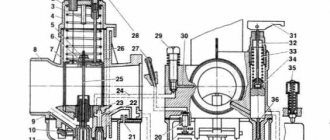
How to increase “horses”? (We boost the motorcycle engine). - Technical zone. - Catalogue of articles
| Many novice motorcyclists are concerned about the topic of boosting the engine of their two-wheeled horse. To have more power, to move faster, and show off - where would we be without them! So the boys begin to play tricks with the engine. It’s good if there is someone experienced and knowledgeable nearby who can advise and warn against serious mistakes. Otherwise, “boyish tuning” gives zero, and sometimes negative, results. In one article, of course, it is impossible to consider all the issues of boosting engines, but let’s try to at least outline the main directions. So, let’s first decide what we’re boosting. There is no particular point in considering Japanese motorcycles - there is a very wide field of activity here, but it all comes down mainly to money. For the “Japanese” there are many kit kits and tuning parts. In order to apply them on your motorcycle, it is better to contact specialists, because... Japanese motorcycles are quite balanced devices, and changing one part or parameter may not give the expected result. Those. an integrated approach is needed. If we are talking about Chinese technology or the domestic Dnepr (Ural), then the situation is different. For the “Chinese” there are practically no ready-made solutions, but for domestic motorcycles there were, but they were all used in sports in the 60s - 80s of the last century and many are outdated. So don’t rush to grab a file and run to the garage. First we have to sit down to the theory. Question - what engine parameters can we change to increase its power? First of all, this is the working volume. What can be done here with Chinese technology? Please note that the Chinese produce engines of various sizes, which are based on the same crankcase. For example, 150cc and 170cc. Those. By installing the second CPG on the crankcase of the first, we get a slight increase in power. Sometimes, to increase the working volume, the cylinder diameter is not increased, but a different crankshaft is used, which gives a larger piston stroke. Check and calculate - perhaps by arranging these units, you can get an even larger working volume. But, an increase in one parameter entails an increase in another - the compression ratio increases (if the cylinder head, and accordingly the combustion chamber, remains unchanged). In itself, this also contributes to an increase in power, but it is important that the compression ratio does not exceed the limits of the anti-knock resistance of the fuel used. Just increasing the displacement and compression ratio certainly gives an effect, but it will be incomplete, because the engine power supply system and timing belt were designed for lower parameters and they will “choke” the engine. Accordingly, you need to choose a carburetor with a large diffuser diameter. You may have to experiment with jets, choosing those that give the engine the most power. Another reserve is the design of the timing belt. If there are several camshaft options for your engine, compare them. The one with the larger height and fullness of the cams is suitable. This will increase valve capacity and increase valve timing. But here it is also important not to overdo it! Check the geometry of the resulting combination - the valves in it, when opened to their maximum, should not reach the piston. If such a phenomenon is present, then you can remove excess metal from the piston, the main thing is that it has a sufficient margin of safety. The valve return springs must be replaced with stiffer ones - this will increase engine speed. Now you will need to redo the exhaust system - after all, the standard one is also a good “choke” for the engine. That is why forced engines are equipped with direct-flow mufflers. You should also increase the flow area of the exhaust system. Next, after replacing the carburetor, think about replacing the air filter. There are two options here - either use a filter from a larger engine, which obviously has a higher throughput, or install a fashionable “zero”. What is the disadvantage of the second option? Usually what we call “zero filters” are just mesh filters. They filter out about 80% of solid particles, while inertial oil filters, say, 95-98%, and foam rubber up to 99%. Accordingly, the use of a low-resistance filter somewhat reduces the life of the CPG. Now we come to the second side of forcing - reducing the life of the engine. In any case, a forced motor “lives” less, but this drawback can be smoothed out to a certain extent. For example, by increasing the displacement and compression ratio, we increase the load on the crankshaft. What does this mean? Firstly, you cannot use used ones. detail. A new crankshaft takes an acceptable time, but a used one. Most likely he will “die” very quickly. It is better to replace the crankshaft support bearings with double-row ones, and if this is not possible, then at least install new ones of good quality. Increased power worsens the thermal conditions of the engine. For dropsy, this is not critical in most cases. But, if the engine still shows signs of overheating, then it is necessary to upgrade the cooling system. For example, replace a standard radiator with another one of larger volume and area. Scooter engines with forced cooling also have some cooling reserves. The