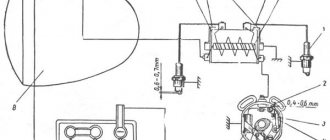
Spring preload adjustment is done using special nuts that are located on top of the main chassis components. On the fork they are located on top of the stay tubes, but on the rear monoshock absorber they are located in its upper part, next to the base of the spring. To adjust the suspension, you will need a standard hex wrench - it is advisable to use a new tool that will not slip, disrupting the optimal parameters.
To set the correct suspension settings, you need to measure the sag of the motorcycle in two positions (racers call these values free sag and driver sag, respectively). First, you should place the motorcycle on a special repair stand or on a large concrete block in order to evenly hang both wheels. Now you need to select the point from which the measurement will be taken. At the rear, it is best to place a mark on any noticeable element of the cladding, and at the front - on the lantern or on the lower edge of the windshield.
You need to measure the distance not to the tire, but to the wheel axle, so that the results are as accurate as possible. After recording the results, lower the motorcycle to the ground and repeat the measurement - you should get a difference of the same 7-15 mm if we are talking about road vehicles. For the third measurement, you will need an assistant to take measurements and take notes.
After first unloading the wheels, place the motorcycle back on the ground, and then jump on it, swinging to achieve compression on both parts of the suspension. Sit up straight and put your feet on the footrests - you can hold on to the wall with your hand so as not to fall. At this time, the assistant should take the required measurements and record the results. The procedure should be performed three times, each time hanging the motorcycle and lowering it down - the cause of the error may be excess friction in the fork, so the end result will be the arithmetic average of these three measurements. Remember that when further adjusting the suspension, you should not touch the preload adjustment, as otherwise you risk making your motorcycle uncontrollable.
In a nutshell about the geometry of the motorcycle.
Before you plunge into the murky world of technical terms outlined in this article, it would be useful to understand the basic logic of the suspension of any motorcycle. The following illustration shows the basic terms you will encounter.
Steering Axis - control axis; Rake Angle - “rake”, the angle of inclination of the fork; Trail - “trail”, the distance on the ground between the wheel axis and a line extended from the axis of the steering column; Wheelbase - wheelbase, the distance between the axes of the front and rear wheels motorcycle.
Sportbikes have a small rake, which means the trail is also not great. A small trail gives less stability and stability, but it makes the motorcycle more easy to control and maneuverable. On the contrary, choppers, cruisers and customs have a large rake. More rake means more trail, which makes such motorcycles stable and stable in a straight line, but they are difficult to steer. Typically on motorcycles the rake fluctuates between 5 degrees. For example, the Yamaha R1 sportbike has a fork angle of 24 degrees, while the BMW K1200LT cruiser has a fork angle of 26.8 degrees.
Fine tuning
We've dealt with springs, now it's time to move on to shock absorbers, which play an equally important role in the operation of the chassis of a two-wheeled vehicle. Modern motorcycles have two damping adjustments, which are responsible for low-speed and high-speed operation of the shock absorber. This is not at all about the speed at which the vehicle moves, but about the pace of movement of the shock absorber rod - low-speed movement corresponds to sagging during acceleration and sudden braking, as well as during turns, while high-speed movement allows you to dampen vibrations caused by driving on a road with poor surfaces.
As a rule, adjusting the motorcycle suspension in terms of damping is done using wrenches of various sizes. The nuts used to adjust the suspension are located on one plug - inside there is one that is responsible for the slow operation of the shock absorber, and on the outside for fast compression. Their parameters may not depend on each other in any way. So, if you want to achieve greater stability, while sacrificing comfort, you should tighten the nut, which is responsible for the low-speed operation of the suspension, as tightly as possible. If you are going to drive on rough roads, you need to unscrew the high-speed setting nut - and, conversely, for track riding it should be tightened almost to the maximum position.
Since getting the damping settings right is such a difficult job, it's a good idea to start with a mid-position setting. If there are no numbers on the nuts, you should tighten them to the maximum position, and then gradually loosen them, counting the number of clicks. When the suspension is in the softest position, you need to divide the number of clicks by 2 and tighten the nuts in accordance with the calculation result. After driving a couple of kilometers with medium settings, listen to your feelings and write them down on paper, dividing them into positive and negative - this will help highlight the main shortcomings of the selected suspension parameters.