main thing is that the cylinder and engine head are clean - dirt greatly contributes to overheating. Motorcycle “air” engines find themselves in the worst position. There is the following possibility - most Chinese engines can be equipped with oil radiators; for this purpose, oil channels are provided, closed in the “drain” with plugs. These are the ones that need to be used, i.e. equip the engine with an oil cooler. And if the oil cooler is already installed, then it is necessary, as in the case of water cooling, to replace the standard radiator with another one with a larger volume. There is one principle here - increasing the volume of oil in the engine helps to reduce its operating temperature. That is why a tray of increased depth was invented for the Dnepr and Urals. But on the “Chinese” there is no such option, so the volume can only be increased by using a radiator. Another reserve is a revision of the ignition system. This in itself does not increase power (contrary to popular misconceptions), but it allows it to be lost less at high speeds by eliminating gaps in spark formation. This is especially critical for archaic systems of domestic technology. Here, replacing the contact system with a BSZ with a Hall sensor already gives a noticeable result. But on Chinese motorcycles BSZ are used everywhere. Therefore, here it only makes sense to install a microprocessor-controlled ignition system, which will make it possible to increase engine performance in some modes. But this is a topic for another article. Addition to the article: Examples of modifications and boosting of motorcycles. Spare parts for motorcycles and ATVs in stock and to order (from A to O) Spare parts for motorcycles and ATVs in stock and to order (from P to X) Spare parts for motorcycles and ATVs in stock and to order (from C-Y) |
krasnyluchmoto.ucoz.ru
Story
Production began in 1977, this truck is still in production today.
The main difference from the Ural-375D line is the presence of a diesel engine.
Initially, the Ural-4320 was equipped with a KamAZ-740 engine, but as a result of a fire at the KamAZ engine plant in 1993, supplies of this engine ceased, and YaMZ-236 and YaMZ-238 engines from the Yaroslavl Motor Plant began to be used. Initially, modifications with the YaMZ-238 engine were externally distinguished by a longer engine compartment, and vehicles with the YaMZ-236 engine retained the same engine compartment as those with the KAMAZ-740 engine (the differences are that vehicles with the YaMZ-236 have an air filter on the right wing). Since the mid-2000s, all cars, regardless of engine model, have been produced with an extended engine compartment.
Since the mid-1990s, a wide bumper with headlights appeared on the Ural-4320 and Ural-5557, and plastic plugs appeared in the wings, at the old headlight mounting points. However, cars with a narrow bumper and headlights in the wings are still supplied exclusively for the needs of the Ministry of Defense, by special order.
Since 2009, a new cabin with a fiberglass front tail began to be installed on cars in the series.
Increasing the power of the Ural engine - Tuning - Ural and Dnepr - Catalog of articles - Moto-rus
| Many motorcyclists dream of increasing the engine power of their Urals. But not everyone understands what should be done for this and what consequences boosting the power unit can lead to. Firstly, work related to changing its design can only be carried out by a very qualified mechanic and with the availability of machine tools. Attempts to do something in a hurry are doomed to failure. Secondly, the engine, boosted according to sports-cross models, has a torque characteristic of little use for economic purposes, shifted to the high-speed zone and unimportant fuel efficiency. So before you start changing anything in the factory design, think carefully about whether you can handle a very serious job and whether you need it. This material is a generalization of the experience of reconstructing the engines of serial road motorcycles M-63, M-66, M 67-36, as well as serial sports engines M-63K (motocross) in preparation for competitions and runs by athletes of the DOSAAF society. ATTENTION! Boosting an engine may be advisable only if it is practically new or has undergone a thorough overhaul. If your power unit does not meet the specified requirements, then there is a risk of losing what you have. To increase engine power, the compression ratio should be increased from 7-7.2 to 8.5. With this value, you can only use gasoline AI-93, A-95, A-98, “Extra” and the like with an octane number of at least 85-95. It is impossible to increase the compression ratio to such limits using standard pistons from Ural. Therefore, taking into account the data in Table 1, you should select pistons from the MT-8 engine (K-650 Dnepr) with a spherical head. In this case, to prevent the piston from colliding with the cylinder head, it is necessary to chamfer the step formed by the transition of the spherical combustion chamber to the mating plane of the cylinder head, ensuring a gap of at least 1-1.5 mm. To prevent the piston skirt from touching the crank pins, a special cut is milled on it, and the valve seats are changed on the piston bottom, since the camber angles of the latter are different for the MT-8 and M-63 engines (Fig. 1). To check whether the valves are touching the bottom of the piston, strips of plasticine 3-4 mm