The disadvantages of tuning can be very different, but there are only two reasons for their occurrence - too hard or too soft damping of vibrations by shock absorbers. In the first case, you need to unscrew the low-speed suspension nut, and in the second, tighten it. Let's consider in what cases these actions should be performed - for convenience, we will put the main disadvantages of the selected settings in the table:
| Situation | Insufficient damping (nut needs to be tightened) | Excessive damping (need to loosen nut) |
| Front suspension compression | Slow reactions to turning the steering wheel, inability to correct the trajectory when tilting strongly. Rapid sagging of the motorcycle towards the front wheel during sudden braking. Perceptible breakdown of the fork when driving over large irregularities. | Strong rye on the steering wheel. When driving over bumps, shocks are observed that reverberate unpleasantly in the driver's hands. The motorcycle bounces on poor surfaces, making it very difficult to maintain a stable position. There is no sag towards the front wheel when braking. |
| Front suspension rebound | When hitting any bumps, strong shaking begins. In fairly sharp turns, which the vehicle goes through at an angle, it first tries to go onto a wider trajectory, and then returns to the desired line. | When accelerating hard, the front wheel may lose contact with the asphalt surface. When driving over bumps, the fork vibrates strongly and may deviate to the side. When accelerating into a corner, the motorcycle begins to slide outward. |
| Rear suspension compression | On uneven surfaces, the chassis often breaks, which leads to a decrease in comfort. The steering is slow due to the constant sinking of the rear wheel during acceleration. The motorcycle sways quite a lot when accelerating. | When accelerating, the rear suspension of the motorcycle practically does not sag. The rear wheel bounces when driving over uneven surfaces; when cornering, the motorcycle often leaves the chosen trajectory. When accelerating, impacts and other unpleasant sensations intensify significantly. |
| Rear suspension rebound | At high speed, the motorcycle sways strongly, and it is impossible to maintain a stable trajectory. When cornering, the motorcycle bounces, and the first signs of rear wheel skidding appear. | When braking in a corner, the rear wheel begins to slide to the outside of the curve. The suspension is very stiff; when driving over any uneven surfaces, shocks and other unpleasant sensations appear. |
It is worth remembering that setting extreme settings, for example, the hardest or softest, is unacceptable. This means that the motorcycle suspension is already working in extreme mode and its wear will be very high. In addition, the slightest weakening of the springs as a result of changes in the rigidity of the metal will lead to improper operation of the chassis. Therefore, in this case it is necessary to use alternative adjustment schemes.
When is a motorcycle fork repair needed?
Over time, forks become unusable. This often happens due to a polluted environment, dirt, and dust on the roads. Poor road surfaces and harsh, careless driving styles can also cause damage. Often, motorcycle owners seek services after accidents on the roads.
The fork is the element that suffers most often in road accidents. Modern motorcycles are made of ultra-light metals. This allows you to significantly reduce the weight of the product. But, unfortunately, such innovations help reduce the strength of the entire structure. This is why the fork is the most vulnerable element in an accident.
Small defects are eliminated by specialists using special equipment. Well, if the damage is serious enough, then the feathers are completely replaced. Faults such as metal pulling, damage, severe deformations, and dents cannot be repaired.
How to check the fork yourself for bends?
This is very easy to do; you just need to turn the pen in the traverse. If it's easy to do, then everything is fine. Otherwise, it's time to seek help from specialists. Using diagnostic methods and special prisms, they will accurately determine the presence of damage.
Causes of part failure
There can be a lot of problems that arise with a fork. They are usually preceded by the following situations:
- leaking oil;
- failure of oil seals;
- excessive and frequent loads;
- influence of aggressive external environment;
- use of low-quality oil;
- poor quality metal.
How else is the suspension adjusted?
In some cases, you may simply not be able to find the nuts mentioned above for adjusting your motorcycle suspension. It is worth carefully reading the factory operating instructions for two-wheeled equipment - it is quite possible that the adjustment controls are located in a different place, and you simply did not see them the first time. However, there are also motorcycles in which the suspension adjustment is carried out according to other schemes in which adjusting nuts are not used. In addition, they are resorted to when the range of factory settings has been exhausted, and the suspension works correctly only in positions close to the extremes.