thick are applied to it, then the cylinder head is completely assembled and the crankshaft is turned. The presence and size of the gap between the valve and the piston are judged by the imprints on the plasticine. It should be at least 2-3 mm. Before installation on the engine, the pistons are weighed, and the difference in weight should not exceed 2 g. When boosting an engine from an M-63K sports motorcycle with cylinder heads trimmed at the factory, metal gaskets 2 mm thick are placed under the cylinders. Between the cylinder and the metal gasket, as well as between the latter and the crankcase, paper gaskets are placed for sealing. When using road bike parts, the gasket under the cylinder can be approximately twice as thin. In any case, its thickness is finally controlled by on-site measurements. The boost stage ends by clarifying the compression ratio in each cylinder. For this purpose, the piston is brought to TDC with the valves closed (end of the compression stroke). The engine is tilted so that the spark plug area on the cylinder head, in which the volume of the combustion chamber is measured, is located horizontally. In this position, spindle oil is poured into the cylinder from a graduated beaker. It is necessary to ensure that the volumes of the combustion chambers in both cylinders (and therefore the compression ratio) are the same. This can be achieved by changing the thickness of the gaskets described above. To improve cylinder filling, it is necessary to reduce the aerodynamic resistance of the intake and exhaust channels. To do this, casting errors in them are carefully cleaned out with rollers, and then polished. The intake and exhaust valve heads are also polished. To ensure a normal service life of the compression piston rings and improve the piston seal, at increased speeds of a forced engine, standard compression rings with a machined internal one-sided chamfer should be used (Fig. 2, a). This allows you to slightly reduce the weight of the rings and reduce their pressure on the cylinder walls. Even better results are obtained by using L-shaped torsion-type rings (Fig. 2, b). To make them, a serial ring is fixed in the chuck of a lathe using a mandrel (Fig. 2, d), then a recess is made. Since it is not always possible to make a new piston with grooves for two L-shaped rings, you can cut one groove for it above the upper groove, right at the edge of the piston bottom. A rectangular ring with a machined chamfer is placed under the L-shaped ring. The lower groove remains empty (Fig. 2, e). When boosting the crankshaft speed, textolite washers are installed under the valve springs to lighten the pushers. Push rods are made of titanium or duralumin tubes with steel tips (Fig. 3). On each cylinder, using a calibration disk mounted on the crankshaft axis, the valve timing is checked according to the data in Table 2. It is better to register the beginning of valve opening using an indicator. Adjustment of the valve timing can be done on the removed cam shaft by filing the cams manually with fine-grained abrasive stones or using a rubber grinding wheel and an electric drill. In this case, it is important to remove the minimum necessary amount of metal in order to preserve the upper cemented layer and distort the overall shape of the cams as little as possible. Their surface must be polished to a mirror shine. Ignition timing is 43 degrees - early, 13 degrees - late. It wouldn’t hurt to replace the standard ignition system with a contactless electronic one installed on the Ural-Solo. Candles can be recommended A 20 DV, A 17 DV from the Zhiguli car, however, due to the large length of the thread, brass washers 8 mm high should be placed under them. If an old engine equipped with K-301 (K-302) carburetors is being boosted, they should be replaced with K-63U (K-65T) with a diffuser diameter of 28 mm and a main jet capacity of 170 cc. cm/min. Carburetors will have to be attached to the cylinders through adapter washers, since the K-301 (K-302) mounting studs are located in a vertical plane, and the holes of the K-63U (K-65T) mounting flange are located in a horizontal plane. A contact-oil air cleaner is completely unsuitable for a forced engine. The best solution is a homemade filter with a paper element from Zhiguli. As a last resort, you can use an air filter with a paper element from the Dnepr motorcycle. The M-63 engine, boosted using the described technology, must develop a power of at least 30 kW (40 hp). According to VNIIMotoprom, with a compression ratio of 8.5:1 and 5900 rpm, the engine power can be up to 33.6 kW (45 hp). |
moto-russ.ru
Model history and purpose
Production of models of the Ural 4320 line began in November 1977. The release of the series in a noticeably modernized form continues at the present time. The predecessor of the car was the Ural 375D, which debuted back in 1961. With this model, the Ural 4320 was unified in many elements. Initially, the car was equipped with a gasoline unit with high fuel consumption (about 40-48 liters per 100 km), which was considered its main drawback. Diesel versions of the truck (with a KamAZ engine) appeared only in 1978. Moreover, their number in the first years of production was limited. However, the plant gradually switched to the mass installation of Kama diesel engines in the Ural 4320. This was the main difference between the first generation of the model and the Ural 375D.
The basis of the design of the Ural 4320 was a supporting frame, providing high strength. Single-ply tires, all-wheel drive and short overhangs ensured good cross-country ability of the vehicle.
In 1986, the truck was updated. At the same time, the appearance of the model has been preserved almost unchanged. The motor range has not undergone any significant changes. The main unit remained the KamAZ-740 engine. It was used until 1993. However, after a fire at the manufacturing plant, supplies of the power plant ceased. Instead, the Ural 4320 began to be equipped with engines from the Yaroslavl Motor Plant (YaMZ-238 and YaMZ-236). Initially, modifications with the YaMZ-238 were distinguished by a long engine compartment; versions with the YaMZ-236 retained the same shape. However, since the mid-2000s, all variations of the Ural 4320 have received an extended engine compartment.
In the mid-1990s, the truck underwent a restyling. The car began to be equipped with a wide bumper with headlights, and plastic plugs were installed on the wings in the previous place where the headlights were attached. For the needs of the Ministry of Defense, cars with a narrow bumper were still produced. In 1996, production of a lightweight version of the Ural 43206 with two axles began.
The next update occurred in 2009. The car has noticeably changed, receiving a modernized cabin with a fiberglass tail at the front. The shapes of the Ural 4320 have become more streamlined. The classic radiator grille with vertical lines on some versions was replaced by a grille with horizontal lines. On some modifications, they began to install the Iveco “P” cabover type from the UralAZ-IVECO joint venture. It was distinguished by an original rounded integral hood. The previous units were replaced with modern diesel engines YaMZ-536 and YaMZ-6565, which comply with the Euro-4 standard.
In 2014, the Ural 4320 series was transformed into the Ural-M series, maintaining most of the characteristics. In the fall of 2015, another modernization took place. Its result was the appearance of the Ural Next series, which was distinguished by a modern GAZelle Next-type cab with a new plastic tail of the engine compartment and improved components.
Increasing the power of the Ural engine - Motorcycle tuning
Many motorcyclists dream of increasing the engine power of their Urals. But not everyone understands what should be done for this and what consequences boosting the power unit can lead to. Firstly, work related to changing its design can only be carried out by a very qualified mechanic and with the availability of machine tools. Attempts to do something in a hurry are doomed to failure. Secondly, the engine, boosted according to sports-cross models, has a torque characteristic of little use for economic purposes, shifted to the high-speed zone and unimportant fuel efficiency. So before you start changing anything in the factory design, think carefully about whether you can handle a very serious job and whether you need it.
This material is a generalization of the experience of reconstructing the engines of serial M-63 road motorcycles. M-66. M 67-36. as well as serial sports engines M-63K (cross) in preparation for competitions and runs by athletes of the DOSAAF society.
ATTENTION! Boosting an engine may be advisable only if it is practically new or has undergone a thorough overhaul. If your power unit does not meet the specified requirements, then there is a risk of losing what you have.
To increase engine power, the compression ratio should be increased from 7-7.2 to 8.5. With this value, you can only use gasoline AI-93, A-95, A-98, “Extra” and the like with an octane number of at least 85-95.
It is impossible to increase the compression ratio to such limits using standard pistons from Ural. Therefore, taking into account the data in Table 1, you should select pistons from the MT-8 engine (K-650 “Dnepr”) with a spherical head. In this case, to prevent the piston from colliding with the cylinder head, it is necessary to chamfer the step formed by the transition of the spherical combustion chamber to the mating plane of the cylinder head, ensuring a gap of at least 1-1.5 mm. To prevent the piston skirt from touching the crank pins, a special cut is milled on it, and the valve seats are changed on the piston bottom, since the camber angles of the latter are different for the MT-8 and M-63 engines (Fig. 1). To check whether the valves are touching the bottom of the piston, strips of plasticine 3-4 mm thick are applied to it, then the cylinder head is completely assembled and the crankshaft is turned. The presence and size of the gap between the valve and the piston are judged by the imprints on the plasticine. It should be at least 2-3 mm. Before installation on the engine, the pistons are weighed, and the difference in weight should not exceed 2 g.