First of all, we are talking about moving the fork in the upper yoke - this allows you to increase the stroke by approximately 10-15 millimeters and change the ground clearance. The rear monoshock can be mounted on special spacers - these can be purchased at most motorcycle parts stores. Thanks to this, it is possible to adjust the angles of the suspension, due to which the settings will be fundamentally changed, and you will be able to achieve the ideal settings. In addition, washers can be placed under the fork leg mounts, which also allow you to change the angles and adjust the characteristics of the shock absorbers.
In addition, you can change the stiffness of the suspension by installing other springs - as a rule, this technique is resorted to when the rider’s weight differs from the statistical average of 75 kilograms, which manufacturers use in their work. You can fundamentally change the behavior of a motorcycle with the help of a different oil poured into the shock absorbers. Most motorcycles are initially designed to work with 2.5 or 5W oil.
To increase rigidity, you need to increase the viscosity, which is hidden under the indicated index. At the same time, experts categorically do not recommend filling in new oil that differs in viscosity by more than 2.5 points - this will lead to the impossibility of choosing the optimal motorcycle suspension settings. If necessary, the oil can be mixed, for example, from liquids 5 and 10W you can get 7.5W if you take half of each and shake them in a canister. It is prohibited to mix oil from different manufacturers, as well as used fluid with new fluid - this will lead to the behavior of the motorcycle suspension becoming unpredictable.
Changing the oil of a standard telescopic fork
The general oil change scheme is very simple: unscrew the drain plugs, wait until the oil drains, rinse the fork with kerosene if necessary, and then fill in new oil and put the plugs in place. But alas, practice shows that this procedure primarily depends on the design of the feathers. If the stay has a lower drain bolt, then the front chassis can be serviced without disassembly, but if the fork is of an inverted design or does not have lower drain holes, then you will have to completely disassemble the front suspension structure. Based on this, we divide the oil change process into two types:
Incomplete disassembly of the front suspension: The case is suitable for stays with an end lower or side lower drain bolt. With proper skill, you don’t have to disassemble the suspension at all, but there is always a risk of getting the brake mechanism or wheel dirty with oil, and then you’ll have to do extra cleaning work. It is best to make the replacement as follows: First of all, we clamp the front brake or rest the wheel against the wall, sit on the motorcycle and with the weight of our body force the fork to work 10 - 15 times, this is necessary to warm up the oil, raise sediment and better clean the mechanism. We place the motorcycle on the main stand so that the front wheel is hanging in the air. Remove the front wheel and free access to the upper oil drain bolts from the feathers (the end part of the feather). Using a suitable spanner, unscrew the upper drain bolts (in some cases it may be necessary to loosen the upper clamps). Place a container to collect the oil under the lower drain bolt. Using a spanner wrench, unscrew the bolt and wait until the oil is completely drained. If necessary, rinse the fork with kerosene. We inspect the anthers and seals, replacing them if necessary.
Fill in fresh oil through the top, after tightening the bottom bolt. We tighten the top bolt and mount the wheel and other removed parts.
Off-road suspension adjustment
If you're going to be tuning the suspension on a motocross bike, you're going to have to deal with a lot of adjustments. On such a two-wheeled vehicle, various screws are responsible for adjusting the compression and rebound. Compression is adjusted at the top of the fork or monoshock, and rebound is adjusted at the bottom.
The optimal settings will depend on the surface you drive on most often. If a motocross motorcycle goes on real off-road only occasionally, and spends most of the time on perfectly compacted dirt tracks or even on asphalt, then you need to loosen the nut that controls the compression and tighten the one that regulates the rebound. Thanks to this, you can achieve ideal stability and eliminate steering wheel wobble that occurs when cornering and braking.
Feeling that the suspension very often closes to rebound and often breaks through, many beginners begin to unscrew the compression adjustment nut, greatly weakening it. However, such actions are fundamentally wrong. The problem is that a decrease in compression rigidity leads to a deterioration in motorcycle control - in sharp turns, hitting bumps can cause a sharp jerk in the steering wheel. Therefore, if you frequently drive on roads and forest clearings with potholes, it is worth increasing the compression rigidity and slightly loosening the rebound nut. Knowing how to set up the suspension of a motocross motorcycle, you can easily find the optimal parameters by making only two or three evaluation rides.