When boosting an engine from an M-63K sports motorcycle with cylinder heads trimmed at the factory, metal gaskets 2 mm thick are placed under the cylinders. Between the cylinder and the metal gasket, as well as between the latter and the crankcase, paper gaskets are placed for sealing. When using road bike parts, the gasket under the cylinder can be approximately twice as thin. In any case, its thickness is finally controlled by on-site measurements.
The boost stage ends by clarifying the compression ratio in each cylinder. For this purpose, the piston is brought to TDC with the valves closed (end of the compression stroke). The engine is tilted so that the spark plug area on the cylinder head, in which the volume of the combustion chamber is measured, is located horizontally. In this position, spindle oil is poured into the cylinder from a graduated beaker. It is necessary to ensure that the volumes of the combustion chambers in both cylinders (and therefore the compression ratio) are the same. This can be achieved by changing the thickness of the gaskets described above.
To improve cylinder filling, it is necessary to reduce the aerodynamic resistance of the intake and exhaust channels. To do this, casting errors in them are carefully cleaned out with rollers, and then polished. The intake and exhaust valve heads are also polished.
To ensure a normal service life of the compression piston rings and improve the piston seal, at increased speeds of a forced engine, standard compression rings with a machined internal one-sided chamfer should be used (Fig. 2, a). This allows you to slightly reduce the weight of the rings and reduce their pressure on the cylinder walls. Even better results are obtained by using L-shaped torsion-type rings (Fig. 2, b). To make them, a serial ring is fixed in the chuck of a lathe using a mandrel (Fig. 2, d), then a recess is made.
Since it is not always possible to make a new piston with grooves for two L-shaped rings, you can cut one groove for it above the upper groove, right at the edge of the piston bottom. A rectangular ring with a machined chamfer is placed under the L-shaped ring. The lower groove remains empty (Fig. 2, e).
When boosting the crankshaft speed, textolite washers are installed under the valve springs to lighten the pushers. Push rods are made of titanium or duralumin tubes with steel tips (Fig. 3).
On each cylinder, using a calibration disk mounted on the crankshaft axis, the valve timing is checked according to the data in Table 2. It is better to register the beginning of valve opening using an indicator. Adjustment of the valve timing can be done on the removed cam shaft by filing the cams manually with fine-grained abrasive stones or using a rubber grinding wheel and an electric drill. In this case, it is important to remove the minimum necessary amount of metal in order to preserve the upper cemented layer and distort the overall shape of the cams as little as possible. Their surface must be polished to a mirror shine.
Ignition timing is 43 degrees - early, 13 degrees - late.
It wouldn’t hurt to replace the standard ignition system with a contactless electronic one installed on the Ural-Solo.
Candles can be recommended A 20 DV, A 17 DV from the Zhiguli car, however, due to the large length of the thread, brass washers 8 mm high should be placed under them.
If an old engine equipped with K-301 (K-302) carburetors is being boosted, they should be replaced with K-63U (K-65T) with a diffuser diameter of 28 mm and a main jet capacity of 170 cc. cm/min. Carburetors will have to be attached to the cylinders through adapter washers, since the K-301 (K-302) mounting studs are located in a vertical plane, and the holes of the K-63U (K-65T) mounting flange are located in a horizontal plane.
A contact-oil air cleaner is completely unsuitable for a forced engine. The best solution is a homemade filter with a paper element from Zhiguli. As a last resort, you can use an air filter with a paper element from the Dnepr motorcycle.
The M-63 engine, boosted using the described technology, must develop a power of at least 30 kW (40 hp).
According to VNIIMotoprom, with a compression ratio of 8.5:1 and 5900 rpm, the engine power can be up to 33.6 kW (45 hp).
legkoe-delo.ru
Maintenance
Like any vehicle, motorcycle engines require regular maintenance. Procedures related to routine maintenance are recommended to be carried out after 2 thousand kilometers.
The list of work that must be carried out during maintenance of K-750 type motors includes:
- Check and, if necessary, adjust the valve clearances of the gas distribution mechanism.
- Replacing engine oil and oil filter.
- Checking the condition of the spark plugs.
There are still a certain number of motorcycles in operation with engines equipped with K-37A, K-52, etc. carburetors. If the motorcycle engine has one of these carburetors, then during maintenance it must also be checked and, if necessary, adjusted.
Boosting motorcycle engines | Soviet motorcycles
From the book by I.M. Grigoriev “Motorcycle without Secrets” DOSAAF, 1973.
In our country, only two motorcycle factories produce motorcycles with engines up to 750 cm3. These are the Irbitsky and Kyiv motorcycle plants. The serial engines of these plants have great boost capabilities.
Engine MT-8 (650 cm3)
1. Check that the ignition is installed correctly on each cylinder. The ignition timing should be 40°-42°. Synchronous operation of the ignition system is achieved by filing the cam in the distributor and bringing it to the same ignition timing on both cylinders.
2. The valve timing is checked using a graduated disk mounted on the axis of the crankshaft. The valve timing must correspond to: Intake beginning to c. m. t. 70°; end after n. m. t. 140°. Release beginning BC. m. t. 110°; end after c. m.t. 90°.
Adjustment of the valve timing can be done on the removed cam shaft by filing it by hand using a drill and cam stones.
3. Cleaning the channels in the cylinder heads from casting errors gives 2 liters. With. And adjusting the compression ratio in each cylinder will also add power due to the uniform operation of the two cylinders.
4. Installing K-301B carburetors with an increased diffuser diameter to 26 mm will also add 2 liters. With.
5. Selection and adjustment of inlet pipes behind the carburetor to the entrance to the air filter / = 345 mm, d = 37 mm.
6. Adjustment of carburetors for synchronized operation, equal jet flow rate of 250 cm3/min.
7. Installation of an air filter from Moskvich-412 (2 pcs.) or Volga GAZ-24 cars.
8. Selection of the length and diameter of exhaust pipes and mufflers (Fig. 1).
The recommendations listed above, implemented on the motorcycle, allow you to increase engine power to 42 hp. s., and if you change the compression ratio, bringing it to 8.5, then the engine power will increase to 45 hp. With. at 5900 rpm (according to VNIIMotoprom). Increasing the cylinder diameter to 80-82 mm by increasing the volume of the cylinders gives good results. Piston rings can be used from a motorcycle ESO-350 or CZ-360, Moskvich-412. This event allows you to further increase engine power, bringing it to 48-50 hp. c. Engine M-66 AM from the Irbit Motor Plant (650 cm3, two cylinders, four-stroke, overhead valve).
Changes made to the engine compared to the M-62 engine:
1. The cylinders are shortened by 2.5 mm and have a hole for the fifth mounting point of the head.
2. In the heads: the angle between the axes of the valves is 68°. The diameter of the sphere is 42 mm. The depth of the sphere of the head is 26.5 mm. The racks and brackets are cast in one piece, the cooling area of the head is increased.
3. The piston has a spherical bottom. The rounding of the piston head with a diameter of 110 mm. The height of the piston head is 7 mm. The compression ratio is 8. The groove for the upper piston ring is shifted down by 1 mm. The upper ring is chrome-plated, the second serial oil scraper ring is 4 mm thick.
4. Valves are made of EP-303B material.
5. Crankshaft. The connecting rod pin with the axle is made in one piece, therefore, the number of press-in points has been reduced and the rigidity of the shaft has increased. Combined rollers 5 X 12 mm are installed.
6. Head covers in a common casting of two halves.
7. K-300 carburetors with a diffuser diameter of 28 mm. Ignition timing is 43° early, 13° late. The gap at the breaker is 0.4 mm. Valve timing: Intake beginning to c. m, t. 70°; end after n. m. t. 140°. Release beginning BC. m. t. 135°; end after c. m.t. 70°.
To increase the time-section factor when opening the valve, it is necessary to machine the outer diameter of the valve plate fitting chamfers, rounding the edges to R = 2 mm.
xn—-ctbjaolrjhaxdmh.xn--p1ai
Device
The basis of the car is a load-bearing riveted frame made of high-strength steel and characterized by increased rigidity. The design provides short rear and front overhangs, thereby increasing cross-country ability. The platform for transporting people and cargo is made of metal. It has lift-up side seats and an opening tailgate. The body assumes the possibility of installing an awning, arches and mounting sides on both sides. Some modifications received a wooden platform. The sides of the Ural 4320 are lattice or solid. The design provides for a front location of the unit. To access the engine, the hood opens upward. On the sides there are wide, flat fenders that protect the cabin from foreign objects and dirt while driving.
The truck has a 6 by 6 wheel arrangement. The model is equipped with single wheels with automatic adjustment of the air filling of the chambers on 3 drive axles. Recommended tires: 14.00-20 OI-25.
Ural 4320 has a dependent front suspension on semi-elliptic springs. It consists of 2-way shock absorbers. The rear suspension of the car is also dependent (on springs with reaction bars). All truck axles are drive axles. The steered wheels are located on the front axle.