Shock absorber
Any spring, if compressed and then released, begins to vibrate. The main task of a shock absorber in a suspension is to dampen (absorb) spring vibrations. The shock absorber converts the vibration energy of the spring into thermal energy (the fluid inside the shock absorber heats up, after which the heat is dissipated).
Properly selected and adjusted suspension components can significantly improve handling. At the same time, a faulty suspension can cause a sharp deterioration in the behavior of the motorcycle. The suspension must always be in good condition.
Selection of optimal parameters
As a rule, suspension tuning on a motorcycle is done empirically - this means that in order to select the optimal parameters, you should listen to your feelings during test rides, identify shortcomings and try to correct them using the recommendations given in the article. If your actions have led to a worsening of the situation, it is worth restoring the factory settings. To do this, you need to open the instructions - it will tell you what specific position of the nuts you need to set when adjusting. There are also motorcycles in which the ability to adjust the suspension is simply not available - this applies to small-scale American equipment and old Japanese models. In them, the settings can be changed by installing different springs and shock absorbers, as well as using oil with a different viscosity level.
What's next?
YOUR ACTIONS TO INCREASE COMFORT WHEN DRIVING AND ADDITIONAL SAFETY
You have completed the road test.
In the most favorable case, thanks to the adjustments of the shock absorbers and front forks, you have achieved a good result. If, after performing a road test and adjustment, you are not satisfied with the result, this can usually be due to three reasons:
- Your shock absorbers and front forks are of good quality.
- Components of your shock absorbers and front forks are worn out.
- Your shock absorbers and front forks may not be well adjusted.
The fundamental solution to your problem may be to simply replace your shocks and front forks with a set of high quality, adjustable shocks and front forks (or front fork springs) that allow you to fully achieve your personal preferences.
You can ask us any question about WP Suspension products.
The HERMIT company is the official WP Suspension service center in Russia and has complete sets of shock absorbers for each motorcycle. If you already have WP Suspension shock absorbers and front forks, you can fully experience the benefits of this user-friendly product, which does not always require a complete shock absorber replacement. As a result, by replacing shock absorber components you can solve problems at a minimal cost.
An additional benefit of WP Suspension shock absorbers is less wear in severe conditions, resulting in longer service life. In front forks from other manufacturers, you can use springs made by WP Suspension as an excellent replacement. We can explain to you in detail which components can be replaced to solve your problems.
By selecting high-quality and necessary products from WP Suspension, you achieve optimal safety and comfortable operating conditions.
Now back to work again!
You have now completed your road test and have made accurate notes on the behavior of your motorcycle. Now you are able to solve your problems.
You need to feel that adjusting the suspension and damping is a very delicate job. When it comes to settings, you do not have 100 percent confidence in your capabilities, it is better to entrust this work to professionals, but with documentation as a guide, you can achieve optimal settings (in the case where adjustment is possible in principle, since in the presence of shock absorbers certain types of adjustment may not be possible at all, and on some types of motorcycles only the initial load and rear suspension can be adjusted).
Let's assume that you managed to adjust your shock absorbers, but the road test still does not give acceptable results. What can you do then.
It is possible that the existing suspension components are worn out or simply of poor quality. If this is the case, then you should contact us, and we can advise you on something.
Sometimes replacing suspension elements is the only possible solution. In this case, you can go quite far, for example, completely replacing the front forks with new, ultra-high quality ones, but, fortunately, impressive results can be achieved at much less cost. An excellent alternative, for example, would be to replace the springs with WP ProLine springs. If the rear shock absorber (or both rear shock absorbers) are not working well, then the only possible solution is to install a new one or new units.
If you are not a jack of all trades by nature, then we recommend entrusting this work to specialists.
Individual work
When replacing shock absorbers with parts manufactured by WP, you can do this taking into account your preferences. WP shock absorbers are usually of a higher quality and, very importantly, WP Suspension has a full range of parts for every motorcycle model. This is exactly what is vital to guarantee optimal safety and comfort.