The car is equipped with a friction clutch with a drive equipped with a pneumatic booster. The 2-speed manual transfer case has a permanently connected drive to the front axle. The Ural 4320 is equipped with a fully synchronized transmission produced by the Yaroslavl Motor Plant. The gearbox has 5 speeds, switched mechanically.
The brake system includes a dual-circuit working and single-circuit spare brake system. There is also an auxiliary braking system with pneumatic drive from the exhaust system. The mechanical parking brake system is equipped with a brake drum on the transfer case.
At the rear of the frame and at the front of the rigid bumper there are powerful towing devices made in the form of a towing mechanism and hooks. Thanks to this, the technical characteristics of the model were improved.
The developers of the Ural 4320 also took care of the driver. The steering in the latest models has a hydraulic booster. The cabin is equipped with a heater that maintains normal temperature in cold weather. The driver's seat is adjustable in 3 directions (up-down, forward-backward and backrest tilt). The instrument panel is located at a convenient distance from the driver. The instruments are easy to read, and the driver can reach the switches and buttons without getting up from the seat. The truck has a convenient and large glove compartment and a shelf for storing items. There is a document box under the passenger seats.
In the basic version, a 3-seater cabin made of stamped sheet metal is mounted on the frame. Thoughtful glazing guarantees good visibility and allows you to control the situation on the road. Large rearview mirrors also help with this.
Other types of cabins are also available:
- 3-seater all-metal 2-door cabin;
- 3-seater all-metal 2-door cabin with sleeping bag (this option is currently discontinued);
- modern spacious bonnet-type cabin with a sprung driver's seat and plastic tail;
- cabin based on the GAZelle Next module (3- and 7-seat versions are available).
Options include luxury cabins, a differential lock system, ABS, battery compartment insulation, an additional tank and a traction winch.
Engine boost Ural motorcycle
Views: 2203
Below, see the technical characteristics of boosting the engine of a Ural motorcycle. Express your opinion about the car in the reviews of the article.
Opinion of a car owner named Radoslav: Passability. Successful ergonomics of the interior. Cheap service. Fuel consumption 9-10 liters. in my mixed cycle. On the highway it goes 140-150 km per hour freely. On the chassis there are more than one difficulties for 100 thousand. They didn't change anything at all. At every TO they say that everything is OK.
Posted by admin: at the request of Antoine
Category: Do-it-yourself repairs
Original name:
Description: The dimensions are as follows: length - 3033, width - 1100, height - 1218 mm. The wheelbase is 2203 mm. Ground clearance 167 mm. The car is equipped with a hybrid power unit. The 4-cylinder engine is equipped with a system that provides engine power output. There are 4 valves per cylinder. The diameter of one cylinder is 74 mm, the piston stroke is 78 mm. The engine crankshaft accelerates to 5000 rpm. Maximum torque is maintained up to 2000 rpm.
Release date: 28.10.2015
Duration: 5:45
Quality: Blu-Ray
Laughter on the topic: Moscow metro. A mother and her son are sitting, a beautiful girl in a white fur coat is standing next to them, a punk is standing next to the girl, chewing gum, headphones in his ears. The child is trying as hard as he can to dirty the girl’s fur coat with his boots, the girl is trying to move away, but there is a terrible crush in the carriage , there is no way to move away. The girl in the fur coat politely asks the mother of the wild child to do something, saying that the fur coat is getting dirty and so on. The mother, having heard complaints in her direction, begins to scream heart-rendingly: “You are crippling my child’s psyche!” There is righteous indignation and confusion on the face of the girl in the fur coat. The mother is going crazy! A guy standing next to a girl in a punkish-looking fur coat takes off his headphones, takes the gum out of his mouth and slowly presses the gum right into the middle of the screaming mother’s forehead! There's a deathly silence, in which the guy's words are clearly heard: “I, too, was not raised until I was five years old!”
Modifications
Ural-4320-****-**
— chassis with a standard (“classic”) metal cabin, load capacity of about 7-9 tons;
Ural-4320-19**-**
— long-wheelbase chassis, with a load capacity of about 12 tons;
Ural-43203-****-**
— chassis with reinforced front suspension;
Ural-43204-****-**
— chassis of a pipe hauling tractor, increased load capacity;
Ural-44202-****-**
— truck tractor for operation with a semi-trailer on all types of roads;
Ural-5557/55571-****-**
— chassis for mounting technological equipment and special installations weighing ~12-14 tons with low-profile wide tires with adjustable wheel inflation, which significantly increases the vehicle’s cross-country ability;
Ural-43206-****-**
— chassis with a 4×4 wheel arrangement;
Other powertrain options
When developing the performance characteristics of the Ural-4320 engine, manufacturers provided for the possibility of installing several types of motors. Among them are the following variations:
- The KamAZ-740.10 unit has a power of 230 horsepower, a volume of 10.85 liters, has 8 cylinders, operates on diesel fuel;
- YaMZ-226 - runs on diesel fuel, power is 180 horses;
- YaMZ-236 HE2 has a volume of 11.15 liters, a power of 230 horses, turbocharging, four strokes;
- In addition, modifications with indices 238-M2, 236-BE2, 7601 were mounted. They differ in horsepower (240, 250 and 300, respectively).
In addition, the performance characteristics of the Ural-4320 with a YaMZ engine provide for the installation of a hydraulic booster, pre-heating and compliance of the engine with the Euro 3 standard.
Technical indicators
The brake assembly includes a main dual-circuit system and a spare single-circuit unit. The additional brake is driven by a pneumatic drive from the exhaust gases. This mechanical type unit with a drum placed on the transfer case (TC) is very effective. The parking brake is a drum brake, mounted on the output shaft of the brake valve.
The performance characteristics of the Ural-4320 are designed for a 6*6 wheel arrangement. High cross-country ability is ensured by single-pitch wheels equipped with automatic inflation of air chambers. The front suspension is dependent, has shock absorbers and semi-elliptical springs. The rear assembly is also of a dependent type with springs and reaction bars. The truck in question has three axles, all of them are driven, the front wheels are equipped with CV joints. The clutch unit has a friction drive, a pneumatic booster, and a disk with a diaphragm extension spring.
Exterior
According to the performance characteristics of the Ural-4320, it is equipped with a metal platform body and a tailgate. The car is equipped with benches, an awning and removable arches. There are also additional lattice sides. The standard equipment includes a three-seat cabin, assembled from thick-walled sheet metal, manufactured by stamping. Thoughtful glazing and rear-view mirrors make it possible to fully monitor the situation on the road and increase visibility.
Structurally, the body is made in the form of short overhangs, which improves cross-country ability. The curb weight of the truck is 8.2 tons. The weight of the transported cargo is up to 67.8 tons with the ability to tow 11 tons.
Tactical indicators
The military performance characteristics of the Ural-4320 have the following capabilities in tactical terms:
- Fording the reservoir (depth) is one and a half meters.
- Crossing swampy terrain is similar.
- Ditches and trenches (depth) - up to 2 meters.
- The maximum lifting height is 60°.
- The minimum turning radius is 11.4 meters.
- The maximum altitude above sea level for normal operation is 4 thousand 650 meters.
Structurally, the powerful truck is designed in such a way as to protect the cabin and driver from dirt when driving off-road (the power plant is located in the front, the hood is raised up, and wide flat fenders are installed on the sides).
The performance characteristics of the Ural-4320 allow it to be used in harsh climatic conditions with a maximum humidity of 98°. The temperature range is from + to -50 degrees. Garage-free storage of the vehicle is permitted. The maximum wind force withstand is 20 meters per second, and the dust content is 1.5 cubic meters.
Malfunctions
One of the features of the power units of Ural motorcycles is the relatively frequent occurrence of minor faults, which must be eliminated quite quickly. Delaying repairs can, and usually does, lead to more serious damage and a significant increase in the cost of repairing them. The main malfunctions and the reasons for their occurrence are summarized in the table.
| FAULT | REASON FOR APPEARANCE |
| The motor does not start. | 1. The fuel supply system is clogged. |
| 2. The spark plugs are out of order (carbon deposits, etc.). | |
| 3. Insufficient compression in the cylinders (valve clearances, rings, etc.). | |
| The power unit operates intermittently. | 1. Uneven fuel supply. |
| 2. Water in the engine or fuel. | |
| 3. The injector jets or nozzles are clogged. | |
| 4. Spark plugs are faulty. | |
| 5. The integrity of the electrical wiring is broken. | |
| 6. Excessively enriched fuel-air mixture. | |
| Extraneous knocking noise in the engine. | 1. Early ignition is set. |
| 2. Motor overheating. | |
| 3. Problems with pistons and rings (loose fit, etc.). |